![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
First vs Second Defense
|
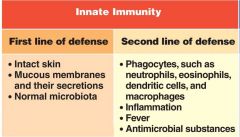
Third line - T cells , antibodies -Specific
|
|
|
First Line Factors
|
Skin (Chem)
Skin (Mechanical) Mucous Membranes (Mechanical) Mucous Membranes (Chemical) |
|
|
Skin (Mechanical)
|
epidermis consists of tightly packed cells
keratin, a protective protein Staphylococcus aureus (penetrate hair follicles and sweat glands) |
|
|
Skin (Chemical)
|
sebum (fatty acid) (protective film and inhibits growth)
low pH (3-5) of skin |
|
|
Mucous Membranes (Mechanical)
|
ciliary escalator: microbes trapped in mucus are transported away from the lungs
lacrimal apparatus: washes eye saliva: washes microbes off urine and vaginal secretions: flows out |
|
|
Mucous Membranes (Chemical)
|
Lysozyme in perspiration, tears, saliva, and tissue fluids
Low pH (1.2-3.0) of gastric juice destroy most bacteria and toxins except Staphylococcus aureus and Botulinum toxin or Salmonella typhi and Helicobacter pylori |
|
|
Normal Microbiota
|
microbial antagonism/competitive exclusion
change chemistry of environment and compete with pathogens for space. |
|
|
Blood Cells
|
Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
Leukocytes (white blood cells) A. Granulocytes B. Agranulocytes |
|
|
Agranulocytes
(WBC) |
1. Monocytes
present in blood / phagocytic 2. Macrophages Fixed in lungs, liver, bronchi Wandering macrophages roam tissues 3. Lymphocytes: Involved in specific immunity • B lymphocytes • T lymphocytes • Natural Killer Cells (non-B non-T cells) non specific resistance |
|
|
Granulocytes
(WBC) |
1. neutrophils: phagocytic
2. basophils: histamine / allergic reactions 3. eosinophils: extracellular killing of parasites |
|
|
lymphatic system
|
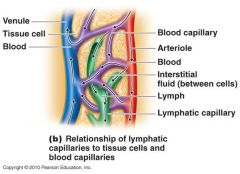
|
|
|
Second Line - Inflammation
|
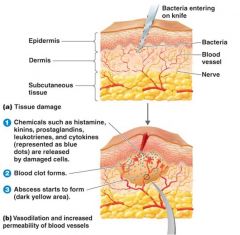
Four Characteristic Signs:
Redness,Pain,Heat,swelling (edema) Resident macrophages activated by presence of bacteria Macrophages release inflammatory mediators ex: TNF-alpha (leukotriene) 1. vasodilation 2. increases capillary permeability 3. margination of neutrophiles 4. diapedesis |
|
|
diapedesis
|
phagocytes squeeze between endothelial cells
|
|
|
Fever
|
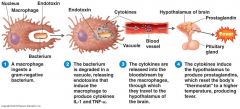
Hypothalamus normally set at 37°C
Gram-negative endotoxin cause phagocytes to release interleukin 1 Hypothalamus releases prostaglandins that reset the hypothalamus to a high temperature Body increases rate of metabolism and shivering to raise temperature Bacterial generation time increases Virus replication time increases |
|
|
Complement Cascade
|
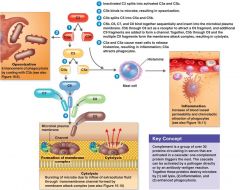
|
|
|
Chemotaxis
|

|
|
|
Activation
|
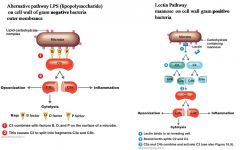
|
|
|
Multiple Causes of Inflammation
|
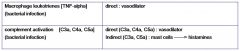
|
|
|
Natural Killer Cells and Eosinophiles
|
Natural Killer Cell (NK cell)
Non-B non-T lymphocytes recognize virus-infected and cancer cells reduced MHC I molecules on surface cause cell to undergo lysis non specific recognition |
|
|
Antiviral Action of α and β Interferon
|

|
|
|
Neutrophils
|
phagocytic
|
|
|
basophils
|
histamine/ allergic reactions
|
|
|
eosinphils
|
wbc that kills parasites
|

