![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
122 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
cations
|
positively charged ion
|
|
|
anions
|
negatively charged ion
|
|
|
endergonic reaction
|
Energy direct inward
|
|
|
exergonic reaction
|
Energy direct outward
|
|
|
Anabolism is a...
|
Synthesis reaction
Typically dehydration synthesis |
|
|
Catabolism is a...
|
Decomposition reaction
typically hydrolytic (uses water to break chemical reactions) |
|
|
exchange reactions
|
Half Anabolism (Synthesis) / half Catabolism (Decomposition)
|
|
|
hydrolysis
|
hydro = water; lysis = to loosen
breaking down by adding water |
|
|
dehydration synthesis
|
releases water
condensation reaction |
|
|
polysaccharides vs di
|
Both can be broken down by hydrolysis.
Poly not sweet nor soluble in water |
|
|
dextran
|
blood plasma substitute
produced as a sugary slime by certain bacteria |
|
|
Chitin
|
polysaccharide
exoskeletons and cell walls of fungi |
|
|
amylases
|
enzymes that can break the bonds between glucose molecules in glycogen
|
|
|
cellulases
|
enzymes that can digest cellulose
|
|
|
Lipid polarity
|
non-polar
|
|
|
Simple lipids consist of what?
|
Glycerol and fatty acids
|
|
|
All fatty acids end with what?
|
-COOH
carboxyl or organic acid |
|
|
Bonding of glycerol to a fatty acid is called what?
|
ester linkage (a dehydration reaction)
|
|
|
primary function of lipids?
|
form plasma membranes
|
|
|
Steroid feature
|
four inter-connected carbon rings
|
|
|
Changes a steroid to a sterol
|
-OH group off of A-ring
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
speed up reactions
|
|
|
bacteriocins
|
proteins that kill bacteria
|
|
|
Alcohol
|
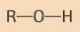
|
|
|
aldehyde
|
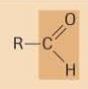
|
|
|
Amino acid structure
|
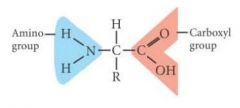
|
|
|
Amino
|
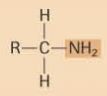
|
|
|
Carboxyl
|
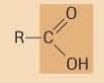
|
|
|
Cholesterol
|
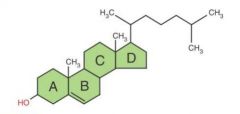
|
|
|
ester
|
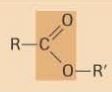
|
|
|
ether
|
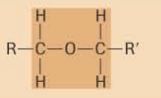
|
|
|
Glucose + fructose = sucrose reaction
|
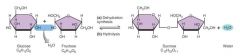
|
|
|
glycerol
|
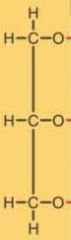
|
|
|
ketone
|
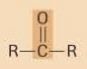
|
|
|
methyl
|
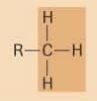
|
|
|
phosphate
|
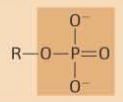
|
|
|
phospholipid
|
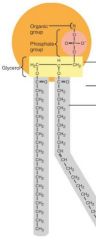
|
|
|
sulfhydryl
|
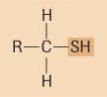
|
|
|
Kilometers to meters
|
1000 = 1 kilo
|
|
|
Decimeter to meter
|
10 deci = 1 meter
|
|
|
Centimeter to meter
|
100 centi = 1 meter
|
|
|
Millimeter to meter
|
1000 mili = 1 meter
|
|
|
Micrometer (um) to meter
|
1,000,000 micro = 1 meter
|
|
|
Nanometer (nm) to meter
|
1,000,000,000 Nano = 1 meter
|
|
|
Picometer (pm) to meter
|
1,000,000,000,000 Pico = 1 meter
|
|
|
objective lenses
|
closed to the object
|
|
|
ocular lens
|
eyepiece
|
|
|
refractive index
|
light bending ability
|
|
|
darkfield microscope
|
used to examine live microorganisms that either are invisible in the ordinary light microscope, cannot be stained by standard methods, or are so distorted by staining that their characteristics then cannot be identified.
|
|
|
phase-contrast microscope
|
Phase-contrast microscopy is especially useful
because it permits detailed examination of internal structures in living microorganisms not necessary to fix (attach the microbes to the microscope slide) or stain the spec imen-procedu res that could distort o r kill the microorganisms. |
|
|
psychrophiles
|
cold-loving microbes (optimum temp 15*C)
|
|
|
mesophiles
|
moderate-temperature loving microbes (optimum temp 25-40* C)
|
|
|
thermophiles
|
heat-loving microbes (optimum temp 50-60* C)
|
|
|
psychrotrophs
|
cold thriving bacteria responsible for food spoilage
|
|
|
optimum temperature pathogenic bacteria:
|
37 °c
|
|
|
acidophiles
|
acid lovers
|
|
|
plasmolysis
|
shrinkage of cytoplasm
|
|
|
extreme halophiles
|
require saline environments
|
|
|
facultative vs obligate halophiles
|
facultative = do not require, but can survive up to 2% salinity
obligate = requires around 30% |
|
|
Half the dry weight of a typical bacterial cell is...
|
carbon
|
|
|
_______ makes up about 14% of the dry weight of a bacterial cell, and _______ and _______ together constitute about another 4%
|
Nitrogen
Sulfur and Phosphorus |
|
|
Organisms use nitrogen primarily to form the...
|
amino group of the amino acids of proteins
|
|
|
Methods of extracting nitrogen
|
-decomposing protein-containing material
-ammonium ions (NH4+) -nitrates (compounds that dissociate to give the nitrate ion, N03-, in solution) -nitrogen fixation (use gaseous nitrogen (N2) directly from the atmosphere |
|
|
Uses of Sulfur synthesis
|
create sulfur-containing amino acids and vitamins such as thiamine and biotin
|
|
|
Sources of sulfur
|
sulfate ion (SO4^2-) hydrogen sulfide, and sulfur containing amino acids
|
|
|
Uses of Phosphorus synthesis
|
-nucleic acids
-the phospholipids of cell membranes -ATP |
|
|
Sources of phosphorous
|
phosphate ion (PO4^-3)
|
|

|
1. Obligate Aerobes
2. Facultative Anaerobes 3. Obligate Anaerobes 4. Aerotolerant Anaerobes 5. Mlcroaerophlhls |
|
|
Singlet oxygen
|
Boosted into a higher-energy state and is extremely reactive.
|
|
|
Superoxide radicals
|
superoxide anions
...are formed in small amounts during the normal respiration of organisms that use oxygen as a final electron acceptor, forming water |
|
|
superoxide dismutase (SOD)
|
an enzyme that neutralizes superoxide radicals, which obligate anaerobes produce when exposed to oxygen
|
|
|
peroxide anion
|
the o2^-2 portion of H2O2
|
|
|
catalase
|
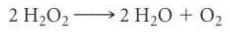
enzyme that converts peroxide into water and oxygen
|
|
|
peroxidase
|
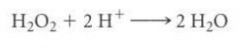
The other enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide
|
|
|
Chlorhexidine
|
Anti-septic
membrane disruption both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria also fungi |
|
|
Biofilms contents
|
Polysaccharides
DNA Proteins |
|
|
inoculum
|
microbes introduced to a medium
|
|
|
agar contents
|
complex polysaccharide derived from marine alga
|
|
|
Properties of Agar
|
Microbes cannot decay
liquefies at 100 C* |
|
|
capnophiles.
|
Microbes that grow better at high CO2 concentrations
|
|
|
Selective media
|
are designed to suppress suppress the growth of unwanted bacteria and encourage the growth of the desired microbes
|
|
|
Differential media
|
make it easier to distinguish colonies of the desired organism from other colonies growing on the same plate
|
|
|
enrichment culture
|
amplifies particular microbes
|
|
|
lyophilization
|
freeze drying and storing bacteria cultures
|
|
|
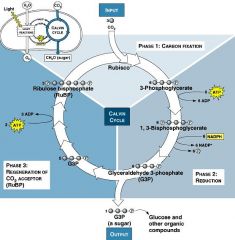
Calvin cycle
|
|
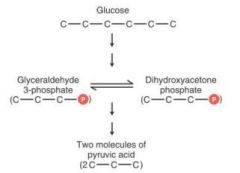
Name of process?
|
Glycolysis
|
|
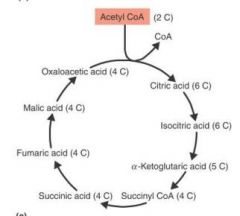
Name of this cycle?
|
Krebs cycle
|
|
|
phenol
|
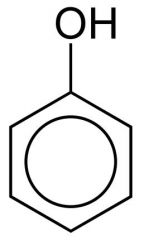
-Lister first applied to surgical instruments
-controls odor in sewage -irritates skins -above 1% significant anti-bacteria effects |
|
|
Bisphenols
|
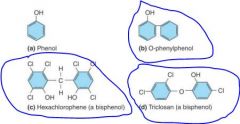
two phenols connected by bridge group
|
|
|
Biguanides
|
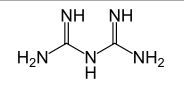
Attack cell walls in gram positive cells and antiviral
-useful in treating hyperglycemia (primary branch in metaformin) |
|
|
emulsification
|
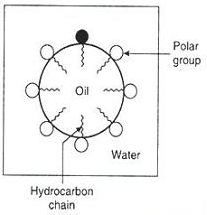
surrounds organic material and allows removal by water
|
|
|
How effective is soap?
|
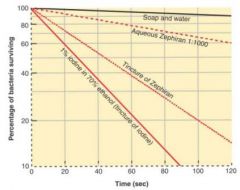
|
|
|
sulfur dioxide
|
prevents wine spoilage
|
|
|
Calcium propionate
|
prevents surface molds
|
|
|
Sorbic acid, potassium sorbate and sodium benzoate
|
prevent mold spoilage in sub 5.5 pH food products
|
|
|
sodium nitrate
|
-preserves red color in meat by forcing bacteria to use nitrate in anaerobic conditions
-prevents botulism spores -downside (may form carcinogenic nitrosamines) |
|
|
DNA polymerase
|
Synthesizes DNA: proofreads and repairs DNA
|
|
|
DNA Gyrase
|
Relaxes supercoiling ahead of the replication fork
|
|
|
DNA Ligase
|
Makes covalent bonds to join DNA strands: joins Okazaki fragments and new segments in excision repair
|
|
|
Endonucleases
|
Cut DNA backbone in a strand of DNA: facilitate repair and insertions
|
|
|
Exonucleases
|
Cut DNA from an exposed end of DNA: facilitate repair
|
|
|
Helicase
|
Unwinds double-stranded DNA
|
|
|
Methylase
|
Adds methyl group to selected bases in newly made DNA
|
|
|
Photolyase
|
Uses visible light energy to separate UV-induced pyrimidine dimers
|
|
|
Primase
|
Makes RNA primers from a DNA template
|
|
|
Ribozyme
|
RNA enzyme that removes introns and splices exons together
|
|
|
RNA Polymerase
|
Copies RNA from a DNA template
|
|
|
snRNP
|
RNA-protein complex that removes introns and splices exons together
|
|
|
Topoisomerase
|
Relaxes supercoiling ahead of the replication fork: separates DNA circles at the end of DNA replication
|
|
|
Transposase
|
Cuts DNA backbone leaving single-stranded "sticky ends"
|
|
|
3* vs 5*
|
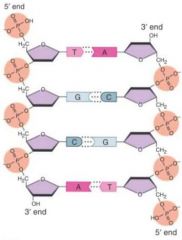
5* carbon with the phosphate group
3* carbon with the alcohol group |
|
|
DNA polymerase can only add to:
3* or 5* |
DNA polymerases can add new nucleotides to the 3' end
only |
|
|
transcription begins at the...
|
promoter
|
|
|
degeneracy
|
biological redundancy used to increase robustness of organism
ex multiple codon combos for amino acid |
|
|
ethylene oxide gas uses
|
non-wetable items
powders, dry plastics, etc. |
|
|
2-3.2 percent alkaline glutaraldehyde (10 hours)
|
wetable
endoscopes |
|
|
2-3.2 percent alkaline glutaraldehyde (10 hours)
|
respiratory devices
non-critical instruments |
|
|
80 percent ethyl alcohol (Lysol® spray)
|
countertops and small surfaces
other agents are inactivated by organic material or ineffective against some organisms |
|
|
phenolics
|
low cost and effective against most organisms except hydrophilic viruses
floors (mop water) |
|
|
4 percent chlorhexidine
|
antimicrobial hand washes
lodophors are equally effective but lack substantive activity; all other active ingredients are inferior |
|
|
Protein synthesis is called
|
translation
|
|
|
base pairs
|
adenine always pairs with thymine, and cytosine always pairs with guanine.
|

