![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
232 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are viruses?
|
Obligatory Intercellular Parasites
|
|
|
What is important to know about the host range of viruses?
|
Viruses will infect any living organism from bacteria and up. Most viruses are very specific-targeting species or related species.
|
|
|
What are the sizes of viruses?
|
20nm (smallest) to 300 nm (largest)
|
|
|
Is the virus structure considered to be simple or complex?
|
Simple
|
|
|
What type of nucleic Acid do viruses contain?
|
DNA or RNA--either double or single stranded but NEVER both DNA and RNA together.
|
|
|
What is a Caspid?
|
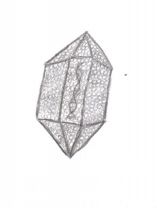
The protective layer all viruses have to protect the nucleic acid.
|
|
|
What is a Capsomer?
|
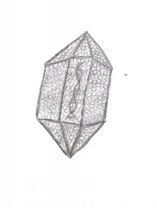
Protein balls that make up the capsid
|
|
|
What is Helical?
|
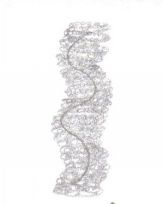
The capsid is coiled like a spring around the nucleic acid.
|
|
|
What is Polyhedral?
|
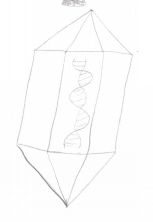
The capsid forms a crystal or diamond like structure around the nucleic acid.
|
|
|
What is Complex?
|
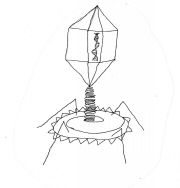
The capsid forms a crystal or diamond-like structure around the nucleic acid, a sheath looking like a spring comes out of the bottom, a plate forms the bottom with pins that look like saw blades, and fibers that look like legs.
|
|
|
What is an envelope in reference to viruses?
|
A protein or carbohydrate outer layer(similar to a capsule in bacteria).
|
|
|
Do all viruses have an envelope?
|
No some do not. If the virus has an envelope it is called "enveloped", if it lacks an envelope it is called "naked"
|
|
|
What does the plate of a complex virus do?
|
It rotates to cut through the cell walls
|
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Poxvirdae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: DNA; Double Stranded
Shape: Complex; Enveloped |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Herpesviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: DNA; Double Stranded
Shape: Polyhedral; Enveloped |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Hepadnaviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: DNA; Double Stranded
Shape: Complex; Enveloped |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Adenoviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: DNA; Double Stranded
Shape: Polyhedral; Naked |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Papoviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: DNA; Double Stranded
Shape: Polyhedral; Naked |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Parvoviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: DNA; Single Stranded
Shape: Polyhedral; Naked |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Orthomyxoviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: RNA; Single Stranded
Shape: Helical; Enveloped |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Paramyxoviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: RNA; Single Stranded
Shape: Helical; Enveloped |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Rhabdoviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: RNA; Single Stranded
Shape: Helical; Enveloped |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Coronaviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: RNA; Single Stranded
Shape: Helical; Enveloped |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Togaviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: RNA; Single Stranded
Shape: Polyhelical; Enveloped |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Bunyaviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: RNA; Single Stranded
Shape: Helical; Enveloped |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Filoviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: RNA; Single Stranded
Shape: Helical; Enveloped |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Flaviviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: RNA; Single Stranded
Shape: Polyhelical; Enveloped |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Picornaviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: RNA; Single Stranded
Shape: Polyhelical; Naked |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Retrovirdae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: RNA; Single Stranded
Shape: Helical; Enveloped |
|
|
What are the structural characteristics of the Reoviridae family?
|
Nucleic Acid: RNA; Double Stranded
Shape: Polyhelical; Naked |
|
|
What disease does the Variola Virus cause?
|
SMALL POX
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of small pox?
|
Fever, Maliase Prstration (so weak you must lay flat),
Rash: starts in mouth and spreads to rest of body, pustuals all over face & body, including internally. Leaves scars. |
|
|
What percentage of people will die outright from the illness of small pox?
|
25% will die outright (from coagulation)
|
|
|
What is the outcome for survivors of small pox?
|
They will have a lifelong immunity to small pox but scarring from illness can be debilitaing.
|
|
|
What is the only viral disease irradicated from the human population.
|
Small pox; last natural case in 1975
|
|
|
How is small pox transmitted?
|
Aerisols (easily)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for small pox?
|
None; just relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for small pox?
|
Vaccine; although it is not considered lifelong lasting 50-60 years and there are possible allergic reactions resulting in 1 in a million vaccinated dies.
|
|
|
What viral family does Variola (small pox) come from?
|
Poxvirdae Family
|
|
|
What does the HSV-1 virus cause?
|
Oral Herpes
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of oral herpes?
|
cold sore or fever blisters; ulcers on mouth. Frequently spreads-typically to the eyes. Can infect the genitals.
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for the oral herpes virus?
|
Close contact (usually transmitted at an early age)
Fomites Easily gotten |
|
|
What is the treatment for oral herpes?
|
None, have it for life.
Acyclovir can cause it to go dormant but does not kill it. Treat symptoms with menthol and camphor |
|
|
What is the control for oral herpes?
|
Very little
|
|
|
What does HSV-2 cause?
|
Genital herpes
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of genital herpes?
|
Ulcers or cold sore lesions that can be oral, in the eyes, or genitalia.
|
|
|
What is a complication of genital herpes?
|
Neonatal herpes simplex: causes miscarriages, 30% mortality rate in children born with this. If virus hits Central Nervous System mortality rate is as high as 80%
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for genital herpes?
|
Sexually transmitted; or in birthing process or transplacental
|
|
|
What is the treatment for genital herpes?
|
None; relieve symptoms with Acyclovir, menthol, and camphor
|
|
|
What is the control for genital herpes?
|
Avoid sexual contact with infected people
|
|
|
What diseases are caused by the v-z virus
|
varicella or chicken pox and zoster or shingles
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of chicken pox?
|
10-21 day incubation; mild fever, rash-pustuals all over body or just one, Severity can range. Pustuals crust over and fall off, leaving no lingering effects. Scarring can occur from scratching, deaths are rare
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for chicken pox?
|
Aerisol
|
|
|
What is the treatment for chicken pox?
|
None; just relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for chicken pox?
|
Vaccine--75% effective
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Shingles?
|
V-Z virus surrounds nerve ending near skin; irritates skin if virus reactivates.
Inflammation of nerve endings causing rash. Painful. Manifests itself around pressure points such as waist line. |
|
|
What is the transmission of shingles?
|
Dormant from chicken pox exposure
|
|
|
What is the treatment for shingles?
|
None; relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for shingles?
|
Vaccine may limit outbreaks
|
|
|
What diseases are caused by viruses belonging to the Herpesvirdae family?
|
Oral herpes, genital herpes, chick pox, shingles, CMV, and Mononucleosis
|
|
|
What disease does the Variola Virus cause?
|
SMALL POX
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of small pox?
|
Fever, Maliase Prstration (so weak you must lay flat),
Rash: starts in mouth and spreads to rest of body, pustuals all over face & body, including internally. Leaves scars. |
|
|
What percentage of people will die outright from the illness of small pox?
|
25% will die outright (from coagulation)
|
|
|
What is the outcome for survivors of small pox?
|
They will have a lifelong immunity to small pox but scarring from illness can be debilitaing.
|
|
|
What is the only viral disease irradicated from the human population.
|
Small pox; last natural case in 1975
|
|
|
How is small pox transmitted?
|
Aerisols (easily)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for small pox?
|
None; just relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for small pox?
|
Vaccine; although it is not considered lifelong lasting 50-60 years and there are possible allergic reactions resulting in 1 in a million vaccinated dies.
|
|
|
What viral family does Variola (small pox) come from?
|
Poxvirdae Family
|
|
|
What does the HSV-1 virus cause?
|
Oral Herpes
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of oral herpes?
|
cold sore or fever blisters; ulcers on mouth. Frequently spreads-typically to the eyes. Can infect the genitals.
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for the oral herpes virus?
|
Close contact (usually transmitted at an early age)
Fomites Easily gotten |
|
|
What is the treatment for oral herpes?
|
None, have it for life.
Acyclovir can cause it to go dormant but does not kill it. Treat symptoms with menthol and camphor |
|
|
What is the control for oral herpes?
|
Very little
|
|
|
What does HSV-2 cause?
|
Genital herpes
|
|
|
What virus causes chicken pox?
|
The V-Z virus
|
|
|
What is another name for chicken pox?
|
Varicella
|
|
|
What are the symptoms for chicken pox?
|
10-21 day incubation period.
Mild fever, Rash with pustuals-can range from just one to covering body. Pustuals crust over and fall off. Scarring can occur from scratching. Deaths are rare. |
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for chicken pox?
|
Aerisols
|
|
|
What is the treatment for chicken pox?
|
None; just relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for chicken pox?
|
Vaccine-about 75% effective
|
|
|
What is the virus that causes shingles?
|
V-Z Virus
|
|
|
What is another name for Shingles?
|
Zosters
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Shingles?
|
This is a reactivation of chicken pox, virus surround nerve endings near skin and irritates causing rash, quite painful. Manifests itself around pressure points such as the waist-line.
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for shingles?
|
It is Dormant from Chicken Pox ezposure
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Shingles?
|
None; relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for Shingles?
|
Vaccine may limit outbreaks
|
|
|
What does Cytomegalovirus infection cause?
|
CMV-inflammation of the cells
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of CMV?
|
Inflammation of salivary or lymph glands. Most are asymptomatic. Cold-like symptoms
|
|
|
What is the major concern for CMV?
|
Can cross placenta and infect fetus causing spleen liver, nerve and occular damage and some miscarriages.
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for CMV?
|
Main mode is sexual; also transplacental, birthing process and any fluid contact can transmit virus
|
|
|
What is the treatment for CMV?
|
Interferon destroys the virus
|
|
|
What is the control for CMV?
|
Avoid exposure-although almost impossible to do so-estimated that at any one time 50% of US population has it
|
|
|
What virus causes Mononucleosis?
|
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Mononucleosis?
|
Effect salivary glands-onset is slow. Fever when it peaks; feel weak, gradually recover in weeks to months. Some concern for spleen and liver.
|
|
|
What is the major complication of Mononucleosis?
|
Burkitts Lymphoma- Bone cancer of the jaw
80% death rate |
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for Mononucleosis?
|
Contact with saliva
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Mononucleosis?
|
None; relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for Mononucleosis?
|
Isolate individuals, use disposable utensils & plates
No blood donation |
|
|
What is another name for serum hepatitis?
|
Hepatitus B-->HBV
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Hepatiitis B?
|
Chronic form; may take months before symptoms show
Mild fever, joint pain, mild rah, affects liver causing jaundice ( yellowing of skin and eyes) |
|
|
What is a complication of Hepatitis B?
|
Liver cancer
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for Hepatitis B?
|
Through blood products (serum)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Hepatitis B?
|
None; Recombinant Interferon helps control growth so body can fight it off
|
|
|
What is the control for Hepatitis B?
|
Vaccine: HBIG Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin shot
Avoid exposure |
|
|
How many Adenoviridae are there and how many cause human infections?
|
80 different strains; 30 cause human infections
|
|
|
What virus causes Keratoconjunctivitus?
|
AV-8 and AV-19
|
|
|
What is another name for Keratoconjunctivitus?
|
Pink Eye
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of "pink eye"?
|
Cold-like symptoms; runny nose, sore throat, infection of the conjunctiva & cornea of eye, crusting of eyes, can scar cornea
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for "pink eye"?
|
Aerisols, close contact
|
|
|
What is the treatment for "Pink Eye"?
|
None, relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for "Pink eye"?
|
Vaccines available but not used for adenoviruses
|
|
|
How many Papoviridae viruses infect humans?
|
40+ viruses
|
|
|
What virus causes Warts or verruca?
|
Human Papillomvirus (HPV)
|
|
|
What are the symptoms for HPV?
|
Warts ranging from small flat bumps to larger cauliflower masses.
Virus invades membranes or epidermis. Type of wart depends on where: Seed warts on skin (fingers) Planter warts on feet Genital Warts: Mucus membranes of genitalia and anus. Major concern: cervix for cancer link |
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for warts?
|
Any direct contact
Sexual contact #1 way Genital warts #1 STD 20% Adult US population 6 million new cases per year recorded |
|
|
What is the treatment for warts?
|
Infection does not go away; removal of warts by surgery, laser, freezing, or chemical called Podophyllin
|
|
|
What is the control for warts?
|
Avoid sexual transmission
|
|
|
What virus causes Erythema infectiosom?
|
Human Parvo Virus B-19
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Erythema infectiosom?
|
Common childhood infection; low fever, mild rash (cheeks usually)
Complication: can cross placenta and cause fatal anemia to fetus-miscarriage |
|
|
What is thr mode of transmission for Erythema Infectiosom?
|
Aerisols
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Erythema Infectiosom?
|
None; relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for Erythema Infectiosom?
|
None
|
|
|
What parts of the flu virus determines the strain of virus?
|
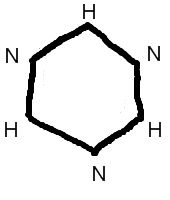
The H antigenic determinite site and the N antegenic determinite site
such as H3N3 |
|
|
What are the symptoms of influenza?
|
Fever, headache, muscle pain, severe coughing
|
|
|
What is a complication of influenza?
|
Weakened immune system can lead to secondary viral pneumonia and can kill
Also link to Reye syndrome in children along with asprin |
|
|
What it the mode of transmission for the flu?
|
Aerisols-easily
Overcrowding can compound transmission |
|
|
What is the control for the flu?
|
Vaccine-usually 3 or 4 strains at a time with an 18 month immunity
Drugs/meds help boost immune system |
|
|
What virus causes Mumps?
|
The mumps virus
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of mumps?
|
Incubation is at least a week; swelling of salivary and lymph nodes aroound jaw
Deaths in children very low. |
|
|
What is a complication of mumps?
|
Infections in males after puberty can lead to infection of testes and epididimus although this will not make them sterile
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for mumps?
|
Aerisols, contact with saliva
|
|
|
What is the treatment for mumps?
|
None, relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for mumps
|
MMR vaccine
|
|
|
What causes Measles (Red Measles or Rubeola)
|
Morbillivirus
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of measles?
|
Fever, dehydration, sore throat, dry cough.
Rash-typically forms in mouth (looks like thrush) and then can cover entire body |
|
|
What is a complication of measles?
|
1 in 1 million cases advances to the brain stem leading to coma and eventually death.
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for measles?
|
Aerisols; very contagious
|
|
|
What is the treatment for measles?
|
None; relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for Measles?
|
MMR vaccine
|
|
|
What does the Respiratory synctial virus cause?
|
RSV-#1 respiratory infection in newborns
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of RSV?
|
Form of bronchitus; coughing and weezing-Rales (very distinct sound)
Can lead to pneumonia which is when most deaths occur |
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for RSV?
|
Aerisols
|
|
|
What is the treatment for RSV?
|
Synagis; blocks receptor site of host cell
|
|
|
What is the control for RSV?
|
none
|
|
|
What virus causes Rabies?
|
The rabies virus
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Rabies?
|
Very slow but progressive infection. Incubation period 7 days, give or take an hour. Multiplies and hits Central Nervous System. After 30 days memory loss, disorientation, aggitation, sore throat and neck pain (due to brain stem pressure)
Second Stage: Hydrophobia (scared of water) yields foaming at the mouth due to sever dehydration. 100% fatal |
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for rabies?
|
Mainly by mammal bite but in rare cases by aerisols or organ transplant
|
|
|
What is the treatment for rabies?
|
Immunoglobulin shot and full course of vaccination-must be given with 7 days of infection or will be too late
|
|
|
What is the control for rabies?
|
Vaccine for domestic animals; in hot spots expensive vaccine for wild animals; vaccine for high risk humans
|
|
|
What is Sever acute respiratory syndrome also known as?
|
SARS
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of SARS?
|
High Fever, Diarrhea, Pneumonia (main cmplication leading to a 10% mortality rate but rare to get to this stage)
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for SARS?
|
Aerisols
|
|
|
What is the treatment for SARS?
|
None; relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for SARS?
|
None
|
|
|
What virus causes Rubella (3 day measles or German Measles)
|
Rubivirus
|
|
|
What are the Postnatal symptoms of Rubella?
|
Incubation time is a few weeks; fever sore throat, malaise (ultimate fatigue or bed ridden) Pink rash on face-spread to extremities and trunk. Death rates are low and it leaves an active immunity
|
|
|
What are the Congenital symptoms of Rubella?
|
Crosses placenta and infects fetus. Mother does not have to be infected or show symptoms, 1st trimester leads to miscarriage, 2nd trimester miscarriage or limb and organ malformation, 3rd trimester miscarriage or neurological disorders
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for Rubella?
|
Postnatal: Aerisols
Congenital: Transplacental |
|
|
What is the treatment for Rubella?
|
None; relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for Rubella?
|
Postnatal: MMR Vaccine
Pregnany females avoid exposure |
|
|
Where is yellow fever most commonly found?
|
Tropical such as places along the equator.
Warm climates |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Yellow Fever?
|
Typically acute fever, headache, muscle pain (flu like) progress to capillary bleeding (gums and nose)
effects liver causing jaundice; deaths occur due to liver and kidney failure. |
|
|
What is the mode of tranmission for Yellow Fever?
|
Mosquito bite--can infect any mammal
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Yellow Fever?
|
None; relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for Yellow Fever?
|
Poor Vaccine-65-70% effective
Insect Repellant, netting, mosquito control |
|
|
What are other names for the Hanta Pulmonary syndrome?
|
Hanta, Muerto Canyon, Sin Numbre
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Hanta?
|
Very quick High fever, severe pneumonia leading to pulmonary failure.
Deaths occur 24-72 hours Death rate is 33% |
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for Hanta?
|
A mouse in infected and urinates or deficates into dust and the dust is swept up forming an aerisol and is breathed in.
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Hanta?
|
None; relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for Hanta?
|
Dust masks
control on mouse habitat (such as not leaving wood pile near house) |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Ebola Fever?
|
Acute: internal hemorraging due to liquification of internal organs and bleeding out of every orafice including pores of skin. Death occurs in about 10 days
Death is rapid so fewer people are exposed |
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for Ebola?
|
Any contact with body fluids
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Ebola?
|
None; relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for Ebola?
|
Good Antisceptic practices, isolation of infected
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of West Nile Virus?
|
Flu-like but can advance to encephalitis which is when most deaths occur
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for West Nile?
|
Mosquito bite
(virus is carried in birds, mosquito bites bird and then mosquito bites human) |
|
|
What is the treatment for West Nile?
|
None; relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for West Nile?
|
Insect repellant
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Non-AB hepatitis?
|
Can be infected and show no symptoms for up to 20 years; fever, rash, joint pain, liver infection causing jaundice
Chronic cases can lead to liver damage and 5% of cases lead to liver cancer |
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for Non-AB hepatitis?
|
Sexually transmitted, sharing of needles, organ transplants (although not so much now)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Non-AB hepatitis?
|
No cure but Interferon and Ribovirin can inhibit growth so immune system can fight
|
|
|
What is the control for Non-AB Hepatitis?
|
Avoid major modes of transmission
|
|
|
What virus causes Poilimyelitis?
|
Polio virus
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Polio?
|
Parallysis of skeletal muscle, from minor to major. Legs are a common target.
Deaths occur when diaphragm is affected |
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for Polio?
|
Fecal/Oral route; Fomites
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Polio?
|
None; relieve symptoms (usually physical therapy)
|
|
|
What is the control for Polio?
|
Vaccine
Salk Injectable 1X Sabbin Oral 3X and Good Sanitation |
|
|
What virus causes the common colds?
|
Rhinovirus
|
|
|
How many Rhinoviruses are there?
|
110-150 unique viruses
|
|
|
What temperature do Rhinoviruses prefer?
|
33 degrees C or mid 80's F
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of a cold?
|
Mild infections; headache, chills, fatigue, nasal drainage lasting 10 days
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for the common cold?
|
Aerisols or direct contact with virus
|
|
|
What is the treatment for the common cold?
|
None; relieve symptoms
possibly get body temp. up above 100 degrees to kill virus |
|
|
What is the control for the common cold?
|
Daily allowance of Vitamin C, proper nutrition, wash hands
|
|
|
What virus causes Hand-Foot-Mouth disease?
|
Coxsackie virus A
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease?
|
Cold-like symptoms, lesions (like ulcers) in mouth (first) and then aorund sole of foot (edge) and edge of hand. Considered mild infection for humans but cattle can die (called hoof-mouth disease)
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease?
|
Fecal/Oral
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease?
|
None; relieve symptoms
|
|
|
What is the control for Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease?
|
Very little; Vitamin C helps for prevention
|
|
|
What causes Short term Hepatitis?
|
HAV or Hepatitis A
|
|
|
What are the symptoms for Hepatitis A?
|
Fever, Rash, Liver infection leading to jaundice
For healthy individuals recovery in 10 days For elderly/immune supressed can be deadly |
|
|
What is the mode of tranmission for Hepatitis A?
|
Fecal/Oral (usuallu traced back to a salad bar in US cases)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Hepatitis A?
|
None; relieve symptoms, let it run its course
|
|
|
What is the control for Hepatitis A?
|
Good sanitation
|
|
|
What are Retroviridae?
|
Viruses that cause immuno deficiencies; very species specific; lots of them
|
|
|
What virus causes AIDS?
|
Human Immuno Virus (HIV)
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of AIDS?
|
low grade fever, fatigue, weight loss, swollen lymph glands
|
|
|
What are some complications of AIDS?
|
Immune system is destroyed so person can get secondary infections, mainly pneumonias, cancers and leukemia
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission for AIDS?
|
Sexually transmitted
Blood transfusions Exposure to blood products Birthing process, transplacental, Breast feeding |
|
|
What is the treatment for AIDS?
|
No cure; Triple Cocktail of AZT, ddI, and 3T3
These are protinase inhibitors that slow virus down so immune system can fight but must be take at specific times and is very expensive |
|
|
What is the control for AIDS?
|
Avoid high risk modes of tranmission; no vaccine available.
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Hepadnaviridea Family?
|
Hepatitis B or Serum Hepatitis
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Adenoviridea Family?
|
Keratoconjunctivitis (or pink eye)
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Papoviridea Family?
|
Warts or verruca (from HPV);
Seed, planter or genital |
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Parvoviridea Family?
|
Erythema Infectiosom
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Orthomyxoviridea Family?
|
Influenza
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Paramyxoviridea Family?
|
Mumps, Measles, RSV
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Rhabdoviridea Family?
|
Rabies
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Coronaviridea Family?
|
SARS
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Togaviridea Family?
|
Rubella, Yellow Fever
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Bunyaviridea Family?
|
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Filoviridea Family?
|
Ebola Fever
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Flaviviridea Family?
|
West Nile Fever, Non-AB Hepatitis
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Picornaviridea Family?
|
Poliomyelitis, Common Colds, Hand-foot-mouth disease, Short term Hepatitis (Hepatitis A)
|
|
|
What disease(s) are caused by viruses in the Retroviridea Family?
|
AIDS
|
|
|
Sheath or Tail Sheath
|
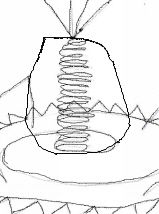
What is this part of a complex virus called?
|
|
|
Tail
|
What is this area of a complex virus called?
|
|
|
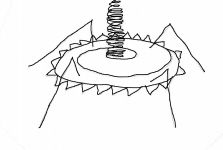
Pins
|
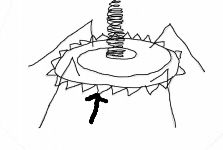
What part of a complex virus is the arrow pointing to?
|
|
|
Fibers
|
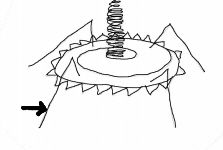
What part of a complex virus is the arrow pointing to?
|
|
|
Plate
|
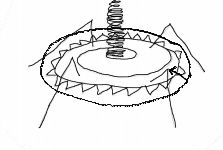
Name the part of the complex virus as indicated
|
|
|
rotates to cut through cell walls
|
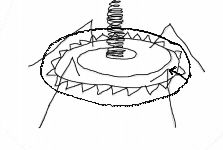
What does this part of a complex virus do?
|

