![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. What happens when Cu+1 becomes oxidized? (Write the oxidized symbol) |
Cu+2 |
|
|
2. When bacteria metabolize lipids, pH will…… |
Decrease. (pH will denaturalize the enzyme, changing shape to no longer function) |
|
|
3. What happens to reaction rates if the optimum temperature is increased? Decreased?
|
It will decrease either above or below optimum temperature. It will stop completely if it is out of the range. (Too high will break bonds) |
|
|
4. What is surcease? Maltase? What are theirsubstrates? |
Digestive enzymes found in the small intestines. Substrate are disaccharides. (Breakdown disaccharides to produce monosaccharides like glucose) Sucrase – Sugar. Maltase - maltose |
|
|
5. What part of an enzyme does an allosteric inhibitor bind to? What part does a competitive inhibitor bind to? What kind of relationship do enzyme and substrate form? |
An allosteric inhibitor (non-noncompetitive binds to the allosteric site of an enzyme, and a competitive inhibitor binds to the active site. Enzymes are substrate-specific and have a lock-and-key relationship. They can have an anabolic or catabolic relationship. A substrate can have many enzymes that work on it, creating different products. The shape of the apoenzyme and coenzyme together allow substrate to bind to the molecule, and the coenzyme can donate molecular components. |
|
|
6. What kinds of products are generated by microorganisms during anaerobic fermentation? What is fermentation? |
Alcohols, acids, and gases. Fermentation is competitive exclusion, not an energy producing process. Converts carbs and makes energy in glycolysis. (Fermentation complements glycolysis and makes it possible for ATP to be continually produced in the absence of oxygen. |
|
|
7. What reactant is required in aerobic reactions? |
Oxygen |
|
|
8. Know the energy and carbon sources for the following: photoautotrophs, photoheterotrophs, chemoautotrophs, and chemoheterotrophs. |
First part – energy source. Second part – carbonsource Photoautotrophs – Sunlight. Carbon fixation (carbon pulled from air – CO2) Cyanobacteria Photoheterotrophs- Sunlight. Fatty acids, alcohol, acids from carbon source. Do not produce oxygen Chemoautotrophs- Chemical (inorganics = hydrogen, nitrogen,sulfur, iron.) Carbon fixation. Oxidizing bacteria Chemoheterotrophs- Chemical. Carbon from glucose or complex carbs. All animals, most bacteria, protozoa, fungi |
|
|
9. True/False Oxygen is needed for respiration to occur. |
False (anaerobic respiration = glycolysis) |
|
|
10. What reaction produces pyruvic acid? What kind of respiration is this? What reaction uses pyruvic acid as a reactant? |
Glycolysis which is an anaerobic respiration. Transition reaction uses pyruvic acid (or “pre-Krebs”) |
|
|
11. What % of ATP is produced by partial catabolism of glucose during glycolysis and the Kreb’s cycle? (How many ATP is this for Eukaryotes? Prokaryotes?) What % is yielded in ETC? (How many ATP is this for Eukaryotes? Prokaryotes?) |
10-11% from the Krebs Cycle. 89% form ETC (32/36 eukaryotes 34/38 pro*???) |
|
|
12. What happens to enzyme activity when enzyme/substrate complexes are saturated? (Draw graph) |
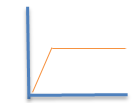
Enzyme activity stops once you reach saturation point, which is when all available enzyme and all available substrate have met up and all reactions have occurred.
Activity activity activity (line going up) and then STOPS
|
|
|
13. Define oxidative phosphorylation. Define substrate-level phosphorylation. Write the symbolic representation of respiration-phosphorylation |
(ADP + P -> ATP) Oxidative phosphorylation: (Redox – lose electron) Part of electron transfer chain, series of reduction and oxidation. Catabolic Substrate level phosphorylation: ADP + P = ATP. The phosphate comes from the substrate. 2 ATP molecules produced **know pic 8.12 7-10 Photophosphorylation: Pigment (chlorophyll, etc) absorbs sunlight. The light is a photon (traveling electron) which is absorbed by pigment orbital, oxidized and reduced.****??? |
|
|
14. How is ATP made in Chemiosmosis? Chemiosmosis is a sub-reaction of what major metabolic reaction?
|
Sub reaction of the electron transfer chain. Atp is made through Protein motive force (H stampede) (ATP synthase) |
|
|
15. Most enzymes have the suffix: |
“ase” or “zyme” |
|
|
1) How do salts and sugars preserve food? |
Creates a hypertonic environment. Plasmolysis dehydrates. Prevents the growth of most bacteria because they do not live in a hypertonic environment. (fungi and some halophiles can live in hypertonic) |
|
|
2) What is a facultative anaerobe? (3 line graph) |
A microbe that can survive with oxygen or without. Greater growth in an aerobic environment but grows without as well. ** graph |
|
|
3) What are the phases of the bacterial growth curve? Which are logarithmic?
|
Lag phase, log phase, stationary phase, and death phase. Log and death are logarithmic |
|
|
4) What is measured or observed to determine metabolic activity? |
Input or output. (Based on amount of certain metabolic product) Indirect means of counting |
|
|
5) Most bacteria grow at what pH? |
7 |
|
|
6) What is in complex media? What ingredient is the source of nutrients? |
Complex media contains peptones (partially digested proteins), salt, water and agar. The source of nutrients are the peptones which are from beef, yeast, plants and other meat. (nutrient agar and broth) |
|
|
7) What is/are the differences between selective and differential media? |
Selective media grows one type of organism over another. Differential produces a chemical change so bacteria appears different (color change) The differential factor is the dye |
|
|
8) During what phase of the growth curve are antibiotics effective? |
Log phase |
|
|
9) What is generation time for bacteria? |
The amount of time it takes for a cell to divide and double population. Rate is species specific and doesn’t change. |
|
|
10) An experiment began with 3 cells and ended with192 cells. How many generations did the cells go through? |
6 generations |
|
|
11) What is the optimum temperature for a mesophile? Draw a 3-line graph representing 1.Growth within range, 2. Growth at optimum temperature, and 3. Growth outside of range. |
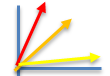
37 degrees . red line is optimum. Orange is within range. Yellow (flat line) is outside of range |
|
|
12) What do you call an organism that can live with or without salt? |
Facultative halophiles |
|
|
13) What do you call an organism killed by oxygen?
|
Obligate anaerobe |
|
|
1) What bacterial parts are vital to a bacterium? |
Cell wall, cell membrane, DNA, protein/enzymes. Chemical methods of disinfecting target one or more of these |
|
|
2) What factors affect removal of bacteria from a surface? |
Temperature (most like 70 degrees F/21 degrees C), PH, organic materials, time (10 min), type of microbe, concentration of microbe, concentration of solution |
|
|
3) What is a zone of inhibition? |
The diameter of the widest part of the cleared circle around an antimicrobial disc placed on a bacterial lawn. It shows where the bacterial are gone. Wider the zone = more susceptible |
|
|
4) What concentration of ethyl alcohol is the most effective? |
70% |
|
|
5) What are the effects of ethyl alcohol on microbes? |
Antiseptic, but mainly degermer. Removes germs. No open wounds, coagulates lipids (forms seal and traps bacteria) good on bacteria, and fungi, or anything with envelopes or membranes. Not good for NON envelop viruses or endospores. |
|
|
6) What treatments yield a sterile product? Which do not? |
a. Sterile: Mainly autoclave, boiling, tyndalization, flaming b. Non sterile: mainly pasteurization, filtration |
|
|
7) Why is autoclaving limited? |
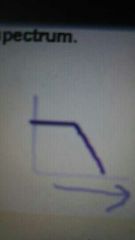
It does not work on oils, foils or jellys (prevents steam from reaching media) It also requires a certain amount of time to work (test strips). (It is heat labile – heat sensitive – rusty metals) Graph shows bacterial death in autoclave. Die rapidly, do not all die at once after ~15 minutes |
|
|
8) Which is more resistant? Gram- or Gram+? Prions or viruses? |
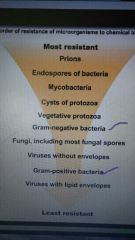
Gram – are more resistant than positive. Prions are most resistant of anything |
|
|
9) What happens each minute an antimicrobial is left on a surface? |
Each minute 90% of microbes are killed for up to 10 minutes |
|
|
10) What are the disadvantages to UV radiation as a method of microbial control? |
It does not penetrate a surface |
|
|
1) What is a gene? |
Sequence of DNA that encodes for a functional product, usually a protein |
|
|
2) What is an “inducible enzyme”? What operon discussed in class produces them? |
Inducible enzymes are enzymes produced in the presence of a substrate in the environment.The operon discussed in class was Lac operon (lactose) |
|
|
3) Know the functions/positions of the regulatory gene, operator, promoter, structural genes, and environmental chemicals-(substrates)-when genes are being transcribed by the inducible and repressible operons. |
Normally off, stops transcription. Lactose operon. ***MORE |
|
|
4) How do transformation, transduction, and conjugation differ from one another? |
3 types of genetic transfer: Transformation: naked DNA from one bacterial cell is taken up by another. Donor and recipient - donor is dead and DNA is picked up by desperate recipient Conjugation: Bacterial sex. DNA transferred from one bacterium to another via sex pilus (physical connection) Horizontal transfer of DNA. Transduction: transfer of bacterial genes from one bacteria to another via bacteriophage. Viral "go between" - goes between 2 bacteria and delivers genetic info Also; vertical transfer is binary fisson |
|
|
5) Knowwhere and how competitive and non-competitive inhibitors work on an enzyme.
|
Competitive enzyme inhibitors bind to and fill the active site of an enzyme. They compete with the substrate for the active site of the enzyme. The inhibitor does not undergo any reaction to form a product. This binding may or may not be reversible Noncompetitive inhibitors interact with the allosteric site, a process that is referred to as allosteric inhibition. The binding of enzyme and inhibitor results in a change in the active side of the enzyme. This prevents binding of the substrate so the reaction cannot occur |
|
|
6) What is feedback inhibition? |
End product serves as inhibitor to the enzyme upstream. Series of steps (to conserve energy). When enough product is produced some of the extra is sent "upstairs" to stop the series. Serves as an allosteric inhibitor (isolucine by E. coli) (It stops an enzyme from producing more end product than it needs by the end product attaching to the original enzyme in the series, shutting down the metabolic pathway.) |
|
|
7) What enzyme dominates the process of transcription?
|
RNA polymerase |
|
|
8) If DNA triplets were TTA-GCT, the mRNA codons would be… |
AAU-CGA |
|
|
9) If DNA triplets were TAT-GCT, the tRNA codons would be…. |
(First find out mRNA, then anticodon tRNA) mRNA: AUA-CGA so…tRNA codons are UAU-GCU |
|
|
10) What does a nucleotide consist of? |
One sugar, one phosphate, and one base |
|
|
11) Name the bonds that hold DNA bases together. |
Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
12) Name the bonds that hold together amino acids. |
Peptide bonds |
|
|
13) What are bacteriophages? |
Viruses that affect bacteria |
|
|
14) How is RNA different from DNA?- |
RNA is a single strand, contains ribose sugar, and uracil base pairing (A-U and C-G) DNA is double strand (helix), contains deoxyribose sugar, and thymine base pairing (A-T and C-G) |
|
|
15) What are the products of transcription? |
Mostly mRNA, but also rRNA, and tRNA |
|
|
16) What does ionizing radiation do to bacteria? |
Causes mutations - sticks to DNA and makes it unreadable and thus useless |
|
|
17) Recognize the difference between a diagram of transcription and a diagram of replication. |
1) Transcription(8.7-8.11)Replication(8.4-8.6) ***** |
|
|
18) What are the specific effects of the following antibiotics on bacteria: tetracycline,chloramphenicol, streptomycin, and erythromycin. |
All affect the 70s ribosome of mitochondria Chloramphenicol: bind to 50s portion. Also prevents translation, protein synthesis, and additionally prevents peptide bond formation Streptomycin: binds to 30s portion. mRNA is read incorrectly forming a kink Erythromycin: blocks tunnel between large and small ribosomal pieces |
|
|
19) What enzyme bonds adjacent nucleotide-bases? |
DNA ligase (side by side) |
|
|
20) What enzyme cuts DNA at specific nucleotide sequences? |
Restriction enzyme |
|
|
21) The two strands of DNA run…. |
Antiparallel (3’ and 5’ or 5’ and 3’) |
|
|
22) What is found on plasmids? |
R Factors (resistant factors) Fancy genes - acquired by desperation. Genes float in cytosol |
|
|
Optimum temperatures and ranges for: Psychophiles |
10-20 degrees. Optimum is 15.
|
|
|
Psychotrophs |
0-30 degrees. Optimum 25. (refrigerator)
|
|
|
Mesophiles |
10-50 degrees. 37 degrees optimum. (normal flora - opportunists)
|
|
|
Thermophiles |
42-72 degrees. Optimum 62. (hot soil)
|
|
|
Hyperthermophiles
|
67-110 . Optimum 94. |
|
|
3 Stop codons (termination) |
UAA . UAG. UGA. nonsense codons. Stops translation |

