![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a firm's aim assumed to be in economics? |
To maximise profit. |
|
|
Profit = ? |
Profit = total revenue - total costs |
|
|
The income earned from labour is known as _____ |
Wages |
|
|
The income earned from land is know as ____ |
Rent |
|
|
The income earned from capital is known as ________ |
Interest |
|
|
The income earned from enterprise is known as ______ |
Profit |
|
|
In the short run it will NOT be possible to... |
Change the inputs of all the factors of production. Some factors will be fixed (their costs do not change). E.g. rent on premises. |
|
|
Variable factors |
Costs that change as output changes. E.g. the cost of materials. |
|
|
Total costs = ? |
Total costs = fixed costs + variable costs |
|
|
In economics, what is the Short Run? |
The period of time over which at least one factor is fixed. |
|
|
Average cost = ? |
Average cost = total costs ÷ output |
|
|
Average revenue = ? |
Total revenue/output |
|
|
When does an economy of scale occur? |
These occur when output is increasing but cost per unit is decreasing. |
|
|
What are the 2 types of economies of scale? |
Internal economies of scale - these occur when a firm gets larger. Average cost of production fall as output increases External economies of scale - these occur within the industry as a whole, rather than an individual firm. |
|
|
What are the different types of internal economies of scale? |
1) Marketing: the marketing budget can be divided across a larger output, meaning average advertising costs per unit will be smaller. 2) Risk bearing: a firm can diversify into new products so if one part isn't successful they have others to fall back on. 3) Financial: banks will lend more cheaply to larger firms as they are deemed less risky. 4) Technical: can afford to invest in capital which lowers the cost of production per unit. 5) Managerial: firms can make use of specialist managers 6) Purchasing: buying in bulk reduces firms raw material costs. |
|
|
When do diseconomies of scale occur? |
When output passes a certain point and average costs start to rise per unit of output produced. |
|
|
Why are there diseconomies of scale? |
Control: It is harder to ensure that a larger workforce is productive. Coordination: It is harder to coordinate more workers if there are more employees. Communication: Workers may feel that they have no stake in a company's success as it goes, leading to falling productivity. |
|
|
What does MES stand for? |
Minimum efficient scale |
|
|
What does a long run cost curve look like? |
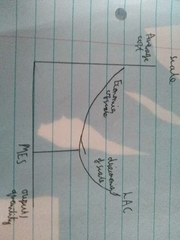
|
|
|
Productivity |
An economic measure of output per unit of input (input is typically factors of production, output is revenue). |
|
|
What is the difference between productivity and production? |
Production is not a measure of efficiency, it is the action of making something from components or raw materials. You can increase production if workers work longer hours, but productivity won't have changed. |
|
|
Labour productivity = ? |
Quantity produced/labour hours |
|
|
How can productivity be improved? |
1) Specialisation: workers become experts in one task and don't waste time switching between tasks. 2) Substitution of labour for capital. 3) Worker involvement in the firm: workers will be more motivated. 4) Greater education and training 6) Technology improvements 7) logistics improvements |
|
|
Competition leads to greater productivity because... |
Firms must be more efficient to reduce costs, allowing them to keep prices low. |

