![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
141 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which protozoa cause GI infections? |
- Giardia lamblia |
|
|
Which protozoa cause CNS infections? |
- Toxoplasma gondii |
|
|
Which protozoa cause hematologic infections? |
- Plasmodium (P. vivax/ovale, P. falciparum, P. malariae) |
|
|
Which protozoa cause visceral infections? |
- Trypanosoma cruzi |
|
|
Which protozoa cause STDs? |
Trichomonas vaginalis |
|
|
Which parasite causes bloating, flatulence, foul-smelling fatty diarrhea (often seen in campers / hikers)? How is it transmitted? Diagnosed? Treated? |
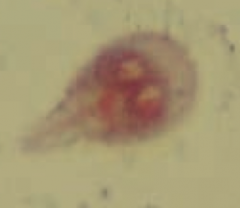
Giardia lamblia (GI protozoa) |
|
|
What disease is caused by Giardia lamblia? Symptoms? |
Giardiasis |
|
|
How is Giardia lamblia transmitted? Diagnosed? |
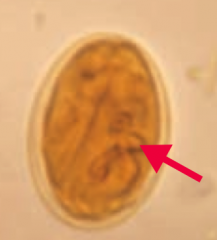
- Transmitted via cysts in water |
|
|
How is Giardia lamblia treated? |
Metronidazole |
|
|
Which parasite causes bloody diarrhea (dysentery), liver abscesses (anchovy paste exudate), RUQ pain (d/t flask-shaped ulcer if submucosal abscess of colon ruptures)? How is it transmitted? Diagnosed? Treated? |
Entamoeba histolytica (GI protozoa) |
|
|
What disease is caused by Entamoeba histolytica? Symptoms? |
Amebiasis |
|
|
How is Entamoeba histolytica transmitted? Diagnosed? |
- Transmitted via cysts in water |
|
|
How is Entamoeba histolytica treated? |
- Metronidazole |
|
|
Which parasite causes severe diarrhea in AIDS or mild disease (watery diarrhea) in non-immunocompromised patients? Transmission? Diagnosis? Treatment? |
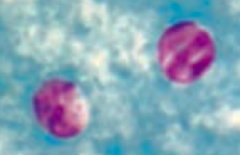
Cryptosporidium (GI protozoa) |
|
|
What disease is caused by Cryptosporidium? Symptoms? |
- Severe diarrhea in AIDS |
|
|
How is Cryptosporidium transmitted? Diagnosed? |
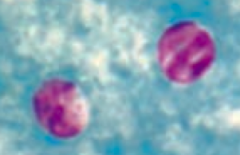
- Transmitted via oocysts in water |
|
|
How is Cryptosporidium treated? |
- Treated with nitazoxanide in immunocompetent hosts |
|
|
How do the protozoa that cause GI infections present? |
- Giardia lamblia: fatty diarrhea, bloating, flatulence |
|
|
How are the protozoa that cause GI infections transmitted? |
- Giardia lamblia: cysts in water |
|
|
How are the protozoa that cause GI infections diagnosed? |
- Giardia lamblia: trophozoites or cysts in stool |
|
|
How are the protozoa that cause GI infections treated? |
- Giardia lamblia: Metronidazole |
|
|
Which protozoa cause CNS infections? |
- Toxoplasma gondii |
|
|
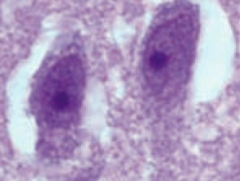
Which parasite causes brain abscesses in HIV patients (ring enhancing brain lesions on CT/MRI)? Transmission? Diagnosis? Treatment? |
Toxoplasma gondii (protozoa) |
|
|
What is the classic presentation of congenital Toxoplasma gondii infection? |
Classic Triad |
|
|
What is caused by Toxoplasma gondii infection? |
Brain abscess in HIV |
|
|
How is Toxoplasma gondii transmitted and diagnosed? |
- Transmitted via cysts in meat or oocysts in cat feces; crosses placenta (pregnant women should avoid cats) |
|
|
How is Toxoplasma gondii treated? |
Sulfadiazine + Pyrimethamine |
|
|
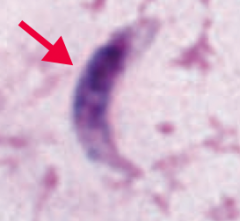
Which parasite presents as rapidly fatal meningoencephalitis? Transmission? Diagnosis? Treatment? |
Naegleria fowleri (protozoa) |
|
|
What kind of disease is caused by Naegleria fowleri infection? |
Rapidly fatal meningoencephalitis |
|
|
How is Naegleria fowleri transmitted and diagnosed? |
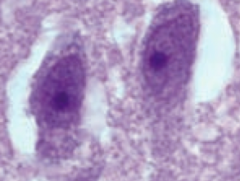
- Transmitted via swimming in freshwater lakes (think Nalgene bottle filled with fresh water containing Naegleria); enters via cribriform plate |
|
|
How is Naegleria fowleri treated? |
Amphotericin B (effective for a few survivors) |
|
|
Which parasite causes African sleeping sickness - enlarged lymph nodes, recurring fever, somonlence, and coma? Transmission? Diagnosis? Treatment? |
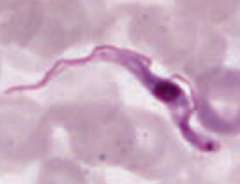
Trypanosoma brucei (protozoa) |
|
|
What are the subspecies of Trypanosoma brucei? |
- Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense |
|
|
What does infection with Trypanosoma brucei cause? |
African sleeping sickness |
|
|
How is Trypanosoma brucei transmitted and diagnosed? |
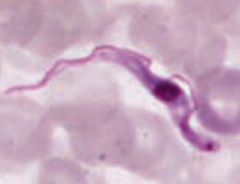
- Transmitted via Tsetse fly, a painful bite |
|
|
How is Trypanosoma brucei treated? |
Treat with SURamin for blood borne disease or MELAsoprol for CNS penetration |
|
|
How do the protozoa that cause CNS infections present? |
- Toxoplasma gondii: brain abscess in HIV and congenital disease (chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus, intracranial calcifications) |
|
|
How are the protozoa that cause CNS infections transmitted? |
- Toxoplasma gondii: cysts in meat or oocysts in cat feces (crosses placenta) |
|
|
How are the protozoa that cause CNS infections diagnose? |
- Toxoplasma gondii: serology, biopsy (tachyzoite) |
|
|
How are the protozoa that cause CNS infections treated? |
- Toxoplasma gondii: Sulfadiazine + Pyrimethamin |
|
|
Which protozoa cause hematologic infections? |
- Plasmodium (P. vivax/ovale, P. falciparum, P. malariae) |
|
|
Which parasite causes malaria: fever, headache, anemia, splenomegaly? Transmission? Diagnosis? Treatment? |
Plasmodium (protozoa) |
|
|
What are the species of Plasmodium? |
- P. vivax / ovale |
|
|
What are the characteristics of P. vivax / ovale? |
- 48 hour cycle (tertian - includes fever on first day and third day) |
|
|
What are the characteristics of P. falciparum? |
- Severe |
|
|
What are the characteristics of P. malariae? |
72 hour cycle (quartan) |
|
|
How is Plasmodium transmitted? |
Mosquito (Anopheles) |
|
|
How do you diagnose Plasmodium infection? |
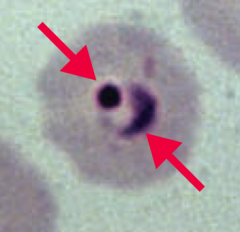
- Blood smear |
|
|
How do you treat Plasmodium infection? |
- Begin with Chloroquine - blocks Plasmodium heme polymerase |
|
|
For what drugs for Plasmodium / Malaria infection should you check for G6PD deficiency? When are these drugs used? |
- IV Quinidine - for life-threatening cases |
|
|
Which parasite presents with fever and hemolytic anemia, predominantly in NE US? Transmission? Diagnosis? Treatment? |
Babesia |
|
|
What does Babesia infection cause? |
Babesiosis |
|
|
How is Babesia transmitted? |
Ixodes tick (same as Borrelia burdorferi of Lyme disease) |
|
|
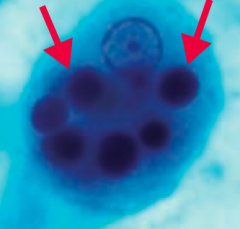
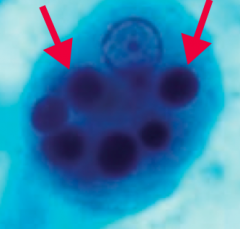
How is Babesia diagnosed? |
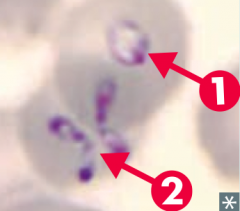
- Blood smear: ring form (1) and "Maltese cross" (2) |
|
|
How do you treat Babesia infection? |
Atovaquone + Azithromycin |
|
|
How do the hematologic protozoa differ in their disease presentation? |
- Plasmodium: malaria - fever, headache, anemia, splenomegaly |
|
|
How do the hematologic protozoa differ in their disease transmission? |
- Plasmodium: mosquito (Anopheles) |
|
|
How do the hematologic protozoa differ in their diagnosis? |
- Plasmodium: blood smear, trophozoite ring form within RBC, schizont containing merozoites |
|
|
How do the hematologic protozoa differ in their treatment |
- Plasmodium: Chloroquine (or if resistant: Mefloquine or Atovaquone / Proguanil), +/- Quinidine if life-threatening, +/- Primaquine if Vivax or Ovale |
|
|
Which protozoa cause visceral infections? |
- Trypanosoma cruzi |
|
|
Which protozoa causes Chagas disease - dilated cardiomyopathy, megacolon, megaesophagus? Transmission? Diagnosis? Treatment? |
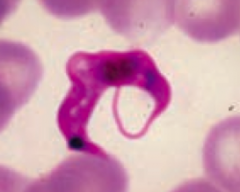
Trypanosoma cruzi (protozoa) |
|
|
What disease does Trypanosoma cruzi cause? Symptoms? |
Chagas disease |
|
|
How is Trypanosoma cruzi transmitted and diagnosed? |
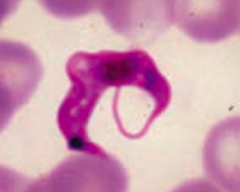
- Transmitted via Reduviid bug ("kissing bug") feces, deposited in a painless bite (much like a kiss) |
|
|
How is Trypanosoma cruzi treated |
Benznidazole or Nifurtimox |
|
|
Which parasite causes visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar) - spiking fevers, hepatosplenomegaly, and pancytopenia? Transmission? Diagnosis? Treatment? |
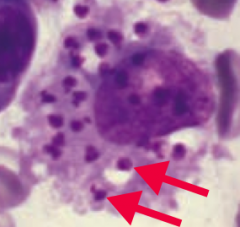
Leishmania donovani (protozoa) |
|
|
What disease is caused by Leishmania donovani? Symptoms? |
Visceral Leishmaniasis (Kala-Azar) |
|
|
How is Leishmania donovani transmitted and diagnosed? |
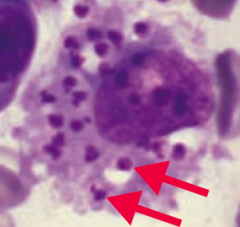
- Transmitted via sandfly |
|
|
How is Leishmania donovani treated? |
Amphotericin B and Sodium Stibo |
|
|
How do the visceral protozoa present? |
- Trypanosoma cruzi: Chagas disease (dilated CM, megacolon, megaesophagus) |
|
|
How are the visceral protozoa transmitted? |
- Trypanosoma cruzi: Reduviid bug (kissing bug) feces, deposited in a painless bite (much like a kiss) |
|
|
How are the visceral protozoa diagnosed? |
- Trypanosoma cruzi: blood smear |
|
|
How are the visceral protozoa treated? |
- Trypanosoma cruzi: Benznidazole or Nifurtimox |
|
|
Which protozoa cause STDs? |
Trichomonas vaginalis |
|
|
Which parasite presents as vaginitis with foul-smelling greenish discharge, itching and burning and causes the cervix to look like a strawberry? Transmission? Diagnosis? Treatment? |

Trichomonas vaginalis |
|
|
How do you distinguish Trichomonas vaginalis from Gardnerella vaginalis? |
- Trichomonas vaginalis: protozoa / parasite |
|
|
How does Trichomonas vaginalis present? |
Vaginitis |
|
|
How is Trichomonas vaginalis transmitted and diagnosed? |

- Transmitted sexually (doesn't exist outside human because it can't form cysts) |
|
|
How is Trichomonas vaginalis treated? |
Metronidazole for patient and partner (prophylaxis) |
|
|
What are the types of intestinal nematodes (roundworms)? |
- Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) |
|
|
What are the types of tissue nematodes (roundworms)? |
- Onchocerca volvulus |
|
|
Which parasite causes intestinal infection causing anal pruritus and is diagnosed by the Scotch Tape test? Transmission? Treatment? |
Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm / nematode) |
|
|
What kind of parasite is Enterobius vermicularis? How is it transmitted? |
- Pinworm - nematode / roundworm |
|
|
What symptoms are caused by Enterobius vermicularis? How is it treated? |
- Intestinal infection causing anal pruritus (diagnosed via Scotch Tape test) |
|
|
Which parasite causes intestinal infection and the eggs are visible in feces under a microscope? Transmission? Treatment? |
Ascaris lumbricoides (giant roundworm - nematode) |
|
|
What kind of parasite is Ascaris lumbricoides? How is it transmitted? |
- Giant roundworm - nematode |
|
|
What symptoms are caused by Ascaris lumbricoides? How is it treated? |
- Intestinal infection |
|
|
Which parasite causes an intestinal infection causing vomiting, diarrhea, and epigastric pain that may mimic the feeling of a peptic ulcer)? Transmission? Treatment? |
Strongyloides stercoralis (nematode) |
|
|
What kind of parasite is Strongyloides stercoralis? How is it transmitted? |
- Nematode (roundworm) |
|
|
What symptoms does Strongyloides stercoralis cause? Treatment? |
- Intestinal infection causing vomiting, diarrhea, epigastric pain (may be peptic-ulcer like) |
|
|
Which parasite causes intestinal infection that leads to anemia by sucking blood from intestinal walls? Transmission? Treatment? |
Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus (hookworms) |
|
|
How are the different intestinal nematodes (roundworms) transmitted? |
- Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm): fecal-oral |
|
|
How do the intestinal nematodes (roundworms) differ in presentation? |
- Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm): anal pruritus (diagnosed via Scotch Tape test) |
|
|
How do the intestinal nematodes (roundworms) differ in treatment? |
- Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm): Bendazoles or Pyrantel Pamoate |
|
|
What are the types of tissue nematodes (roundworms)? |
- Onchocerca volvulus |
|
|
Which parasite causes hyperpigmented skin and river blindness? Transmission? Treatment |
Onchocerca volvulus (nematode / roundworm) |
|
|
What kind of parasite is Onchocerca volvulus? How is it transmitted? |
- Nematode (roundworm) |
|
|
What symptoms does Onchocerca volvulus cause? How do you treat it? |
- Hyperpigmented skin and river blindness |
|
|
Which parasite causes swelling in the skin and the worm can be visualized in the conjunctiva? Transmission? Treatment? |
Loa loa (nematode / roundworm) |
|
|
What kind of parasite is Loa loa? How is it transmitted? |
- Nematode / roundworm |
|
|
What symptoms does Loa loa cause? Treatment? |
- Swelling in skin |
|
|
Which parasite blocks lymphatic vessels leading to elephantiasis 9 months to 1 year after bite? Transmission? Treatment? |
Wuchereria bancrofti (nematode / roundworm) |
|
|
What type of parasite is Wuchereria bancrofti? How is it transmitted? |
- Nematode / roundworm |
|
|
What symptoms does Wuchereria bancrofti cause? Treatment? |
- Blocks lymphatic vessels → elephantitis |
|
|
Which parasite causes visceral larva migrans? Transmission? Treatment? |
Toxocara canis (nematode / roundworm) |
|
|
What kind of parasite is Toxocara canis? How is it transmitted? |
- Nematode / roundworm |
|
|
What symptoms does Toxocara canis cause? Treatment? |
- Visceral larva migrans |
|
|
How are the tissue nematodes / roundworms transmitted? |
- Onchocerca volvulus: female blackfly bite |
|
|
What symptoms do the tissue nematodes / roundworms cause? |
- Onchocerca volvulus: hyperpigmented skin and river blindness, allergic reaction to microfilaria possible |
|
|
How are the tissue nematodes / roundworms treated? |
- Onchocerca volvulus: Ivermectin (for rIVER blindness) |
|
|
Which nematodes are ingested? |
You'll get sick if you EAT these! |
|
|
Which nematodes are acquired through a cutaneous route? |
These get into your feet from the SANd? |
|
|
Which nematodes are acquired via a bite? |
Lay LOW to avoid getting bitten |
|
|
What are the cestodes (tapeworms)? |
- Taenia solium |
|
|
Which parasite causes cysticercosis (cysts in skin) and neurocysticercosis (cysts in brain) after ingestion of larvae encysted in undercooked pork? Disease? Transmission? Treatment? |
Taenia solium (cestodes / tapeworms) |
|
|
What kind of parasite is Taenia solium? How is it transmitted? |
- Cestode (tapeworm) |
|
|
What diseases are caused by Taenia solium? How are they treated? |
- Intestinal infection treated with Praziquantel |
|
|
Which parasite causes a vitamin B12 deficiency by competing for B12 in the intestine, leading to anemia? Transmission? Treatment? |
Diphyllobothrium latum (cestode / tapeworm) |
|
|
What kind of parasite is Diphyllobothrium latum? How is it transmitted? |
- Cestode / tapeworm |
|
|
What disease does Diphyllobothrium latum cause? How is it treated? |
- Vitamin B12 deficiency (tapeworm competes for B12 in intestine), which causes anemia |
|
|
Which parasite causes hydatid cysts in liver, causing anaphylaxis if antigens are release? Transmission? Treatment? |
Echinococcus granulosus (cestode / tapeworm) |
|
|
How are the Cestodes (Tapeworms) transmitted? |
- Taenia solium: ingestion of larvae encysted in undercooked pork or ingestion of eggs |
|
|
What diseases do the Cestodes (Tapeworms) cause? |
- Taenia solium: intestinal infection and cysticercosis and/or neurocysticercosis |
|
|
How are the Cestodes (Tapeworms) treated? |
- Taenia solium: Praziquantel and Albendazole for Neurocysticercosis |
|
|
What are the Trematodes (flukes)? |
- Schistosoma |
|
|
Which parasite causes liver and spleen granulomas, fibrosis, and inflammation or if chronic, can lead to squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder (painless hematuria)? Transmission? Treatment? |
Schistosoma (trematode / fluke) |
|
|
What kind of parasite is Schistosoma? How is it transmitted? |
- Trematode (fluke) |
|
|
What kind of disease does Schistosoma cause? Treatment? |
- Liver and spleen granulomas, fibrosis, and inflammation |
|
|
Which parasite causes biliary tract inflammation and pigmented gallstones and is associated with cholangiocarcinoma? Transmission? Treatment? |
Clonorchis sinensis (trematode / fluke) |
|
|
What kind of parasite is Clonorchis sinensis? How is it transmitted? |
- Trematode / fluke |
|
|
What disease does Clonorchis sinensis cause? Treatment? |
- Biliary tract inflammation, which can lead to pigmented gallstones |
|
|
How are the trematodes / flukes transmitted? |
- Schistosoma: snails are host, cercariae penetrate skin of humans |
|
|
What diseases do the trematodes / flukes cause? |
- Schistosoma: liver and spleen granulomas, fibrosis and inflammation; chronic infection associated with squamous cell carcinoma of bladder |
|
|
How are the trematodes / flukes treated? |
- Schistosoma: Praziquantel |
|
|
Which parasite should you associate with biliary tract disease and cholangiocarcinoma? |
Clonorchis sinensis - trematode / fluke |
|
|
Which parasite should you associate with brain cysts and seizures? |
Taenia solium (neurocysticercosis) - cestode / tapeworm |
|
|
Which parasite should you associate with hematuria and bladder cancer? |
Schistosoma haematobium - trematode / fluke |
|
|
Which parasite should you associate with liver (hydatid cysts)? |
Echinococcus granulosus - cestode / tapeworm |
|
|
Which parasite should you associate with microcytic anemia? |
Nematodes / roundworms: |
|
|
Which parasite should you associate with perianal pruritus? |
Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) - nematode / roundworm |
|
|
Which parasite should you associate with portal hypertension? |
Trematodes / flukes (cause liver granulomas, fibrosis, and inflammation) |
|
|
Which parasite should you associate with vitamin B12 deficiency? |
Diphyllobothrium latum - cestode / tapeworm |

