![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
105 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define:
Obligate aerobe Obligate anaerobe Facultative anaerobe Aerotolerant Microaerophilic Which is most common? |
Obligate aerobe; Needs O2 to grow
Obligate anaerobe: O2 is toxic *Facultative anaerobe: grows in both environments Aerotolerant: Anaerobe not killed by O2 Microaerophilic: requires CO2 to grow |
|
|
Give an example of an aerotolerant bacteria
|
Clostridium tertium
|
|
|
Define:
Lag phase Log phase Stationary phase |
Lag phase: slow growth. >24h old
Log phase: Best growth. 18-24h Stationary phase: Good for transportation (ex: boric acid in urine) |
|
|
Preferred collection for N gonorrhea?
|
Charcoal swap
DO NOT REFRIGERATE |
|
|
Transport media for swabs
|
Stuart or Aimes transport media. Preserves viability
|
|
|
Urine collection
|
in boric acid, refrigerate
MUST CULTURE WITHIN 24h |
|
|
Gram stain steps
|
1. Crystal violet
2. Iodine (mordant) 3. Acetone (decolorizer) 4. Safranin (counterstain) |
|
|
Criteria for sputum rejection
|
>25 squames/lpf
* can still accept for AFB and fungus, just no good for bacteria (spit contamination) |
|
|
Indications for CSF baterial antigen test
|
Best in partially treated patients. Always culture also.
|
|
|
Organisms detected with CSF bacterial antigen test? Why is this test falling out of favor?
|
HIB,
N mening, S pna, GBS |
|
|
What is a selective media?
Differential media? |
Selective: something added to the media that selects for certain growth (ex. PEA for gpc)
Differential: something added to ID with color (chromagar) MacConkey is BOTH |
|
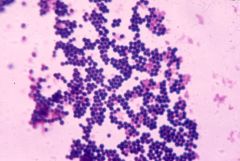
|
Staphylococcus
gpc in clusters |
|
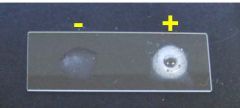
What test is this?
|
Catalase test.
Staph is +, strep is - * blood has innate catalase activity, beware contamination with sheep blood agar |
|

What test is this?
When should it be read? |
Coagulase test.
rabbit plasma + organism, 35C. Read at 4h AND at 24h. S. aureus is + "coag-negative-staph" are - |
|
|
What is the major virulence factor for S aureus?
|
Protein A
capsular polysaccharide coagulase toxins hemolysins |
|
|
What diseases are caused by S aureus?
|
Toxic shock syndrome (TSST1)
Scalded skin syndrome Food poisoning Endocarditis Soft tissue infection (Panton valentine leucocidin) |
|
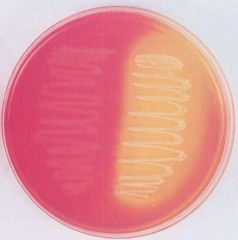
Mannitol salt agar. What ferments mannitol and turns it yellow?
|
S. aureus tolerates 7.5% salt and ferments mannitol
|
|
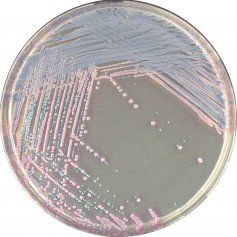
What organism has mauve colonies on chromagar?
|
S aureus
Chromagar + oxacillin = surveillance screen for MRSA |
|
|
What coag neg staph is responsible for subacute endocarditis?
What is its new claim to fame |
S. epidermidis (normal skin flora)
BIOFILMS! |
|
|
What coag neg staph is responsible for UTIs in reproductive-age females?
How to ID? |
S. saprophyticus
NOVOBIOCIN RESISTANT by KB disk |
|
|
What coag neg staph is responsible for line-related sepsis?
|
S. hemolyticus
|
|
|
What is the only coag-neg staph that hemolyzes on SBA and therefore can be confused with S. aureus?
|
S. hemolyticus
|
|
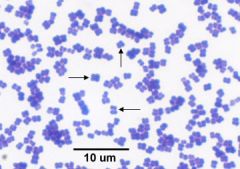
|
Micrococcus
gps in TETRADS |
|
|
Micrococcus
yellow pigment normal flora, rarely causes infection |
|
|
ID of micrococcus
|
bacitracin susceptible
modified oxidase (microdase) + does NOT ferment glucose (vs staph) |
|
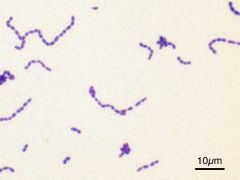
Organism?
How to ID vs. staph? |
Streptococcus
gpc in chains catalase NEGATIVE |
|
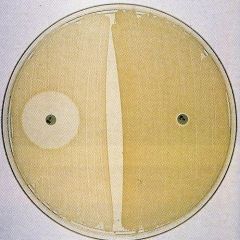
Novobiocin KB disk test
|
R; Resistant = Staph saprophyticus
L: susceptible = Staph epidermidis |
|
|
Beta-hemolytic streps
|
Lancefield groupings: Group ABCFG strep
Based on C carbohydrate in cell wall |
|
|
GAS
|
S. pyogenes (Group A beta-hemolytic strep)
Bacitracin susceptible SXT resistant PYR positive no resistance to penicillin |
|
test? organism?
(Disk = A) |
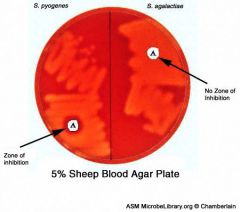
GAS = s. pyogenes
BACITRACIN SENSITIVE A stands for "GAS" not bacitracin... |
|
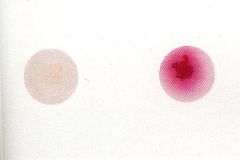
What test is this? Which is GAS?
|
PYR test.
GAS is PYR + and turns RED |
|
|
What organism is universally susceptible to penicillin?
|
GAS = S. pyogenes
|
|
|
Major virulence factor of GAS?
Diseases? |
M PROTEIN (vs staph: protein A)
Also: capsule, exotoxins, streptolysin O & S Pharyngitis Impetigo Erysipelas Cellulitis Puerperal sepsis Toxic Shock |
|
|
What organisms causes rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis?
|
GAS
|
|
|
Which strep is the LEAST beta-hemolytic?
Unique testing characteristics? |
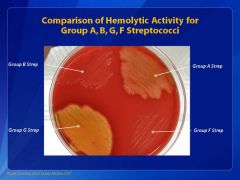
GBS
Camp test + Rapid hippurate hydrolysis |
|
|
How to ID GBS vs. listeria
|
Both look similar on culture; affect same patient population
but GBS is CATALASE NEGATIVE, listeria is + |
|
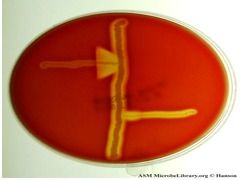
Unique test for GBS? Which is GBS?
|

Camp test
S. aureus strain with camp factor perpendicular to GBS; intensifies GBS toxin production. Top one was GBS, looks like an arrow = camp test + |
|
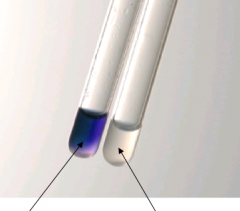
Rapid hippurate hydrolysis. Which is GBS?
|
purple = positive
read at 4 hrs |
|
|
What test do most people do for GBS?
|
Lancefield groupings (serology?)
|
|
|
important gamma-hemolytic streps
|
Enterococcis
GDS not enterococcus |
|
|
ID of enterococcus
|
BILE ESCULIN +
6.5% SALT + PYR + (~GAS) |
|
|
All enterococci are resistant to:
|
Cephalosporins
Clindamycin Bactrim |
|

Test?
|
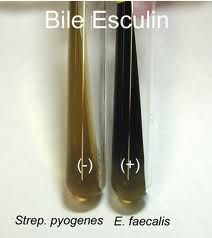
Bile esculin (enteroccus is +)
|
|
|
GDS (not enterococcus) vs enterococcus?
|
Both are Bile esculin +!
GDS is salt negative, PYR negative |
|
|
GDS
clin sig? always susceptible to? |
S. bovis
In blood = GI ca PCN |
|

|
Strep pneumoniae
gpc lancet shaped cocci, with capsule |
|
|
S. pna
|
|
|
alpha-hemolytic strep
|
S. pneumoniae
S. viridans (many types) |
|
|
Virulence factor in S. pna
|
polysaccharide capsule (resists phagocytosis)
|
|
|
S. pna ID in lab?
|
Bile soluble on SBA (sodium deoxycholate)
OPTOCHIN SENSITIVE |
|
|
resistance mechanism of S. pna to pcn?
|
Acquired resistance by PBPs
|
|
|
Quellung reaction
|
biochemical reaction in which antibodies bind to the bacterial capsule of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus influenzae, and Salmonella. The antibody reaction allows these species to be visualized under a microscope. If the reaction is positive, the capsule becomes opaque and appears to enlarge.
Can type the ~90 types of S. pna to see if covered by vaccine |
|
|
What is optochin?
|
a chemical
=ethyl hydrocupreine hydrochloride |
|
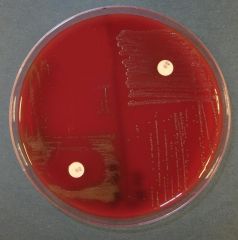
Optochin disk test. Which is S. pna?
|
the one on the L; need 14mm of inhibition.
R is S. viridans THE DISK HAS "P" ON IT, NOT AN O! (for pneumococcus) |
|
|
Name some viridans streps.
ID pattern? Dz? |
NF in mouth S. mutans (tooth decay)S. sanguis S. mitis S. salivarius Bile esculin negative |
|
|
More virulent group of alpha-hemolytic strep?
|
anginosus group: anginosus, constellatus, intermedius
Normal oral flora but more virulent than “normal” viridans Strep perhaps due to capsule Deep tissue abscesses, endocarditis, intraabdominal infections |
|
|
Blood culture grows gpc, but doesn't grow on media
|
Nutritionally variant strep (B6 deficient)
(Abiotrophia, Granulacatilla) |
|

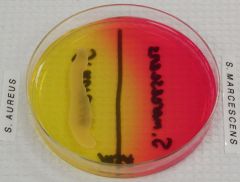
gpc that will not grow on regular media, but grows next to staph
|
nutritionally variant streptococcus
(NOTE: This also works for haemophilus so look for gram stain! There is sufficient hemin in blood for growth of Haemophilus, but the medium is insufficient in NAD. S. aureus produces NAD in excess of its own needs and secretes it into the medium, which supports the growth of Haemophilus as satellite colonies. |
|
|
Sugar fermentation of GNCs
|
N. gonorrhoeae Gluc + Mal - Lac - Suc -
N. meningitidis Gluc + Mal + Lac - Suc - N. lactamica Gluc + Mal + Lac+ Suc- M. catarrhalis all negative, Dna’ase + |
|
|
Neisseria
gram negative diplococci |
|
|
Can you dx neisseria on gram stain alone?
|
Trick question. Depends on sex
Females: NO! Acinetobacter can look very similar and is normal flora in female genital tract Males: Yes. there is no normal GU flora that looks like this |
|
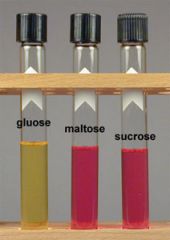
organism?
|
N gonorrhea
Ferments glucose only (YELLOW!) |
|
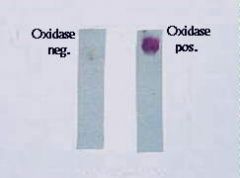
T/F: All neisseria are oxidase positive.
|
TRUE
|
|
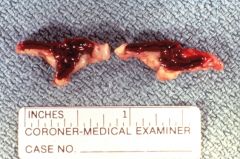
|
Waterhouse Friederichsen syndrome
Adrenal necrosis and hemorrhage associated with NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS |
|
|
What type of N mening is causing epidemics in college dorms?
|
Type C
|
|
|
What immunodeficiency predisposes to N mening?
|
Complement 7, 8, 9 deficiency (MAC complex!)
|
|
|
Prophylaxis for N mening? Treatment?
|
Proph = rifampin
Thx = PCN |
|
|
transport for N gon?
|
Charcoal swab
|
|
|
Treatment for PPNG?
|
(penicillinase-producing N gon)
Ceftriaxone Quinolone |
|
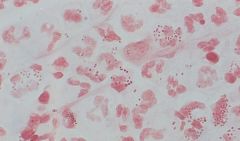
sputum
colonies? ID? |
moraxella catarrhalis
GNCs in diplococci. causes pneumonia, OM, sinusitis, eye. HOCKEY PUCK COLONIES OXIDASE + DNAase + |
|
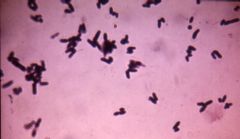
ID?
|
Corynebacterium
GPBs, chinese letters CATALASE + NO SPORES |
|
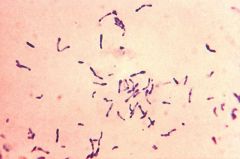
Methylene blue stain of culture growing on Loeffler slant
What is it? What is in Loeffler slant? |
Metachromatic granules of Corynebact diptheriae
Loeffler slant has EGG in it |
|

Cysteine tellurite agar
Black colonies with brown halo |
Corynebacterium diptheriae
|
|
|
GPB on KB disk that is ONLY susceptible to vancomycin and tetracycline
|
Corynebacterium jeikeium
(normal skin flora; plastic catheters & lines. resistant to most antibiotics) |
|
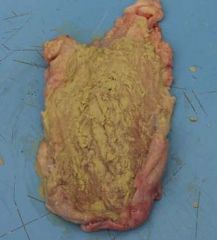
Alkaline encrusted cystitis
|
corynebacterium urealyticum
rare Pure culture of GPB that is rapid urease + |
|
|
Only spore-forming gpb?
|
Bacillus
Clostridium |
|
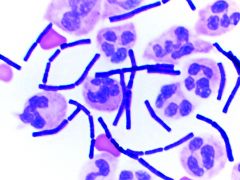
|
Bacillus
GPB boxcar shaped |
|
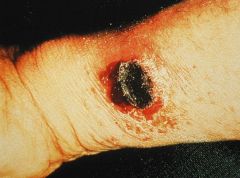
|
Black eschar skin lesion of bacillus anthracis
|
|
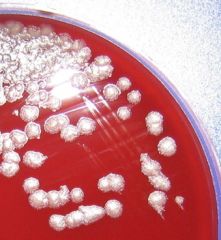
Non-hemolytic,
non-motile, PCN sensitive |
Bacillus anthracis
Medusa head colonies on SBA |
|
|
Fried rice food poisoning within 1-6h
|
B. cereus!
Emetic endotoxin |
|
|
B cereus vs B anthracis?
|
B cereus: Beta hemolytic & motile!
B anthracis: Not hemolytic and not motile! |
|
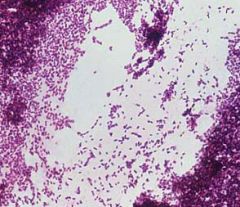
|
Listeria
small gpb, beta-hemolytic (~to GBS but catalase+!) |
|
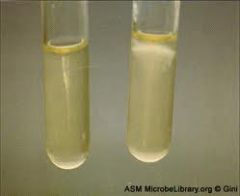
What is on the right?
|
Listeria.
Motile. Likes oxygen so grows near the top. Will grow better at 25C than 35C. Loves cold - grows at 4C |
|
|
Endocarditis in drug users
Catalase negative Alpha hemolytic |
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
catalase negative gpb |
|

What is the ONLY GPB that makes H2S?
|
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
|
|
|
GPB that causes pharyngitis
(and is beta-hemolytic, and catalase negative!) |
Arcanobacterium hemolyticum
Confuse with S.pyogenes (GAS) but this is a GPB! |
|
|
Transport media for anaerobes |
eSwab or vial (port o cult) no oxygen |
|
|
Transport for CSF for bacterial culture |
sterile container, room temp or incubate at 35 degrees |
|
|
How to judge quality of gram stain |
Polys if blue --> under-decolorized if washed out --> over-decolorized |
|
|
Broth tubes are good to detect... |
low numbers of bugs that might not grow on agar - sterile body fluids |
|
|
What is PEA (polyethyl acohol)? |
added to media to select for GPC |
|
|
MacConkey agar |
Differential and selective Only gram negatives will grow Pink = lactose fermentation Clear = lactose nonfermenter |
|
|
GBS susceptible to... |
penicillin |
|
|
E faecium vs E faecalis |
faecium = arabinose + faecalis = arabinose - |
|
|
Enterococcus: natural resistance to ... |
cephalosporins Treat with ampicillin or vancomycin |
|
|
Agar to screen for VRE |
Bile esculin |
|
|
Gluc + Mal - Lac - Suc - |
N. gonorrhoeae |
|
|
Gluc + Mal + Lac - Suc - |
N. meningitidis |
|
|
Gluc + Mal + Lac+ Suc- |
N. lactamica |
|
|
all sugars negative, Dna’ase + |
M. catarrhalis |
|
|
What % of N gonorrhoeae disseminate? |
10-20% ascend 0.5% disseminate |
|
|
HOCKEY PUCK COLONIES OXIDASE + DNAase + |
Moraxella catarrhalis |
|
|
M catarrhalis resistance |
Ampicillin by beta-lactamase |
|
|
Toxin for Coryne diphtheriae |
phage mediated toxin Detected by Elek immunoprecipitation |
|
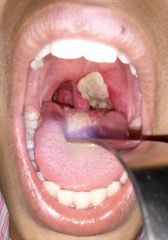
|
Diphtheria |

