![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is money? |
Anything that is generally accepted as a means of payment for goods and services. |
|
|
What is legal tender? |
Money that firms must accept in a certain country. (In the UK, legal tender is Royal mint coins and bank notes). |
|
|
Cheques, debut cards and credit cards are... |
Cheques, debut cards and credit cards are not money but allow money to be transferred. |
|
|
How do debit cards work? |
Debit cards take money from your account and transfer it to the seller. If you don't have the money in your account, the card gets declined. |
|
|
How do credit cards work? |
Credit cards allow you to but goods whether or not you have the money in your account. The bank lends you the money, and you pay it back later. If you can't pay it back in a certain time period you start paying interest. |
|
|
Interest payment = ? |
Interest payment = initial amount borrowed X (interest rate/100). |
|
|
What does the financial sector consist of? |
Financial institutions such as banks, building societies, investment banks and insurance companies. |
|
|
What does the role of the financial sector involve? |
The flow of capital and thus the lending and borrowing of money in the short term and long term. |
|
|
Why do we need a healthy financial sector? |
Banks allow money to move between consumer, producers and governments. A healthy financial sector is needed to maintain a stable economy (according to the GCSE course, *cough* financial crisis *cough*). |
|
|
What is the difference between a bank and a building society? |
Banks are normally companies listed on the stock market, and are therefore owned by and run for their share holders. As a result of not having to pay dividends to shareholders, building societies claim to offer higher interest rates on savings and cheaper loans. |
|
|
What is a mortgage? |
A mortgage is a loan from a bank or building society in exchange for a house, with the condition that if the debtor doesn't pay their debts and interests the bank/building society gets to keep the house. |
|
|
What are the 2 parts of a mortgage repayment? |
The principle (the actual debt) and the interest (the cost of borrowing). |
|
|
What is the role of the central bank (in the UK, the bank if England)? |
The central bank set the bank rate but (the rate at which banks can borrow from the bank of England). Interest rates on savings and loans move in the same direction as the bank rate, affecting AD. |
|
|
An increase in the bank rate will lead to... |
An increase in the interest rate on savings accounts/loans. |
|
|
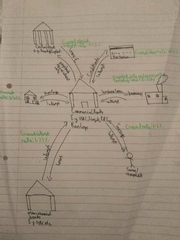
Draw a diagram of the financial sector. |
|

