![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

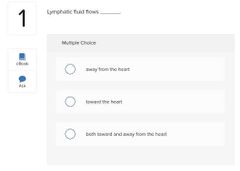
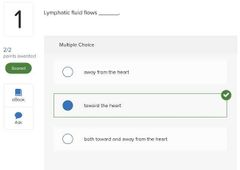
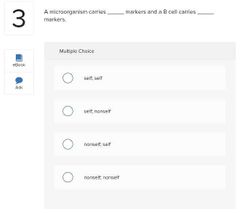
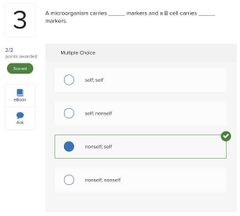
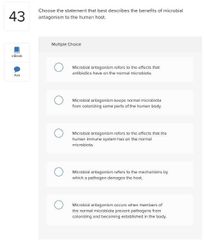
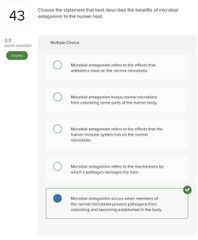
○ disruption ○ a superinfection ○ microbial antagonism ○ a nonliving reservoir |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
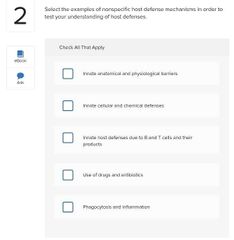
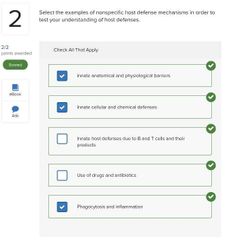
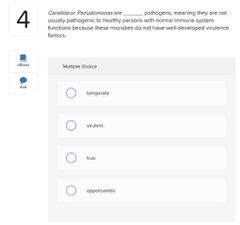
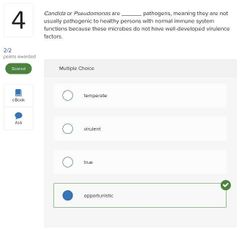
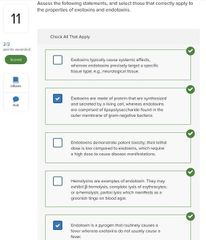
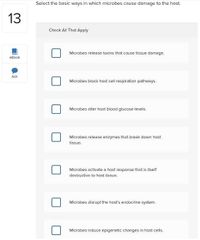
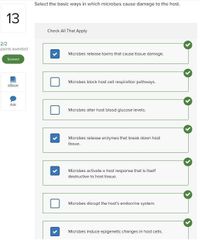
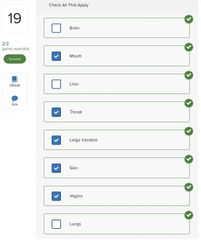
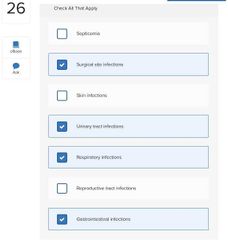
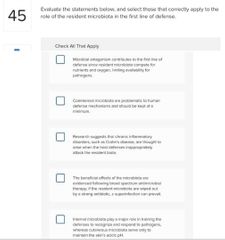
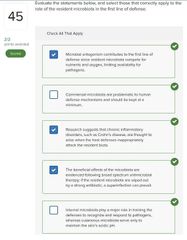
Select three basic ways in which microbes cause tissue damage.
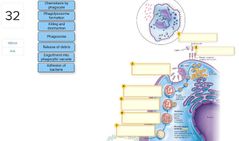
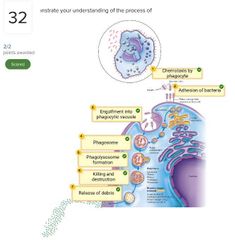
□ Release toxins that cause tissue damage □ Block host cell respiratory pathways □ Alter host blood glucose levels □ Release enzymes that breakdown host tissues □ Activate a host response that is itself destructive to host tissues □ Disrupt host endocrine system |
■ Release toxins that cause tissue damage □ Block host cell respiratory pathways □ Alter host blood glucose levels ■ Release enzymes that breakdown host tissues ■ Activate a host response that is itself destructive to host tissues □ Disrupt host endocrine system |
|
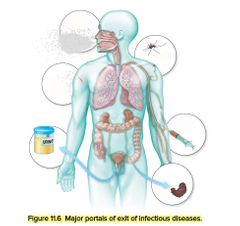
|
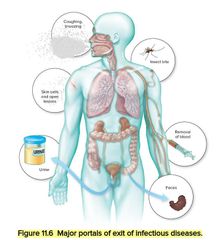
|
|
|
Select all of the examples of reportable diseases from the list below.
□ Impetigo □ Diphtheria □ Listeriosis □ Giardiasis □ Cholera □ HIV □ Tetanus □ Rotavirus |
□ Impetigo ■ Diphtheria ■ Listeriosis ■ Giardiasis ■ Cholera ■ HIV ■ Tetanus □ Rotavirus |
|
|
Select three basic ways in which microbes cause tissue damage. □ Release toxins that cause tissue damage □ Block host cell respiratory pathways □ Alter host blood glucose levels □ Release enzymes that breakdown host tissues □ Activate a host response that is itself destructive to host tissues □ Disrupt host endocrine system |
■ Release toxins that cause tissue damage □ Block host cell respiratory pathways □ Alter host blood glucose levels ■ Release enzymes that breakdown host tissues ■ Activate a host response that is itself destructive to host tissues□ Disrupt host endocrine system |
|
|
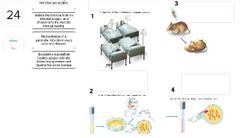
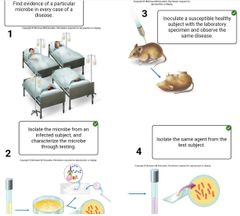
Select those circumstances in which Koch's postulates cannot be readily applied or would be inappropriate to establish the cause of a disease.
|
The suspected pathogen cannot be cultured in the laboratory.There is not a suitable experimental host for the suspected pathogen. The disease is polymicrobial, caused by more than one pathogen. |
|
|
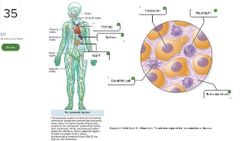
Living reservoirs |
- animals - humans - arthropods |
|
|
Nonliving reservoirs |
- soil - water - air - the built environment |
|
|
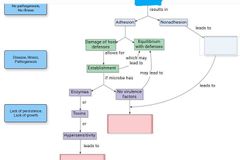
List the four stages of disease in a human. |
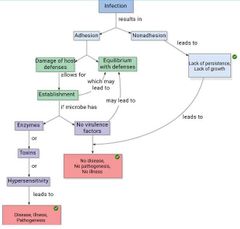
1 - portal of entry 2 - adhesion/attachment to host 3 - become established 4 - cause disease |
|
|
The study of the occurrence and distribution of health related states or events in specified population. |
Epidemiology |
|
|
List the goals of epidemiology. |
1) monitor the health of the population 2) understand the determinants of health and disease in communities 3) investigate and evaluate interventions to prevent disease and maintain health |
|
|
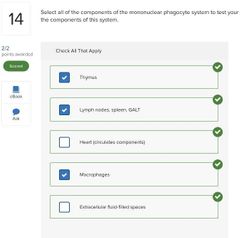
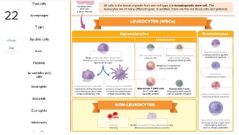
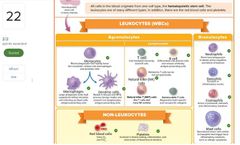
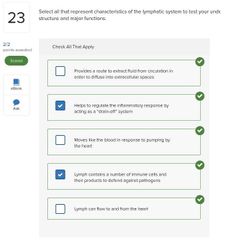
List the body systems that participate in immunity. |
- extracellular fluids - reticuleodothelial system - lyphatic system - cardiovascular system |
|
|
Pro inflammatory |
Macrophages and dendritic cells |
|
|
Anti inflammatory |
Glucocorticoids |
|
|
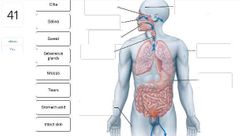
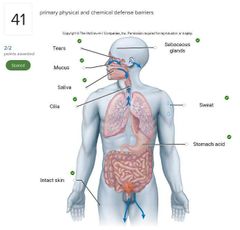
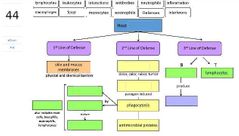
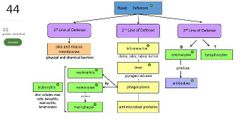
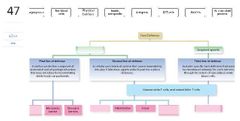
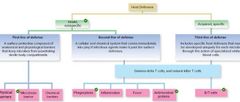
List 3 components of the first line of defense. |
- physical barriers - chemical barriers - genetic components |
|
|
List 5 types of antimicrobial proteins. |
- interferon - complement - iron-binding - antimicrobial proteins |

