![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Typical length of bacteria |
1 - 3 ųm |
|
|
Bacillus |
Rod-shaped |
|
|
Coccus |
Spherical |
|
|
Spirillum |
Spiral-shaped |
|
|
What causes the shapes of bacteria? |
Their rigid cell wall's unique structure |
|
|
What is found in the cell wall? |
Peptidoglycan / murein |
|
|
How does peptidoglycan enforce the cell wall? |
Cross-linking provides strong and flexible framework and prevents the cell from lysis |
|
|
What is peptidoglycan made from? |
A mixture of hexose sugars and amino acids |
|
|
Characteristics of Gram- positive bacteria |
Thicker cell wall No lipopolysaccharide layer Are stained purple by crystal violet/iodine complex |
|
|
Characteristics of Gram-negative bacteria |
Thinner cell wall Have a lipopolysaccharide layer Are stained red by counterstain saffranin |
|
|
What protection does the lipopolysaccharide layer provide? |
Protection from lysozyme Resistance to penicillin |
|
|
Process of Gram-staining |
Heat the slide to fix bacteria Flood the slide with crystal violet dye Rinse with water Flood the slide with iodine (binds with dye) Rinse with water Decolourize with ethanol (+ve stay purple) Rinse with water Flood the slide with saffranin (-ve turn red) |
|
|
Autotrophic |
Carbon obtained from CO2 |
|
|
Heterotrophic |
Carbon obtained from organic compounds |
|
|
Chemotrophic |
Energy obtained from external chemical compounds |
|
|
Phototrophic |
Energy obtained from light |
|
|
Obligate aerobes |
Require oxygen for metabolism |
|
|
Faculative anaerobes |
Can respire anaerobically if there is little or no oxygen available |
|
|
Obligate anaerobes |
Can only survive in the absence of oxygen (oxygen is toxic to them) |
|
|
Antigens |
Unique proteins found on the surface of bacteria |
|
|
How can bacteria be classified from their antigenic features? |
By carbohydrate or protein antigens Found on the cell wall or the capsular polysaccharide |
|
|
Vertical transmission |
Transfer of DNA via asexual reproduction of bacteria |
|
|
Horizontal transmission |
Transfer of DNA in plasmids via pili |
|
|
What nutrients are needed for bacterial growth |
Carbon compounds (organic) (eg. Glucose for energy) Nitrogen compounds (organic or inorganic) to produce amino acids for proteinsynthesis Mineral salts and vitamins |
|
|
What is the optimum temperature for bacterial growth? |
25 - 45 °C |
|
|
Optimum temperature for mammalian pathogens |
37°C (don't grow at this temperature when cultivating bacteria that don't require this temperature) |
|
|
Other requirements for bacteria growth |
Oxygen - does depend on if an aerobe or anaerobe but does prevent growth of harmful pathogens if present Water |
|
|
Optimum pH for bacterial growth |
Slightly alkaline (pH 7.4) |
|
|
Why would the pH of the medium change during bacterial growth? |
Production of acidic/alkaline products by bacteria |
|
|
How to prevent change of pH of medium? |
Use of an appropriate sterile buffer solution |
|
|
Bacterial growth curve |
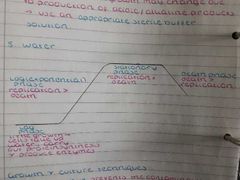
|
|
|
Aseptic technique function |
Prevents the contamination of the environment by the microbes and the contamination of the culture by unwanted microbes |
|
|
Sterilisation |
The removal/killing of microorganisms on an object or in any material |
|
|
Methods of sterilisation |
Heat the equipment in an autoclave at 121°C for 15 minutes Heat the inoculating loop in a Bunsen Burner flame Irradiation of heat labile plastics |
|
|
Aseptic technique methods |
Wash work bench with disinfectant Wash hands with antibacterial soap Flame bottle neck of culture solution Flame inoculating loop Have a Bunsen Burner near work area Never open Petri dish fully Don't place bottle lid on workbench |
|
|
Where we should measure bacterial growth |
In food premises inspected by environmental food officers Water boards check water supplies In the production of food products in fermenters |
|
|
Viable count |
A count of the living cells only |
|
|
Viable count method |
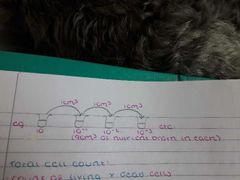
Spread a known volume of organisms from each serial dilution onto an what plate and allow it to incubate at 25°C |
|
|
Viable count formula |

|
|
|
Total cell count |
Count of both living and dead cells |
|
|
Total cell count method |
Use turbidimetry (measure of cloudless of solution by using a colorimeter) Turbidity increases = Cell numbers increase |

