![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Microscopy |
Discovery of the very small |
|
|
Robert Hooke |
Published Micrographia in 1665. Led to discovery of the cell |
|
|
Anton von Leeuwenhoek |

Created the single-lens microscope. Discovered tiny, living animals using his microscope, which he called animalcules |
|
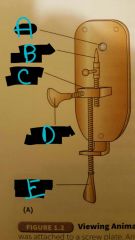
Single-lens Microscope |
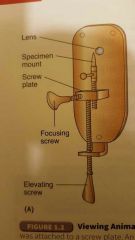
|
|
|
Spontaneous Generation |
Suggested that some forms of life could arise from nonliving, decaying matter if provided with the "vital force" |
|
|
Francesco Redi |
Italian naturalist who, in 1668, performed one of history's first known biological experiments. His experiment was designed to test whether maggots could arise spontaneously from rotting meat |
|
|
Louis Pasteur |
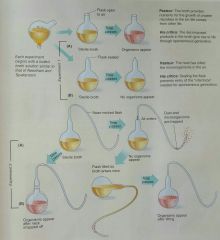
French chemist who, in 1861, proved spontaneous generation of animalcules is not possible. Proposed germs cause infectious disease, and created pasteurization to kill pathogens. Proved yeast causes fermentation. |
|
|
Edward Jenner |
In 1796, determined that disease (smallpox) could be prevented through vaccination using a similar but milder disease causing bacteria |
|
|
Miasma |
a highly unpleasant or unhealthy smell or vapor. Does not transmit disease |
|
|
Disease Transmission |
Transmitted from person to person by direct or indirect contact. Viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi all cause infectious disease. Malaria, measles, and respiratory illnesses are examples of infectious diseases. |
|
|
Ignaz Semmelweis |
Hungarian obstetrician who, in 1847, determined the source of puerperal fever or blood poisoning of women and children by medical staff not washing their hands |
|
|
Puerperal Fever |
fever caused by uterine infection following childbirth |
|
|
John Snow |

An English surgeon who, in 1854, discovered the cause of cholera transmission in London. Discovered you can interrupt disease, which he did by having a street pump handle removed from a water source |
|
|
Joseph Lister |
Developed antisepsis by using carbolic acid, phenol, spray on open wounds Demonstrated germs can come from the environment and can be controlled through cleanliness
|
|
|
Robert Koch |
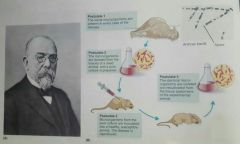
Koch's postulates became standards for linking a specific organism to a specific disease. Developed pure culture techniques; by adding gelatin to his broth, he was able to grow bacterial colonies in a petri dish |
|
|
Fanny Hesse |

Used agar to solidify jams, jellies, creating an ideal mix for bacterial culture |
|
|
Ivanowsky and Beijerinck |
Their observations of filterable viruses showed that liquid filtrate causes tobacco mosaic disease |
|
|
Walter Reed |
Said that a filterable viruses causes yellow fever in humans |
|
|
Anton de Bary |
Studied Fungi linked to plant diseases |
|
|
Charles Laveran |
Discovered a protozoan parasite in blood caused malaria |
|
|
Winogradsky |
Recognized the beneficial roles of nitrogen fixing bacteria in soil |
|
|
Prokaryotes |
A microscopic single-celled organism that has neither a distinct nucleus with a membrane nor other specialized organelles. Prokaryotes include the bacteria and cyanobacteria. Over 10 million different species that are spherical, spiral, or rod shaped. Have 2 domains (bacteria and archaea)
|
|
|
Viruses |
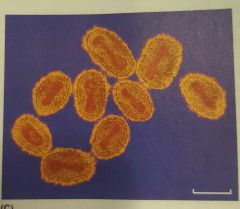
Are not microbes or cells (not cellular and cannot be grown in pure culture). Have a DNA or RNA core surrounded by a protein coat. Cannot replicate without a host cell. Over 100 million types. |
|
|
Fungi |

Around 100,000 species. Most live in their food medium and may cause human disease. Some make useful antibiotics or help flavor foods |
|
|
Protists |
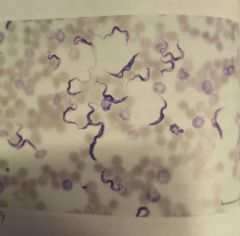
Single celled protozoa and algae. Some are free living and some live symbiotically with other organisms. Some can cause disease in humams. |
|
|
Beadle and Edward |
Using fungus, demonstrated that one gene codes for one enzyme |
|
|
Luria and Delbrück |
Used E. coli to show that mutations could occur spontaneously |
|
|
Avery, MacLeod and McCarty |
Suggest DNA is the genetic material in cells by using the bacterial organism Streptococcus pneumoniae |
|
|
Hershey and Chase |
Confirmed DNA as the substance of the genetic material by using a virus to infect bacterial cells |
|
|
Crick |
Used E. coli and a virus to show how the DNA genetic code works to make individual proteins |
|
|
Eukaryotic cells |
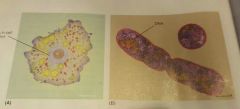
eu = true karyon = nucleus Plant, animal, fungi, protist. Contain a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles |
|
|
Antibiotics |
Used to cure infectious disease. However, many pathogens are becoming resistant to antibiotics. |
|
|
Erlich |
Developed Salvarsan, a chemical that cured individuals or syphilis |
|

Fleming |
Observed that a species of Penicillin mold killed bacterial cells |
|
|
Chain and Florey |
Developed penicillin |
|
|
Bioterrorism |
Intentional use of biological agents to cause fear or death |
|
|
Global warming can cause? |
Larger spread of disease |
|
|
Microbiology today is concerned with... |
The relationship of microorganisms with their environment |
|
|
Microbial Evolution |
Represents a model system to observe evolutionary processes |
|
|
5 Major Microbial Groups |
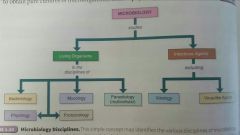
Bacteriology - study of bacteria Virology - study of viruses Mycology - study of fungi Protozoology - study of protozoa Phycology - study of the algae
|

