![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Rickettsia prowazekii
|
epidemic typhus;transmitted by lice;flourishes in crowded and unsanitary surroundings
|
|
|
Rickettsia typhi
|
endemic murine typhus;transmitted by rat fleas
|
|
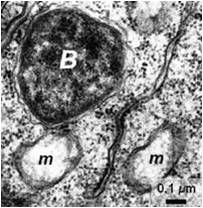
Wolbachia
|
symbiont of insects;most common infectious bacterial genus in the world;infects over a million species of insects, millipedes, mites, spiders, crustaceans and nematodes;75% of animal species infected
|
|
|
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
|
causes crown gall;contains Ti plasmid with T-DNA;
|
|
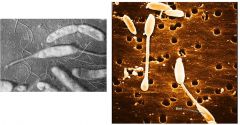
Hyphomicrobium
|
reproduces by budding
lives in low-nutrient aquatic environment grows in laboratory water baths |
|
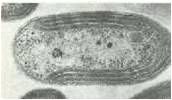
Nitrobacter
|
Oxidizes nitrite to nitrate;nitrifying bacteria;Chemoautotrophic
|
|
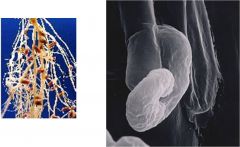
Rhizobium
|
endosymbiont of legumes;causes formation of root nodules;nitrogen fixation
|
|
|
Azospirillum
|
soil bacterium that grows in close association with the roots of many plants, especially tropical grasses (sugar cane, but also corn)
|
|
|
Burkholderia cepacia
|
extraordinary nutritional spectrum;capable of degrading more than 100 different organic molecules;
factor in contamination of equipment and drugs in hospitals;grows in disinfectant solutions;problem for people with cystic fibrosis;recently emerged as an important opportunistic pathogen of the lower respiratory tract, affecting immunocompromised individuals (like cysitc fibrosis) |
|
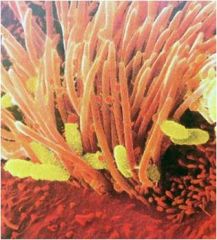
Bordetella pertussis
|
attach to ciliated cells in trachea; impede ciliary action and destroy cells;1996 new acellular vaccine (DTaP)
|
|
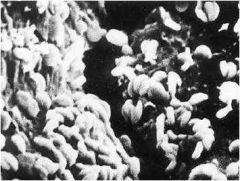
Thiobacillus
|
chemoautotroph;oxidizes sulfur or hydrogen sulfide to sulfate
|
|
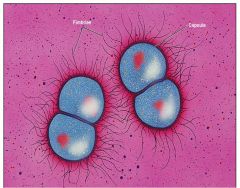
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
|
gonorrhea - most common reportable communicable disease in US
|
|
|
Nitrosomonas
|
oxidizes ammonium to nitrite
Spirillum;found mainly in fresh water |
|
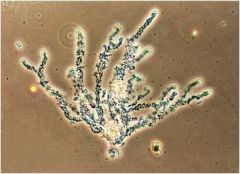
Zoogloea
|
important in aerobic sewage-treatment processes;forms fluffy, slimy masses that are essential to the proper operation of such systems
|
|
|
Beggiatoa alba
|
resembles filamentous cyanobacteria;not photosynthetic;uses hydrogen sulfide as an energy source - oxidizes it;chemoautotrophic
|
|
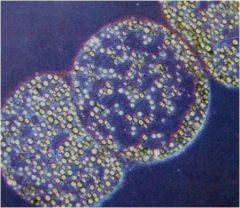
Thiomargarita namibiensis
|
750 micrometers in diameter
interior vacuole that stores nitrate during periodic upwellings oxidizes hydrogen sulfide chemoautotrophic anaerobic respiration with nitrate as final electron acceptor |
|
|
Francisella tularensis
|
tularemia;
zoonose - transmitted by contact with infected animals (rabbits and ground squirrels) |
|
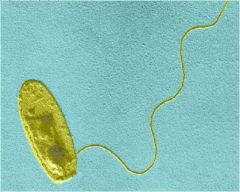
Legionella pneumophila
|
legionellosis - Legionnaires’ disease (1976)
|
|
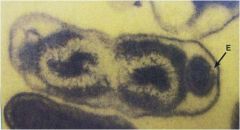
Coxiella burnetii
|
Q fever;most commonly transmitted by aerosols of contaminated milk;spread to humans by ingestion of unpasteurized milk and by inhaling aerosols in dairy barns
|
|
|
Azomonas and Azotobacter
|
nitrogen fixation - reduce nitrogen gas to ammonium
free living in soil |
|
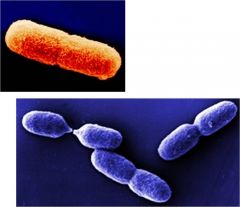
What is this bacteria?
|
Azotobacter
|
|
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
blue green pigmentation
infects urinary tracts, burns, wounds |
|

Vibrio cholerae
|
cholera
profuse watery diarrhea;produce an exotoxin - cholera toxin |
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae
|
occasionally causes a serious form of pneumonia in humans
|
|
|
Salmonella enterica
|
infectious to warm-blooded animals;differences in antigens on flagella (H), capsules (K) and cell walls (O)
|
|
|
Salmonella typhimurium
|
causes typhoid fever
|
|
|
Most virulent serotype of Salmonella is?
|
Salmonella typhi which cause typhoid fever (not found in animals)
|
|
Serratia
|
red pigment;used to test bioweapon dispersal in Bay Area - thought harmless, but many sickened
|
|
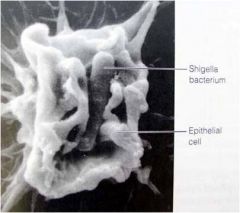
Shigella
|
bacillary dysentery - shigellosis
|
|
|
Yersinia pestis
|
plague - Black Death - bubonic plague
|
|
|
Haemophilus influenzae
|
common cause of meningitis in young children
frequent cause of earaches, epiglotitis, septic arthritis, bronchitis and pneumonia |
|
|
Haemophilus ducreyi
|
sexually transmitted disease - chancroid
|
|
Bdellovibrio
|
attack other gram-negative bacteria
penetrate outer membrane reproduce in periplasm; host cell lyses releasing them |
|
|
Desulfovibrio
|
sulfur reducing bacteria;reduce oxidized forms of sulfur (S or sulfates) to hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
|
|
|
Campylobacter jejuni
|
leading cause of foodborne intestinal disease
|
|
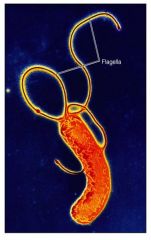
Helicobacter pylori
|
most common cause of peptic ulcers;a cause of stomach cancer;produces an abundance of urease that converts urea to ammonia (alkaline) which combats the very low pH of gastric juices;urea breath test for diagnosis
|
|
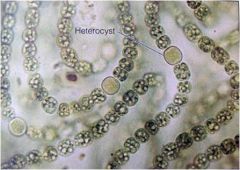
Anabaena
|
a filamentous cyanobacterium
|
|
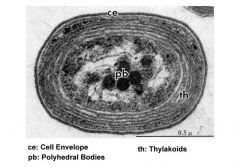
Prochlorococcus
|
probably the most abundant organism on Earth; and contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b
|
|
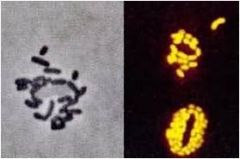
Chlorobium
|
green sulfur bacteria;
|
|
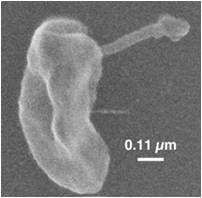
Dehalococcoides
|
Green non sulfur bacteria;uses these chemicals as final electron acceptors in anaerobic respiration.
Halorespiration; dehalorespiration; halorespiring bacteria |
|
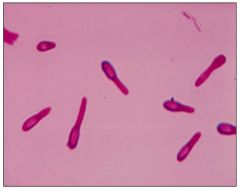
Clostridium tetani
|
tetanus;potent neurotoxin - tetanospasmin
|
|
|
Clostridium botulinum
|
botulism (type of food poisoning);in anaerobic conditions, germinating endospores produce the most potent of all natural toxins
|
|
|
Clostridium perfringens
|
gastroenteritis and gas gangrene
gastroenteritis;one of the more common, if under recognized, forms food poisoning in the US;associated with meats or meat stews contaminated with intestinal contents during slaughter |
|
|
Clostridium difficile
|
severe diarrhea in patients taking antibiotics
|
|
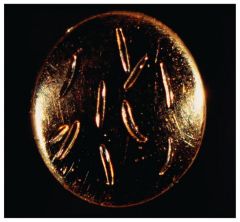
Epulopiscium fishelsoni
|
large bacterium;lives symbiotically in gut of Red Sea surgeonfish;has a large genetic capacity - 25X as much DNA as a human cell;as many as 85,000 copies of one gene
|
|
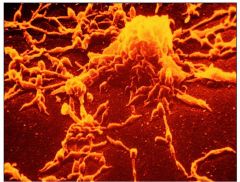
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
|
It causes the disease Mycoplasma pneumonia, a form of bacterial pneumonia
|
|
|
Bacillus anthracis
|
anthrax
disease of cattle, sheep and horses can be transmitted to people; possible bioweapon |
|
|
Bacillus thuringiensis
|
crystalline toxin (Bt toxin) cuts up the guts of some insect larvae;Gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, commonly used as a pesticide
|
|
|
Listeria monocytogenes
|
one of the most virulent foodborne pathogens with 20 to 30 percent of clinical infections resulting in death
|
|
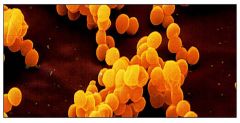
Staphylococcus aureus
|
coagulase positive;yellow-pigmented colonies;grow and survive in nasal secretions;MRSA - methycillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus
|
|
|
Lactobacillus
|
used commercially in the production of sauerkraut, pickles, buttermilk and yogurt;sold as a treatment for diarrhea
|
|
|
Streptococcus pyogenes
|
cause of Group A streptococcal infections;erysipelas;impetigo
|
|
|
Streptococcus agalactica
|
inhabits vagina of more than 60% of women;can cause deadly sepsis in newborns
|
|
|
Streptococcus mutans
|
cariogenic;lives in our mouth;teeth coated with dextran
|
|
|
Frankia
|
nitrogen fixing symbiont in alder tree roots
root nodules form |
|
|
Gardnerella vaginalis
|
vaginitis;often present in male urethra
|
|
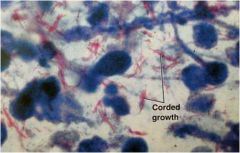
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
causative agent of most cases of tuberculosis
|
|
|
Mycobacterium leprae
|
grows in the peripheral nervous system;Temperature optimum 30oC;causes leprosy
|
|
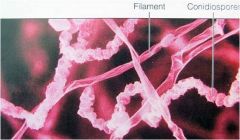
Streptomyces
|
produces conidiospores;produce most of our commercial antibiotics; isolated from soil
|
|
|
Chlamydia trachomatis
|
trachoma (a common form of blindness),
|
|
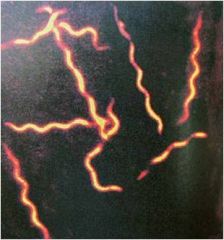
Borrelia burgdorferi
|
most common tickborne disease in US
|
|
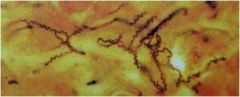
Treponema pallidum
|
syphilis - yaws
|
|
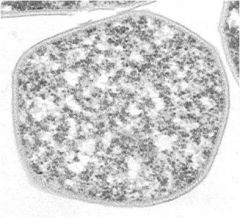
Picture of what?
|
Sulfolobus solfataricus
|

