![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the relationship between microbes and termites? |
Protozoa, bacteria and archaea get a consistent environment and nutrients from the Termites The termites in return gain the ability to eat wood which gives them nutrients |
|
|
What do Protozoa do in their mutalistic relationship with Termites? |
they produce ATP from glucose of cellulose and produce acetate that will feed the bacteria as well as the termite |
|
|
What do Bacteria do in their mutalistic relationship with Termites? |
they fix nitrogen to make amino acids for termits and the protozoa |
|
|
What do methanogenic archaea do in their mutalistic relationship with Termites |
consume waste products from the protozoa to produce methane |
|
|
Mutualism of zooanthellae and coral reefs |
Coral reefs- get 95% of alages photosynthesis process Algae- gets nitrogen compounds, phosphates, Co2 and UV protection * this allows them to grown in nutrient poor conditions
|
|
|
Mutualistic Rumen ecosystem |
The cow gets all of its food broken down by bacteria, archea, protists, and fungi living in the different rumens The other microbes gain a safe place to live and gain other nutrients from each other off of the by-products made through each individuals process |
|
|
Mutalism: Lichens and Fungi |
Fungus will obtain organic compounds and O2 from the lichen the Fungus will then in turn protect the phycobiont form high light intensities and provides H2O, minerals and substrate
|
|
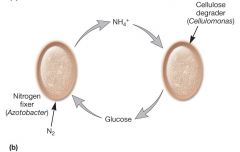
|
2 |
|
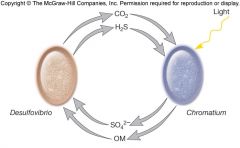
**** |
Syntophism- growth of an organism improved by the another organism nearby Nitrobacter-oxidises nitrate by Nitrosomonas Desulfovibrio and Chromatium- linked by their C and S cycle and use each others waste as part of their metabolism OM- organic matter |
|
|
Bdellovibrio |
is an example of Predation as it invades G- bacteria and replicates between outer and inner membranes |
|
|
Vampirococcus |
attaches to prey cell and secretes an enzyme that will degrade the prey cytoplasm |
|
|
Amensalism |
adverse effect of one organism on another organism release of an antibiotic by one organism has (-) effect on another |
|
|
Competition |
species in a community try to acquire same resource in most cases, one organism over takes the other |
|
|
What do normal Microbiota have to overcome in the human body |
1. dry, acidic pH 2. high NaCl 3. shedding of outlayers 4.lysozyme that kills G+ |

