![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What things affect the taste of wine
|
tannins and polyphenols
|
|
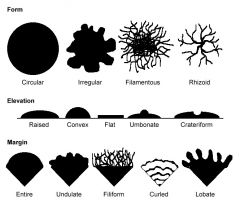
|
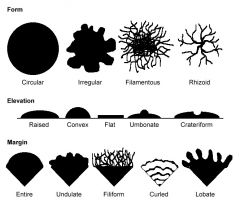
|
|
|
true of false
Antibodies are bivalent, Y-shaped molecules. |
true
|
|
|
true of false
Antibodies are composed of two heavy chains and two light chains bound by disulfide linkages |
true
|
|
|
true of false
Antibodies can react with multivalent antigens to form a lattice network. |
true
|
|
|
Precipitation =
|
A bivalent antibody reacts with a multivalent antigen that is soluble (e.g. a protein or carbohydrate) and forms a lattice network of alternating Ab-Ag. A precipitation was formed in the Ouchterlony gel diffusion experiment
|
|
|
Agglutination =
|
A bivalent antibody reacts with a multivalent antigen that is insoluble: particulate or cellular (e.g. bacteria, viruses, tumor cells, foreign red blood cells etc..) and forms a lattice network of alternating Ab-Ag. An agglutination is demonstrated by hemagglutination seen in blood typing
|
|
|
Rh factor =
|
This refers to a protein found on the surface of red blood cells called RhD. Some people have it (Rh+) and some don’t (Rh-). A person who has type A blood and is Rh+, has A+ blood.
|
|
|
If an ___ woman is carrying a child of an ___ man, after the first pregnancy she may begin to produce antibodies to the Rh factor. If not treated with Rhogam than this can be a problem in subsequent pregnancies, as the mother may produce antibodies against the unborn child if it is Rh+.
|
RH-
RH+ |
|
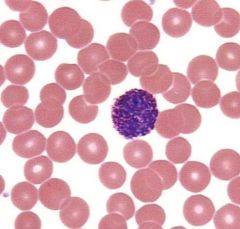
what is this
|
basophil
|
|
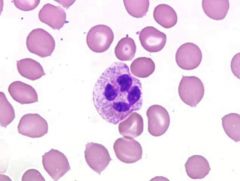
what is this
|
neutrophils
|
|
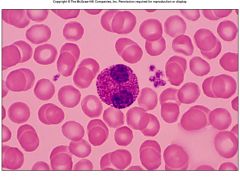
what is this
|
eosinophils
|
|
|
how to remember abundance of white blood cells
|
never let monkeys eat bananas
neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte, eosinophil, basophil |
|
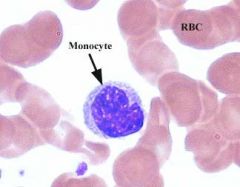
what is this
|
monocyte
important |
|
|
|
|
|
All coliforms are normal flora bacteria that are present in the
|
GI tract of every warm blooded animal
|
|
|
Coliforms are Gram____, ____-spore forming rods that are aerobic or facultatively anaerobic. All are _____
|
negative
non lactose fermenters. |
|
|
what does PA stand for and what does this qualitative test measure
|
To simply determine if coliforms are present, the presence absence test (PA test) can be used. This is a qualitative test that can detect a single coliform in a 100 mL water sample. The broth contains lactose and a pH indicator
turns from purple to yellow if positive |
|
|
what is the membrane filtration method
|
To determine the number (quantitative) of coliforms present, the membrane filtration method can be used. Endo medium inhibits the growth of Gram-positive organisms (What selective ingredients do this??). It also differentiates between coliforms that ferment lactose (red or dark pink colonies) and those that don’t (light, colorless colonies).
|
|
|
what is the multiple tube fermentation method
|
determines, quantitatively, how many coliforms are present. This test has three stages. The first stage is the quantitative stage, the other two are merely confirming that a coliform has been identified
|
|
|
in the IMViC test (Indole, methyl Red, VP and Citrate) test what is reading for fecal coliform
and nonfecal coliform |
+ + - -
- - + + |
|
|
Streptomyces
|
a. belongs to the bacterial group called Actinomycetes.
b. has filamentous growth (looks like a fungus but is not). c. Produce geosmin, a compound that gives soils their earthy odor. d . is a source of antibiotics (e.g. streptomycin) e . can be isolated using Jensen’s molten agar. |
|
|
Molds -
|
Generally found in well-aerated soils and most are saprophytes. Often capable of digesting complex polysaccharides such as cellulose.
b. Selected for using Martin’s molten agar. This agar contains two selective ingredients: Rose Bengal dye and streptomycin that inhibit the growth of non-mold soil organisms. |
|
|
Azotobacter and Rhizobium were the two N2 fixing genera discussed in class
what is the difference between how they live |
Rhizobium is a symbiotic organism of root nodules but Azotobacter is free living which is why we were able to isolate it from soil using nitrogen-free media.
azotobacter can form cysts |
|
|
Lactococcus is used in the production of___cheese and Lactobacillus in the production of ___cheese
|
hard
soft |
|
|
Streptococcus is used to make
|
sour cream and yogurt
|
|
|
Acetobacter is used in the production of
|
vinegar
|
|
|
The two types of food-borne disease are
|
food infections and food intoxications
food infection is when the microorganism itself is living inside causing infection food intoxication is when a chemical produced by a microorganism is ingested |
|
|
Used to detect the amount of Lactobacillus present in saliva.
2. Attempts to positively correlate the amount of Lactobacillus with susceptibility to cavities |
Snyder's Test for Susceptibility of Dental Caries
|
|
|
yogurt is made with this ration of these bacteria
|
1:1 ratio of Streptococcus thermophilis and Lactobacillus bulgaricus
|

