![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Contamination |
Prensence of unwanted microbes |
|
|
|
Pathogen |
Disease causing microbe |
|
|
|
Asepsis |
No unwanted microbes present |
|
|
|
Aseptic technique |
Prevents unwanted microbes protecting sample, handler and tests. |
|
|
|
Aseptic technique includes use of |
Bunsen burners Loops for transferring And special handling techniques to minimize contamination Use of PPE |
|
|
|
Culturing |
Microbes grown in lab using aseptic technique |
|
|
|
Culture |
One or more microbes are grown using nutrient media and in controlled temperatures Also with has composition moisture and time |
|
|
|
Incubators |
Help control growth conditions |
|
|
|
Sterile |
Absent of all living things |
|
|
|
Pure or axenic culture |
Only one species of microbe |
|
|
|
Subculture |
Cultures transferred to new.media |
|
|
|
Colonies |
Millions of single celled individuals |
|
|
|
Colony characteristics |
Help identify species |
|
|
|
Colony forming units |
When colonies are counted or quantified |
|
|
|
Broth and trubidity |
Liquid media that are clear when sterile and become cloudy when microbial growth is present becoming turbid. |
|
|
|
Colony morphology |
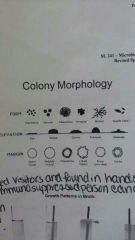
|
|
|
|
Growth patterns in broth |
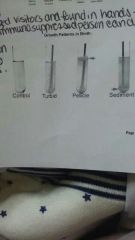
|
|
|
|
Streak plate |
Used to isolate colonies |
|
|
|
Spread plate/standard plate count |
Used to count microbes based on colony forming units cfu/ml |
|
|
|
Pour plate |
Microbe growth and isolation to determine the number of microbes/no so colonies per plate. Disadvantage is that it can get rid of aerobes and some colonies may get overlooked. |
|
|
|
Dilution series or serial dilution |
Quantitatively reducing the concentration of microbes in a liquid culture by transferring liquid from one tube to another causing 10 fold dilutions. |
|
|
|
Purpose of serial dilution |

200- too many to count Less than 20- too few 20-200 just right |
|
|
|
Determine cfu/ml in original sample |

|
|
|
|
OCD calculation |

|
|
|
|
Genetic engineering and biotechnology |
Manipulate genes of organisms to introduce new characteristics to receipient (useful) ex insulin |
|
|
|
Transformation |
Ability for bacteria to incorporate free or makes the from the environment into their cell. They express it and it can be taken up by chromosomal DNA fragment or a plasmid. |
|
|
|
Competence |
Ability for bacterialcell to take DNA from their environment for transformation and express it |
|
|
|
PGreen plasmid |
Green fluorescent protein gene for ampicillin resistance from bioillimunecent jelly fish. It is a reporter molecule |
|
|
|
Amp |
Ampicillin resistance portion of plasmid that contains gene for ampicillin resistance that encodes enzyme beta lactamase wich destrys ampicillin and allows it to survive and form colonies in amp medium. Without amp transformation they cannot grow. |
|
|
|
Transformation of pGreen |
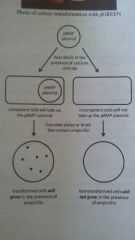
- not transformed negative comtrol + transformed. Positive control |
|
|
|
Anatomy of a microscope |

|
|
|
|
Bacterial morphology |

|
|
|
|
Gram stain |
Differential stain Psitive- blue purple Negative- pink |
|
|
|
B lactam antibiotics |
Target cell wall and gets to positive purple Negative is more complex because of lipoproteins |
|
|
|
Eukaryotes |
Fungi and protisrs that are large |
|
|
|
Fungi |
Mold Multicellular fuzzy colornies Yeast unicellular white circular colonies |
|
|
|
Molds |
Grow long tangled filaments called hyphae and possible rough cotton like colonies called mycellial mats with fruiting bodies wich are reproductive structures. |
|
|
|
Yeast |
Unicellular fungi Reproduce by budding |
|
|
|
Protists |
Single celled Can be free living or parasitic Amoeba Paramecium Spirostonum Stentor Flaggenated euglena And algae volvox.
Motility and Brownian movement |

|
|
|
Plant like protist |
Algae use amyotrophic nutrition |
|
|
|
Animal like protest |
Proozoa heterotrophic nutrition |
|
|
|
Factors that influence transformation efficiency |

|
|
|
|
Calculating transformed efficiency |

|
|
|
|
Calcium chloride and heat transformation |
Neutralizes charge of cell wall Heat = opens pores for permeability |
|
|
|
Tranformation |
Untransformed in - nutrient = can grow no amp Untransfprmed - in amp- no growth bc no amp resist gene no lactamase Transformed + in nutrient= grow Transformed + with amp- grow with late of media bc of beta lactamase |
|
|
|
Protest |

|
|

