![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Zacharias Janssen
|
1600 compound microscope (rudimentary)
|
|
|
Anthony van Leeuwenhoek
|
1673 single lens microscope
|
|
|
parafocal
|
retain focus between two objectives
|
|
|
resolution- human eye
|
0.2mm
|
|
|
resolution- brightfield microscope
|
0.2 (u italics)m
can see bacteria |
|
|
resolution- electron
|
0.2nm
see virsues |
|
|
meter
|
3.28 ft
|
|
|
bacteria need from environment:
|
Macronutrients chnops
micronutrients growth factors ( vitamins) water |
|
|
auxotroph
|
have growth requirements
|
|
|
prototroph
|
no growth requirements
|
|
|
synthetic or defined
|
Burks media,
|
|
|
complex or rich
|
TSA, Nutrient broth
some ingredients unknown extracts prepared media |
|
|
Broth
|
used to make media to create mass organisms
|
|
|
general
|
provides basic needs for bacterial growth tsa, na, blodd agar
|
|
|
selective
|
used to suppress growth of unwanted microorganisms and favor growth of desired organisms MacConkey, msa, cna
|
|
|
differential
|
distinguish colonies of desired organisms from other colonies growing on same plate MacConkey, msa
|
|
|
how high can temperatures get with 15 p.s.i?
|
121 degrees celsius
|
|
|
bacteria
|
ubiquitous, exist in mixed cultures
|
|
|
pure culture
|
one type of bacteria
|
|
|
Robert Koch
|
created agar
|
|
|
Columbia CNA Agar
|
Selective for G +, inhibits G-
|
|
|
MacConkey Agar
|
selective for G-, inhibits G+
Inhibitory: Bile Salts indicator: neutral red(pH drop around colony causes color change) |
|
|
MacConkey Agar results
|
Lactose fermenters: pink or red colonies
lactose non-fermaenters: clear colonies |
|
|
Mannitol Salt Agar
|
Growth of Staphylococcus species
inhibitor: sodium chloride 7.5% indicator: phenol red |
|
|
MSA results
|
S. saprophyticus: yellow colonies and yellow meida (ferments mannitol)
S. epidermidis: grows but does not ferment mannitol(media not yellow) |
|
|
Blood Agar
|
enrich blood for fastidious organisms G+, G-
indicator: blood |
|
|
Blood agar results
|
Beta, alpha, gamma
beta- complete homolysis alpha- incomplete hemolysis gamma- no hemolysis |
|
|
Linnaeus
|
Binomial system
|
|
|
Carl Woese
|
1978 introduced 3 domains Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
|
|
|
Christian Gram
|
1884 important differential staining techniques allows identification of bacterial groups based on peptidoglycan in cell wall
|
|
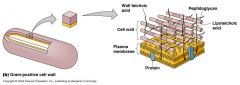
Gram + or Gram -?
|
gram positive
|
|
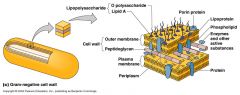
Gram pos or gram neg?
|
gram negative
|
|
|
Steps for gram stain
|
Crystal violet
Iodine Alcohol Safranin |
|
|
negative stain
|
to see bacterial cell morphology, size of cells, capsules, cell shape, and association between cells.
|
|
|
Nigrosin stain
|
negatively charged
dark background, visible bacteria no heat applied |
|
|
Sab
|
selective for fungi due to low pH (5.6) and high glucose content
|
|
|
Joseph Lister
|
Aseptic surgery carbolic acid
|
|
|
Factors affecting effectiveness of antimicrobial treatments
|
microbial characteristics
# of microorganisms time of exposure |
|
|
Alexander Flemning
|
Penicillin 1928
|
|
|
What are the major modes of action of antibotics?
|
-cell wall synthesis
-plasma membrane -folic acid synthesis -nucleic acids -protein synthesis (50s, 30s units) |
|
|
Mueller-Hinton
|
low inhibitors sulfonamides, trimethoprim, and tetracycline inhibitors
neutral pH |
|
|
mycology
|
study of fungi
|
|
|
fungi characteristics
|
eukaryotic, chemoheterotrophs (non-photosynthetic), lack tissue diffrentation, absorptive metabolism
cell wall: chitin |
|
|
Fungi- multicellular
|
molds, mushrooms
|
|
|
Fungi- unicellular
|
yeasts
|
|
|
molds and fleshy fungi connected by chains of?
|
hyphae
|
|
|
An interconnected mass of hyphae is called?
|
mycelium
|
|
|
fungi can reproduce by
|
fragmentation-asexually
formation of spores- sexually and asexually |
|
|
Name two types of electron microscopes: (to view structural details of bacteria
|
Transmission Electron
Scanning Electron |
|
|
resolution
|
distance between two points that can be distinguished from one another as two separate things
|
|
|
light source
|
helps to illuminate the organism
|
|
|
course focus adjustment
|
brings the stage up to put the object in focus
|
|
|
diaphragm
|
adjusts the amount of light
|
|
|
magnification
|
10X, 40X, 100X
|
|
|
wet mount
|
place 1-2 drops of sample in center of slide, cover slip
|
|
|
auxotroph
|
requires growth requirement
auxein- to increase, trophos- nourishment |
|
|
prototroph
|
wild type organism or one with no growth requirments
|
|
|
nutrient agar slants
|
used to maintain stock cultures
|
|
|
nutrient agar plates
|
used to isolate pure cultures of organisms
|
|
|
nutrient broth tubes
|
used to grow large numbers of organisms
|
|
|
agar
|
ingredient to make solid media
|
|
|
Agar will not go into the solution until has been
|
autoclaved
|
|
|
Name three ingredients of media which are required for bacterial growh
|
maronutrients
micronutrients water |
|
|
aseptic
|
used to keep area free of bacterial contamination
|
|
|
negative stain
|
nigrosin (-) does not react with bacteria surface (-) dries to form dark background
|

