![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Genetics
|
Study of what genes are
how they carry information (deoxyribonucleotide sequence) how information is expressed (transcription and translation) how genes are replicated (DNA synthesis) |
|
|
Gene
|
segment of DNA that encodes a functional product, usually a protein
|
|
|
Genome
|
all of the genetic material in a cell
|
|
|
Genomics
|
molecular study of genomes
|
|
|
Genotype
|
genes of an organism
|
|
|
Phenotype
|
expression of the genes
|
|
|
Flow of Genetic Information
|
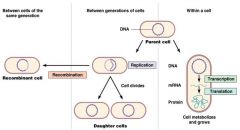
|
|
|
Mutation
|
Change in the genetic material (as little as one deoxyribonucleotide)
Mutations may be neutral, beneficial, or harmful |
|
|
Mutagen:
|
agent that causes mutations
UV light and chemicals that react with DNA |
|
|
Spontaneous mutations:
|
occur in the absence of a mutagen
Frequency [1 mutation per million cells to 1 mutation per billion cells] Ex:Neisseria gonorrhoeae penr (spontaneous) |
|
|
Change in a Population of Bacteria
|
Colony: all identically identical cells? no
Mutation (change in existing gene) Recombination (pick up new genes) |
|
|
Recombination
|
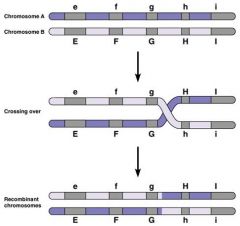
exchange of genes between two DNA molecules
Crossing over occurs when two chromosomes break and rejoin ex: Genetic recombination Crossing over Donor and recipient cell DNA |
|
|
Transformation
|
uptake fragments of DNA in environment
|
|
|
Conjugation
|
cell to cell transfer of DNA involves contact
|
|
|
Transduction
|
cell to cell transfer of DNA via virus
|
|
|
Recombination Scenarios
|
1.Transformation
2.Conjugation 3.Transduction significance is bacteria acquire new virulence factors and antibiotic resistance genes Ex: gene for capsule production gene for penicillin resistance |
|
|
Transformation Experiment
|
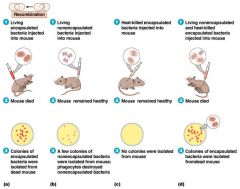
|
|
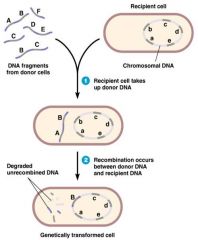
Transformation Mechanism
|
|
|
|
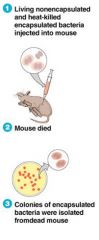
Fredrick Griffith (1928)
|
(Transformation)
Streptococcus pneumoniae virulent or S strain (smooth colonies) avirulent or R strain (rough colonies) transformation factor Competent (recipient strain) |
|
|
Oswald Avery (1944)
|
demonstrated the transformation factor was DNA
|
|
|
Conjugation
|
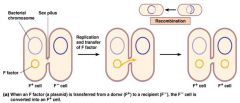
direct cell to cell contact
conjugative plasmid present in donor cell plasmid genes code for pili copy of plasmid transfers to recipient cell donor cells called F+ recipient cells (F-) become F+ intergenic transfer : Escherichia, Salmonella, Shigella, Serratia |
|
|
Conjugative plasmid
|
(Plasmids)
Carries genes for (F Factors) pili and transfer of the plasmid |
|
|
Dissimilation plasmids
|
(Plasmids)
Encode enzymes for catabolism of unusual compounds |
|
|
R factors
|
(Plasmids)
Encode antibiotic resistance |

