![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
QUIZ 7
1. What is not a function of relaxase? a. Nicks the plasmid at the orit. b. May have helicase avtivity to separate the double stranded plasmid c. Has a tyrosine that forms a cavalent bond with the 3' OH in the nicked strand d. Recyclizes the single stranded plasmid in the recipient cell e. Primes replication of the second strand in the recipient cell |
e. Primes replication of the second strand in the recipient cell
|
|
|
QUIZ 7
2. Which component of the mating pair formation complex does the relaxase bind to? a. Pilus b. Channel c. Coupling protein d. Relaxosome e. Primase |
c. Coupling protein
|
|
|
QUIZ 7
3. Which of the following statements about enzymes used in recombination DNA technology is incorrect a. In constructing recombination DNA, a restriction enzyme is used to cut the vector and the gene of interest in specific palindromic nucleotide sequences. b. DNA ligase catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the cut gene fragment and the vector DNA. c. To promote religation between the two cut ends of a vector that had been digested with a single enzyme, the vector is treated with alkaline phosphatase. d. Reverse transcriptase synthesizes a complementary DNA strand using mRNA as template. |
c. To promote religation between the two cut ends of a vector that had been digested with a single enzyme, the vector is treated with alkaline phosphatase.
|
|
|
QUIZ 7
4. Briefly describe the main differences in DNA transfer by transduction, conjugation and transformation. |
Transduction is the process by which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus. It also refers to the process whereby foreign DNA is introduced into another cell via a viral vector.
Conjugation transferofDNA from one bacterial cell to another Transformation:process in which a bacterial cell takes up naked DNA fromits outside environment.�=�
|
|
|
QUIZ 7
5. Describe 2 differences between integrating conjugative elements and mobilizable plasmids. |
ICEs –Integrating Conjugative Elements.
non-plasmid,self-transmissible elements: Integratesin recipient’s chromosome cannotexist autonomously HasoriTand Trafunctions of plasmids, and phage like integrase and excisase Somemobilize foreign DNA elements (islands) into recipient cells Somecarry antibiotic resistance genes Mobilizable plasmids arenot self-transmissible, but can be shuttled along by ones that are. Parasitic. AnoriTregion is the sole criterion of a hypothetical mobilizableplasmid. wouldbe shuttled by a self-transmissible plasmid with similar oriTsequences. Mostencode for a Dtrcomponent, i.e., helicase and relaxase. Genesencoding for Dtrcomponent are called mobgenes. Shuttledonly if coupling protein on a self-transmissible plasmid can recognize the relaxaseprotein of the mobilizableplasmid. Relaxase of mobilizableplasmids have a much broader range of coupling protein recognition than thosein self-transmissible plasmids. Bothplasmids compete for coupling protein so typically only one of the two istransferred to the recipient cell |
|
|
QUIZ 7
6. Briefly describe two approaches by which cloning vectors have been designed such that one can easily tell that the GOI has inserted in the cloning vector. |
Screeningfor insert (in pUC19): disruption of lacZgene by insertion of a DNA fragment produces white colonies on X-Gal ampicillin
Selectingfor insert: disruption of a lethal gene by insertion of a DNA fragment allows transformantswith inserts to grow |
|
|
QUIZ 7
7. Draw and describe the process of tri-parental mating. |
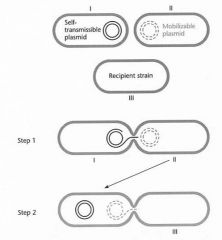
Tri-parental mating:
Usedfor complementation and to deliver transposons Increasesmating efficiency for some mob plasmids Performedwhen helper plasmid and mobilizableplasmids are incompatible Mobilizableplasmids can be transferred for at least 6 generations |

