![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name importance of fermented foods to humans
|
preservation, enhancement of the diet through new flavors aromas and textures, enhancement of nutrient value, detoxification, decreases cooking time and fuel
|
|
|
Explain how coenzymes are regenerated and how catabolism works. Aerobic and anaerobic.
|
AEROBIC
NAD+ is oxidized via the krebs cycle which features a complete catabolic breakdown and produces maximal energy. Byproduct is CO2. OVerall process is breaking down of molecules to form pyruvic acid (H is removed) To regenerate the coenzymes (NADH-->NAD+), the aerobic cycle goes through the chemiosmotic cycle which dumps H+ and transports electrons through the inner membrane to create ATP ANAEROBICALLY Pyruvic acid is still created via catabolism, but fermentation regenerates the coenzymes through an inefficient process that creates a variety of byproducts. No ATP is produced in fermentation |
|
|
What are the major byproducts of all the fermentation pathways?
|
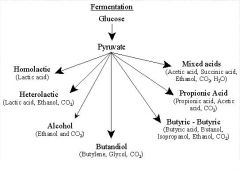
Thji
|
|
|
What are the major fermentation players in respect to yeasts, molds, and bacteria?
|

de
|

