![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acellular organisms |
Fully dependent on host for existence.
"Non-living" and borderline qualified to be called an organism.
Ex: Prions and Viruses |
|
|
Prion |
Infectious agent composed of protein.
Known diseases are untreatable and fatal. |
|
|
Prokaryotic Organism |
Single-celled organism. No nucleus or mitochondria.
All components are within the cell membrane/plasma membrane.
Ex: Archaea and bacteria |
|
|
Eukaryotic Organisms |
Any organism with a nucleus and other membrane-bound structures. Contains many unicellular organisms. Contains all multi-cellular organisms.
Micro Ex: Fungi, protozoa, algae Macro Ex: Plants and animals |
|
|
Antonie van LeeuWenhoek |
c. 1600's Dutch scientist. Commonly called "Father of Microbiology" and considered 1st microbiologist. Made improvements on the microscope. First to observe micro-organisms. "Animalcules" Did drawings and wrote down observations. |
|
|
Edward Jenner |
c. 1700's physician and scientist.
Discovered vaccine for smallpox, using cowpox. |
|
|
Joseph Listier |
c. 1800's British surgeon .
Pioneer of antiseptic surgery.
Promoted idea of sterile surgery. |
|
|
Louis Pasteur |
c. 1800's French chemist & microbiologist. Known for: 1st vaccines for rabies & anthrax. Life creates life; cellular division. Pasteurization for milk and wine. Popularly known as "Father of Microbiology."
|
|
|
Robert Koch |
c. 1800's German physician & microbiologist. Founder of modern bacteriology. Named several bacteria. Improved laboratory techniques. Developed principles for linking specific microorganisms to specific diseases. Cholera and TB research.
|
|
|
Walther Hesse |
Developed Augar as a medium for culturing microorganisms (used in petri dishes). |
|
|
Alexander Fleming |
c. 18-1900's Scottish biologist & pharmacologist. Bad methodology. Discovered penicillin while growing staphylococcus in petri dishes. |
|
|
Selman Waksman |
c. 1900's Ukranian biochemist & microbiologist.
Discovered streptomycin which is effective against TB. |
|
|
Compound Microscope |
Multiple lenses. Condenser, oil immersion, objective, & ocular lenses. 1000x max magnification Can see as small as 100 nm organism.
Res = .5(lambdah/Na) = nm |
|
|
Coccus |
Spherical-shaped bacteria |
|
|
Bacillus |
Rod-shaped bacteria |
|
|
Spirillium |
Spiral-shaped bacteria |
|
|
Gram Stain Positive (GM+) |
Blue-purple
|
|
|
Gram Stain Negative (GM-) |
Red-pink |
|
|
Decolorization for stain |
Acetone or alcohol |
|
|
Acid-fast |
Resistance to decolorization by acids during staining.
Need more in-depth testing than regular staining. |
|
|
Mycobacterium |
GM- Aerobic! Cause of TB. Acid-fast bacteria. |
|
|
Endospore |
A reduced dormant structure produced by a bacteria that is non-reproductive, containing DNA and ribosomes. Can revive centuries later. Very few bacteria can make it; usually large bacteria. Heat resistant (to boiling water) Ex: Bacillus and Clostridium |
|
|
Bacillus anthracis |
Rod-shaped GM+ Endospore Aerobic/Anaerobic Causes anthrax |
|
|
Clostridium botulinum |
Rod-shaped GM+ Anaerobic Endospore Causes botulism |
|
|
Electron microscope |
Magnification down to 1 nm. |
|
|
Eukaryotic Cell |
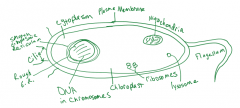
|
|
|
Prokaryotic Cell |
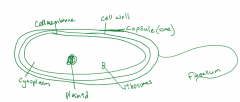
|
|
|
Mitochondria |
Generates ATP Very important to cell growth and may deal with the aging process. |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Protein synthesis in all living organisms |
|
|
Chitin |
Protective physical shell of fungi cells. |
|
|
Cellulose |
Protective physical shell of algae cells |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum |
Rough and smooth, ribosomes are attached. |
|
|
Golgi |
Packaging apparatus used for transporting stuff around the cell. |
|
|
Vacuoles |
Remove excess water from cell. |
|
|
Plasmids |
Contain ancillary information such as antibiotic resistance or environmental conditions that are bad for the cell. |
|
|
Enterobacter aerogenes |
Rod-shaped GM- Butenediol Fermentation Looks identical to E. coli so needs Voges Proskour test |
|
|
Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
Rod-shaped; has a cell wall GM- Anaerobic Mixed Acid Fermentation Test for using Methyl Red (MR+) Capsule Ex: Food poisoning |
|
|
Salmonella |
Rod-shaped GM- Capsule Ex: Typhoid fever |
|
|
Streptococcus |
Spherical chains GM+ Anaerobic Homolactic acid Fermentation Capsule |
|
|
Staphylococcus |
Spherical clusters GM+ Anaerobic Homolactic acid Fermentation |
|
|
Clostridium |
Rod-shaped GM+ Anaerobic Butyric Acid Fermentation Endospore |
|
|
Bacillus |
Rod-shaped GM+ Anaerobic Endospore |
|
|
Rhizobium |
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria N2 -> NH4
GM-
|
|
|
Archaea |
Produce methane. Can be found in the stomachs of cows.
|
|
|
Thiobacillus |
GM- Terminal Acceptor: S -> SO4 Found in strip mining runoff |
|
|
Neisseria |
GM- Anaerobic Spherical (coccus) |
|
|
Lactobacillus |
Rod-shaped chains GM+ Anaerobic Homo lactic acid fermentation
|
|
|
Phagolysosome |
Phagosome traps a pathogen then fuses with a lysosome. The pathogen is then digested with enzymes and peroxides. |
|
|
Metabolism |
ATP is created to use as energy Involves redox reactions
|
|
|
Terminal Electron Acceptor |
Last in chain of redox reactions.
Ex: Oxygen during respiration |
|
|
Fermentation |
Chain of redox reactions without a terminal electron acceptor. The electron moves back up the chain when it reaches the last acceptor. |
|
|
Fermentation Process |
Glycolysis --> Acids, gases or alcohol products
Anaerobic process |
|
|
Glycolysis |
Glucose -> 2 ATP -> 2 NADH -> Nad+ H- -> 2 pyruvate |
|
|
Homo Lactic Acid Fermentation |
--> Lactic Acid
Ex: Cheese, Streptococcus, Lactobacillus |
|
|
Hetero Lactic Acid Fermentation |
--> Lactic Acid + EtOH + CO2
Ex: Sourkraut |
|
|
Ethanolic/Alcoholic Fermentation |
--> Ethanol + CO2
Ex: Yeast |
|
|
Mixed Acid Fermentation |
Important for digestion. Lowers PH b/c it produces a lot of acid. Products: Acetic acid, formic acid
Ex: E. coli |
|
|
Butanediol Fermentatin |
--> Butandiol + CO2
Ex: Enterobacter aerogenes |
|
|
Propionic Acid Fermentation |
Propionic Acid + CO2
Ex: Swiss Cheese |
|
|
Butyric Acid Fermentation |
Products: Acetone, Butanol, CO2
Ex: Clostridium |
|
|
Kreb's Cycle |
Series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy. Creates CO2 and ATP and NADH |
|
|
Electron Transport Chain or Oxidative Phosphorylatin or Chemiosmosis |
Uses NADH or FADH to generate ATP
In Eukaryote, occurs in mitochondria membrane |

