![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Microbe |
a unicellular microorganism that is capable of independent life. |
|
|
Archaea |
lived in conditions when the earth was young, such as hotsprings, mud and live without oxygen. |
|
|
Obligate aerobes |
require oxygen for respiration |
|
|
Obligate anaerobes |
conduct respiration in the absence of oxygen |
|
|
Facultative Anaerobes |
prefer environments with oxygen but can survive without oxygen |
|
|
Fermentation |
a chemical change to make alcohol |
|
|
Binary Fission |
a form of asexual reproduction in which one cell split into two |
|
|
Conjugation |
a form of sexual reproduction in which genetic material is exchanged between two cells |
|
|
Plasmids |
small rings of genetic material |
|
|
Endospores |
contain genetic material encapsulated in a thick resistant cell wall. They form when environmental conditions are unfavorable. |
|
|
Pathogen |
disease causing agents |
|
|
Antibiotics |
chemicals produced synthetically or by microorganisms to destroy other microorganisms |
|
|
Heterotrophs |
organisms who are not capable of making their own food. They eat autotrophs or heterotrophs |
|
|
Autotroph |
are capable of making their own food through photosynthesis |
|
|
Parasite |
Needs to feed off of a host |
|
|
Soprophyte |
eats dead things |
|
|
Endoplasm |
a fluid part of the cytoplasm that fills the inside of the cell |
|
|
Ectoplasm |
a thin layer of the cytoplasm under the plasma membrane |
|
|
Cilia |
hairlike structures used by microorganisms for movement or to attach to a substrate |
|
|
Spore |
a reproductive cell that can produce a new organisms without fertilization |
|
|
Moneran Vs. Viruses |
Moneran ( bacteria): "illa" "occi" "illus" Virus: cold, HIV, polio, rabies, smallpox |
|
|
Disease symptoms are caused by: |
1. they reproduce in great numbers 2. they attack and destroy cells/ tissues. 3. they produce toxins |
|
|
How are infectious diseases spread? |
droplets in the air, dust, direct contact, oral-fecal contamination , animal bites/ wounds. |
|
|
what does protection against these organisms include? |
antibiotics, antiseptics, exterminating animals that carry the disease, disinfection/ sterilization, body's defense mechanism, immunization. |
|
|
what is the difference between antiseptics and disinfectants? |
Antiseptics: applied to the living tissue disinfectants: applied to inanimate objects/ surfaces |
|
|
What are the stages of sewage treatment? |
Primary: the removal of coarse solid materials such as plastics, fabrics, metals. Secondary: sludge is produced from heavier matierials settling out Advanced sewage: uses chemical and physical processes to remove pollutants from water. ozone, hydrogen peroxide, chlorination and Uv light are also used. |
|
|
What three shapes do bacteria display? |
spherical ( cocci , singular: coccus), rod-shaped ( bacilli, singular: bacillus) or spiral ( spirilla, singular: spirillum) |
|
|
What three characteristics are used to classify prokaryotes? |
by shape, how they move, and how they get energy |
|
|
What color does gram negative and gram positive change to be? |
Gram negative: Pink Gram Positive: Purple |
|
|
Innoculating loop |
a tool used to take an inoculum from a culture of microorganisms |
|
|
What is a moneran and where are they found? |
The oldest and most abundant living organisms. found in boiling mud, hotsprings, coal-mines, polar ice caps, hot water vents. |
|
|
What is a colony of bacteria? |
Group or clusters of individual cells. They are NOT multicellular organisms. |
|
|
What are the two different groups of monerans? |
Archaebacteria and eubacteria.
|
|
|
What does the two different groups of monerans do? |
archae: live without oxygen, conditions when the earth was young, high salt concentration, high temp, high acidity eubacteria: largest group of monerans, recognized as bacteria. |
|
|
How do monerans reproduce? |
Binary fission: asexual reproduction of splitting in two. |
|
|
What happens to endospores when suitable growing conditions return? |
the wall breaks down and an active bacterium emerges . |
|
|
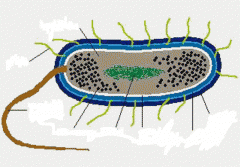
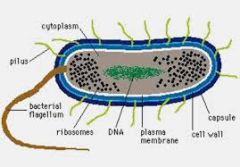
What are the characteristics of bacterial cells? |
1. prokaryotic, single celled 2. cytoplasm has no membrane bound organelles 3. single chromosome 4. reproduce by binary fission 5. show great metabolic diversity. |
|
|
List some examples of how bacteria can be harmful and beneficial: |
Beneficial: decomposes natures raw materials, produces cheese, produces antibiotics, produces a source of vitamins Harmful: Strep throat/ scarlet fever, spoils food, spoils gasoline, souring of milk |
|
|
How does antibiotic resistance occur? |
Through a mutation in the bacteria population |
|
|
|

