![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
describe what is required for stable colonization once oral microbes enter the mouth
|
Stable colonization requires continual attachment, growth, and generation of
daughter cells that detach and must re-adhere to freshly exposed epithelial cells. |
|
|
Question 2: name 2 predominant species that colonise the tongue
|
Streptococcus mitis
S. salivarius |
|
|
Question 3: briefly describe why saliva both hinders and helps microbial colonization of the oral mucosa
|
aid bacterial adherence, and molecules in saliva that act as carbon and nitrogen sources for bacteria assist their growth.
However, antibacterial components are also present in the saliva including agglutinins, lysozyme, histatins, peroxidase, thicyanate, and lactoferrin. |
|
|
Question 4: state 2 functions of salivary agglutinins
|
helps to clump bacteria together
block adhesion of bacteria |
|
|
Question 5: list 3 components of the salivary pellicle
|
- Albumin
- Lysozyme - Histatins - Alpha amylase |
|
|
Question 6: give 6 examples of defense mechanisms in the oral mucosa and salivary glands
|
surfaces are continuously flushed
Mucosal Epithelia (Salivary antibody) Innate Defences - Mucosal barrier, defensins, calprotectins,adherent mucin, desquamation, Adaptive Defences - S-IgA is the primary immune agent produced by plasma cells, - lymphocytes (B cells and T cells) Inflammatory (part of innate) |
|
|
Question 7: identify on important hurdle to overcome in the development of a caries vaccine.
|
There is lack of convincing evidence that the vaccines are effective
Vaccine trial is difficult due to fear of side effects (could damage the heart) Incidence of dental caries is falling hence there is less interest in terms of economy |
|
|
Question 1: State why hepatitis A virus is an important consideration for dental health care professional considering the virus causes no oral pathologies.
|
HAV causes no oral pathologies. However, the contagious manner of HAV is a consideration for oral health care professionals.
|
|
|
Question 2: Describe 4 features common to viruses in the family Herpesviridae and give 2 examples of viruses in this family and their relative prevalence in the population.
|
- large viruses (200 nm)
- large double stranded genomes consisting of around 200,000 bases. - have an icosahedral nucleocapsid - have a lipid envelope. HSV-1 is a common virus and present in about 50% of the population. HSV-2 is present in 5% of the population. |
|
|
Question 3: Explain the basis of recurrent oral disease due to Herpesviruses.
|
remain dormant within the cells until immune system is lowered
active viruses are removed by immune system but those laying dormant are not removed symptoms remerge as the immune system falls again |
|
|
Give 2 examples of Human herpesviruses that may cause cancer and the types of cancer the viruses cause.
|
HHV-4 (Epstein-Barr Virsus - EBV) causes various cancers
In B-Cells (Burkitt’s lymphoma) Nasopharyngeal cancer HHV-8: Aetiological agents of Kaposi’s sarcoma. This is a tumour of the blood vessels in the skin (common in AIDS pt) |
|
|
Question 5: Define HPV and the most common oral clinical presentations caused by these viruses.
|
HPV are members of the family Papovaviridae and are named because of the clinical conditions they cause: papillomas and warts
Most common clnical presentation of HPV oral disease: warts on the oral mucosa |
|
|
Compare and contrast 3 different forms of syphilis
|
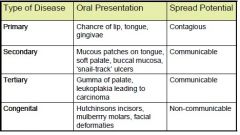
|
|
|
Question 7: Name 2 non-syphilitic oral diseases that originate from systemic bacterial infections.
|
Tuberculosis
· Leprosy |
|
|
Question 8: briefly describe acute suppurative parotitis including 2 bacterial pathogens that commonly cause these diseases and 2 predisposing factors.
|
Suppurative means ‘pus forming’. Acute suppurative parotitis occurs mostly in adults with salivary gland abnormalities, or in dehydrated or post-operative individuals.
Very common pathogen: alpha haemolytic streptococci, S. aureus Predisposing factors include: -Drugs that reduce salivary flow – histamines -Salivary abnormalities – calculus or mucous plug -Sjogrens syndrom (progress degenerative disease affecting salivary glands) |
|
|
Question 1: Name the single most common fungal species isolated from lesions of the oral mucosa and 3 predisposing factors that increase susceptibility to this pathogen.
|
Candida albicans
P Factors Age: very old or very young Co-existing infections: HIV Physical conditions: dentures, smoking Immune system: leukemia |
|
|
Question 2: comment on 5 fundamental features of Fungi.
|
Fungi are in the domain Eukarya,
only 150 causes disease out of millions of types of species Fungi are vegetative, do not synthesize chlorophyll Share some structural and metabolic features of animal cells (nucleus, mitochondria, ribosome) Non-motile, Fungal replication can be sexual or asexual. Rigid cell wall around the plasma membrane that contains sterol |
|
|
Question 3: describe 3 ways in which oral fungal pathogens are spread.
|
Many oral fungal infections, including notable candidiasis, are communicably spread.
Portal of Exit- leaving this niche (ie mouth) and causing disease in other sites in the body such as the genitourinary tract Portal of Entry (route of entry) - respiratory intake of fungal spores for Candida, and direct skin contact for other fungi |
|
|
Question 4: define 2 sources of aspergillum
|
airborne
rotting vegetables, pepper, spices |
|
|
Question 5: indentify and briefly describe 4 non-candida oral fungal diseases.
|
Aspergillosis:Saprophytic, Allergic, Acute invasive Aspergillosis
Cryptococcosis: reservoires are birds, rotten fruites&vegetables. Oral lesions present as ulceration or nodules on the tongue, palate, gingival tissue Histoplasmosis: Reservoir is soil enriched with excreta from chickens and bats. Prevalent among HIV patients, and presents as ulcerated or nodular lesions, affecting the palate, tongue, buccal mucosa, gingiva, and lips. Blastomycosis:symptoms similar to tuberculosis. Oral lesions are due to dissemination from pulmonary disease |
|
|
Question 7: compare angular stomatitis and median rhomboid glossitis.
|
Median rhomboid glossitis
commonly presents as a diamond-shaped lesion on the dorsum of the tongue near the midline. Angular Stomatitis: These lesions present in one or both angles of the mouth |

