![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Genetics |
Science of heredity and covers the structure, replication and transmission of genetic information |
|
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) |
The genetic material for all cells and many viruses |
|
|
Nucleotides |
A component of a nucleic acid consisting of a carbohydrate molecule, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base |
|
|
Polynucleotide |
A chain of linked nucleotides |
|
|
Double helix |
The structure of DNA, in which the two complementary strands are connected by hydrogen bonds between complementary nitrogenous bases and wound in opposing spirals |
|
|
Gene |
A unit of heredity (except for some viruses); a DNA segment |
|
|
Genome |
The complete set of genetic information for an organism or virus |
|
|
Chromosomes |
Thread-like fibers associated with proteins |
|
|
Nucleoid |
The chromosomal region of a bacterial and archaeal cell |
|
|
Supercoiling |
A twisting and tight packing caused by a number of abundant NAPs |
|
|
Nucleoid-associated proteins (NAPs) |
A protein that causes the DNA double helix to twist (supercoil) |
|
|
Supercoiled domain |
A loop of wound DNA consisting of 10,000 bases |
|
|
Looped domain structure |
The term used to describe organization and packing of the prokaryotic chromosome |
|
|
Plasmid |
A small, closed-loop molecule of DNA apart from the chromosome that replicates independently and carries nonessential genetic information |
|
|
F plasmid |
A DNA plasmid in the cytoplasm of an F+ bacterial cell that may be transferred to a recipient bacterial cell during conjugation |
|
|
R plasmid |
A small, circular DNA molecule that occurs frequently in bacterial cells and carries genes for drug resistance |
|
|
DNA replication |
The process of copying the genetic material in a cell |
|
|
Initiation |
The unwinding and separating of DNA strands during replication.
The beginning of translation |
|
|
Replication origin |
(oriC) The fixed point on a DNA molecule where copying of the molecule starts |
|
|
DNA helicase |
An enzyme that unwinds and separates the 2 polynucleotide strands during DNA replication |
|
|
Stabilizing protein |
A protein that keeps the DNA template strands separated during DNA replication |
|
|
Replication factory |
Replisome. Where DNA synthesis and replication will occur |
|
|
Replication Fork |
V-shaped; identifies the area active in the replication process |
|
|
Elongation |
The addition of complementary nucleotides to a parental DNA strand
The addition of amino acids onto the forming polypeptide during translation |
|
|
DNA polymerase |
An enzyme that catalyzes DNA replication by combining complementary nucleotides to an existing strand |
|
|
Mutation |
A permanent alteration in a DNA base sequence |
|
|
Termination |
The completion of DNA or RNA synthesis
The release of a polypeptide from a ribosome during translation |
|
|
Terminus |
The point where RNA synthesis stops |
|
|
Describe the replication of the circular chromosome of E. coli |
1. DNA replication involves the addition of complementary bases to the parental (template) strand within replication factories 2. Each replication factory contains some 15 proteins involved with DNA replication. At the replication fork, both leading and lagging strand synthesis occurs. The discontinuous synthesis on the lagging strand results from the DNA polymerase moving away from the replication fork, resulting in the formation of short DNA fragments that are eventually joined by a DNA ligase |
|
|
Semiconservative replication |
The DNA copying process where each parent (old) strand serves as a template for a new complementary strand |
|
|
Leading strand |
During DNA replication, the new strand that is synthesized continuously |
|
|
Lagging strand |
During DNA replication, the new strand that is synthesized discontinuously |
|
|
Okazaki fragments |
A segment of DNA resulting from discontinuous DNA replication. About 1,000 to 2,000 nucleobases long. Named after Reiji Okazaki who discovered them in 1968. |
|
|
Gene expression |
Requires DNA and RNA |
|
|
Transcription |
The biochemical process in which RNA is synthesized according to a code supplied by the template strand of a gene in the DNA molecule |
|
|
Genetic code |
The sequence of bases in the DNA or codons in the RNA specifying a specific polypeptide |
|
|
Translation |
The biochemical process in which the code on the mRNA molecule is converted into a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide |
|
|
Central dogma |
The doctrine that DNA codes for RNA through transcription and RNA is converted to protein through translation |
|
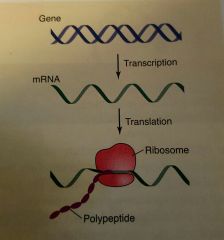
What process is this? |
Central Dogma, the flow of genetic information proceeds from DNA to RNA to protein (polypeptide) |
|
|
RNA polymerase |
A large enzyme involved in carrying out transcription |
|
|
Promoter |
The region of a template DNA strand or operon to which RNA polymerase binds |
|
|
Terminator |
A set of nucleobases that stops RNA synthesis |
|
|
Messenger RNA (mRNA) |
An RNA transcript containing the information for synthesizing a specific polypeptide |
|
|
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) |
An RNA transcript that forms part of the ribosomes structure |
|
|
What is the transcription process during elongation? |
For transcription to occur, a gene must be unwound and the base pairs separated. The enzyme RNA polymerase does this as it moves along the template strand of the DNA and adds complementary RNA nucleotides. Note that the other DNA strand of the gene is not transcribed. |
|
|
Transfer RNA (tRNA) |
A molecule of RNA that unites with amino acids and transports them to the ribosome in protein synthesis |
|
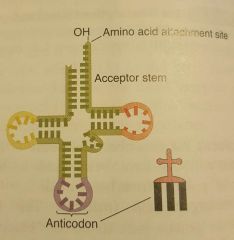
What structure is this? |
tRNA |
|
|
Explain RNA processing and gene activity? |
In bacterial cells, gene DNA is almost entirely protein-coding information that is transcribed and translated into a protein having structural or functional roles in the cytoplasm, or gene regulation roles. In eukaryotic cells, some of the intron RNA may be degraded, used to regulate gene function, or be associated with other RNAs or proteins in the cytoplasm |
|
|
Anticodon |
A 3-base sequence on the tRNA molecule that binds to the codon on the mRNA molecule during translation |
|
|
Introns |
A non-coding sequence in a split gene |
|
|
Exon |
The coding sequence in a split gene |
|
|
Genetic code |
The sequence of bases in the DNA or codons in the RNA specifying a specific polypeptide |
|
|
Sense codons |
A nucleotide sequence that specifies an amino acid |
|
|
Redundancy |
Referring to multiple codons coding for the same amino acid |
|
|
Start codon |
The starting nucleotide sequence (AUG) in translation |
|
|
Stop codons |
The nucleotide sequence that terminates translation |
|
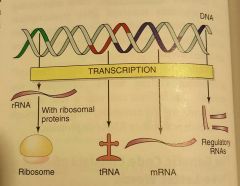
What is this a picture of? |
The transcription of RNA |
|
|
Formylmethionine |
The presence of a formyl group (H-CO--) attached to methionine |
|
|
Explain translation: chain initiation |

|
|
|
Explain translation: chain elongation |

|
|
|
Explain translation: chain termination |

|
|
|
Termination factor |
A protein that triggers the release of a polypeptide from a ribosome |
|
|
Polysome |
A cluster of ribosomes linked by a strand of mRNA and all translating the mRNA |
|
|
Polysome |
A cluster of ribosomes linked by a strand of mRNA and all translating the mRNA |
|
|
Operon |
The unit of bacterial DNA consisting of a promoter, operator, and a set of structural genes |
|
|
Structural gene |
A segment of a DNA molecule that provides the biochemical information for a polypeptide |
|
|
Operator |
A sequence of bases in the DNA to which a repressor protein can bind |
|
|
Promoter |
The region of a template DNA strand or operon which RNA polymerase binds |
|
|
Regulatory gene |
A DNA segment that codes for a repressor protein |
|
|
Repressor protein |
A protein that when bound to the operator blocks transcription |
|
|
Negative control |
A form of gene regulation where a repressor protein binds to an operator and blocks transcription |
|
|
Mutation |
A permanent alteration of a DNA sequence in an organism or virus |
|
|
Spontaneous mutation |
A mutation that arises from natural phenomena in the environment |
|
|
Wild type |
The common or native form of a gene or organism |
|
|
Induced mutation |
A change in the sequence of nucleotide bases in a DNA molecule arising from a mutagenic agent used under controlled laboratory conditions |
|
|
Mutagen |
A chemical or physical agent that causes a mutation |
|
|
Niche |
The functioning of a species in relation to other species and its physical environment |
|
|
Base analog |
A nitrogenous base with a similar structure to a natural base but differing slightly in composition |
|
|
Explain ultraviolet light and DNA interaction |
When cells are irradiated with ultraviolet light either naturally or through experiment, the radiations may affect the cells DNA. The UV light can cause adjacent thymine molecules to pair within the DNA strand to form a thymine dimer |
|
|
Point mutation |
The replacement of one base in a DNA strand with another base |
|
|
Silent mutation |
A change in a base sequence that produces no change to the protein made |
|
|
Missense mutation |
A base substitution that codes for an incorrect amino acid |
|
|
Nonsense mutation |
A base substitution that codes for a stop codon |
|
|
Mismatch repair |
A mechanism to correct mismatched bases in the DNA |
|
|
Nucleotide excision repair |
A process that removes a thymine dimer, along with adjacent nucleotides, and replaces them with the correct sequence |
|
|
Transposable element (TE) |
A fragment of DNA called an insertion sequence or transposon that can cause mutations |
|
|
Insertion sequence (IS) |
A segment of DNA that forms a copy of itself, after which the copy moves into areas of gene activity to interrupt the genetic coding sequence |
|
|
Transposase |
An enzyme that moves insertion sequences to a new DNA location |
|
|
Transposon |
A segment of DNA that moves from one site on a DNA molecule to another site, carrying information for protein synthesis |
|
|
Mutant |
An organism carrying a mutation |
|
|
Phenotype |
The visible (physical) appearance of an organism resulting from the interaction between its genetic makeup and the environment |
|
|
Auxotroph |
A mutant strain of an organism lacking the ability to synthesize a nutritional need |
|
|
Prototroph |
An organism that contains all its nutritional needs |
|
|
Positive selection |
A method for selecting mutant cells by their growth as colonies on agar |
|
|
Carcinogen |
Any physical or chemical substance that causes tumor formation |
|
|
Ames test |
A diagnostic procedure used to detect potential cancer-causing agents in humams by the ability of the agent to cause mutations in bacterial cells |
|
|
Screening test |
A process for detecting mutants by examining numerous colonies |
|
|
Revertant |
Referring to a mutant organism or cell that has reacquired its original phenotype or metabolic ability |

