![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Product differentiation causes the demand curved faced by a monopolistically competitive firm to have what shape?
|
downward slope
|
|
|
Firms that sell a differentiated products in a competitive market have an incentive to do this
|
Advertise
|
|
|
The primary goal of any firm is to maximize what?
|
Profit
|
|
|
If Belmont enrolls 10 students at a tuition rate of $500 per student, and cost is $400 per student, their revenue is this:
|
$5,000
|
|
|
A cost that does not require an outlay of money is known as this:
|
Explicit cost
|
|
|
In the short run, capital inputs are a fixed cost but labor inputs are:
|
Variable
|
|
|
We use this phrase to describe a situation in which each successive unit of a variable input increases production by less
|
Diminishing marginal product
|
|
|
Total cost - fixed cost = ?
|
variable cost
|
|
|
Average total Cost (ATC) intersects marginal cost (MC) at what point?
|
minimum ATC
|
|
|
When a firm is operating at efficient scale it is operating as this
|
minimum ATC
|
|
|
LRATC will, at low levels of output, decrease as output increases because of these:
|
Gains from specialization of inputs
|
|
|
Buyers and sellers are price takers in this type of market
|
perfectly competitive
|
|
|
In a perfectly competitive market, price is the same as this
|
marginal revenue
|
|
|
In order to maximize profit, a firm operating in a competitive market chooses the quantity where marginal revenue equals this
|
marginal cost
|
|
|
When firms in a competitive market are earning profit in the short run, this will occur in the long run:
|
new firms will enter the market
|
|
|
A firm will shut down in the short run if this is true
|
P less than AVC
|
|
|
The demand curve faced by a monopolist has this shape
|
Downward sloping
|
|
|
Patents, copyrights, ownership of a key resource are examples of these:
|
barriers to entry
|
|
|
When a firm's ATC is always downward sloping, it is known as this:
|
Natural Monopoly
|
|
|
Because a monopolist must lower its price in order to sell another unit of its product, its marginal revenue has this relationship to price:
|
Less than or below
|
|
|
The business practice of selling the same product to different consumers for different prices is known as this
|
price discrimination
|
|
|
In an oligopoly, each firm's profits depend not only on how much output they produce but also on this:
|
the other firm's output
|
|
|
An Agreement among firms in a market about quantities to produce or prices to charge is known as this:
|
What is collusion
|
|
|
In order to reduce the inefficiency associated with oligopoly markets, public policy should promote this
|
increased competition
|
|
|
Under what conditions will a firm shut down temporarily?
|
In the short run the firm will shut down temporarily if the total revenue it would receive from producing is less than the total variable costs it would incur from producing
|
|
|
Under what conditions will a firm exit a market?
|
When price < average total cost, firms will choose to exit the market.
|
|
|
Does a competitive firm's price equal marginal cost in the short run, in the long run, or both?
|
Both
|
|
|
Does a competitive firm's price equal the minimum of average total cost in the short run, in the long run, or both?
|
only in the long run
|
|
|
Many small boats are made of fiberglass, which is derived from crude oil. Suppose that the price of oil rises.
1. What happens to the profits of boat makers in the short run? 2. What happens to the number of boat makers in the long run? |
1. decreases
2. decreases |
|
|
a. Calculate the company's average fixed costs, average variable costs, average total costs, and marginal costs at each level of production. (Please round your answers to the nearest hundredth.)
b. The price of a case of ball bearings is $50. Seeing that she can't make a profit, the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) decides to shut down operations. What are the firm's profits/losses? c. Vaguely remembering his introductory economics course, the Chief Financial Officer tells the CEO it is better to produce 1 case of ball bearings, because marginal revenue equals marginal cost at that quantity. What are the firm's profits/losses at that level of production? |
a.
b. loss $50 c. loss $100 |
|
|
A firm in a competitive market receives $500 in total revenue and has marginal revenue of $10.
What is the average revenue? How many units were sold? |
$10
50 units |
|
|
Is a monopolist's marginal revenue always less than the price of its good?
Can marginal revenue ever be negative? |
yes
yes |
|
|
Bob's lawn-mowing service is a profit-maximizing, competitive firm. Bob mows lawns for $27 each. His total cost is $280, of which $30 is a fixed cost. He mows 10 lawns a day.
1. Should Bob continue to operate or shut down in the short run? 2. Should Bob remain in the market or exit the market in the long run? |
1. Continue to operate
2. exit the market |
|
|
Does a monopolistic competitor produce too much or too little output compared to the most efficient level?
What practical considerations make it difficult for policymakers to solve this problem? |
The firm produces too little output
both of these |
|
|
A profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market is currently producing 100 units of output. It has average revenue of $10, average total cost of $8, and fixed costs of $200.
a. What is its profit? b. What is its marginal cost? c. What is its average variable cost? d. Is the efficient scale of the firm more than, less than, or exactly 100 units? |
a. 200
b. 10 c. 6 d. less than 100 units |
|
|
How might advertising with no apparent informational content in fact convey information to consumers?
|
By spending a large sum of money on advertising, a firm may signal the high quality of its product.
|
|
|
For each of the following characteristics, say whether it describes a monopoly firm, a monopolistically competitive firm, both, or neither.
1. Faces a downward-sloping demand curve 2. Has marginal revenue less than price 3. Faces the entry of new firms selling similar products 4. Earns economic profit in the long run 5. Equates marginal revenue and marginal cost 6. Produces the socially efficient quantity of output |
1. Both
2. Both 3. monopolistically competitive firm 4. monopoly firm 5. both 6. neither |
|
|
For each of the following characteristics, select whether it describes a perfectly competitive firm, a monopolistically competitive firm, both, or neither.
1. Sells a product differentiated from that of its competitors 2. Has marginal revenue less than price 3. Earns economic profit in the long run 4. Produces at the minimum of average total cost in the long run 5. Equates marginal revenue and marginal cost 6. Charges a price above marginal cost |
1. monopolistically competitive firm
2. monopolistically competitive firm 3. neither 4. perfectly competitive firm 5. both 6. monopolistically competitive firm |
|
|
If a group of sellers could form a cartel, what quantity and price would they try to set?
|
The cartel would try to set the monopoly price and quantity
|
|
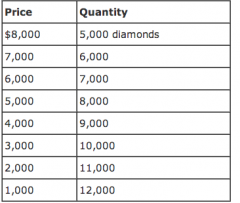
A large share of the world supply of diamonds comes from Russia and South Africa. Suppose that the marginal cost of mining diamonds is constant at $1,000 per diamond, and the demand for diamonds is described by the following schedule:
1. If there were many suppliers of diamonds, what would be the price and quantity? Price: $ Quantity: 2. If there were only one supplier of diamonds, what would be the price and quantity? Price: $ Quantity: 3. If Russia and South Africa formed a cartel, what would be the price and quantity? Price: $ Quantity: 4. If the countries split the market evenly, what would be South Africa's production and profit? Production: diamonds Profit: $ million 5. If South Africa increased it's production 1,000 while Russia stuck to the cartel agreement, would the country's profits increase or decrease? |

|
|
|
The New York Times (Nov. 30, 1993) reported that "the inability of OPEC to agree last week to cut production has sent the oil market into turmoil... [leading to] the lowest price for domestic crude oil since June 1990."
1. Why were the members of OPEC trying to agree to cut production? 2. The newspaper also noted OPEC's view "that producing nations outside the organization, like Norway and Britain, should do their share and cut production." What does the phrase "do their share" suggest about OPEC's desired relationship with Norway and Britain? |
1. So that they could raise the price of oil and increase profits
2. OPEC would like Britain and Norway to join OPEC so that all of the OPEC countries could operate as a single monoploy |

