![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
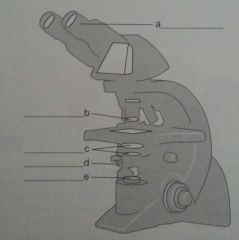
pg 73, Ch 3 Review
3. label a. |
a. ocular lens |
|
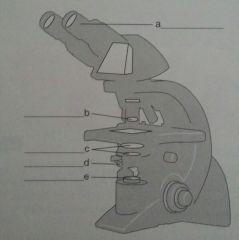
pg 73, Ch 3 Review 3. label b.
|
b. objective lens |
|
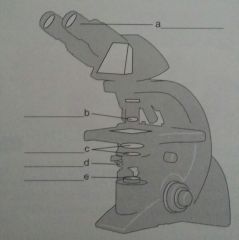
pg 73, Ch 3 Review 3. label c.
|
c. condenser lenses |
|
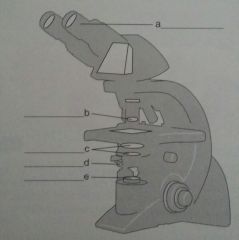
pg 73, Ch 3 Review 3. label d.
|
d. diaphragm |
|
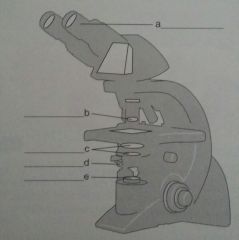
pg 73, Ch 3 Review 3. label e.
|
e. Illuminatoer |
|
|
Magnification of the compound light microscope 10X eyepiece * 4X Objectivelens = |
40X magnification |
|
|
Magnification of the compound light microscope 10X eyepiece * 10X Objective lens =
|
100X magnification |
|
|
Magnification of the compound light microscope 10X eyepiece * 100X Objective lens =
|
1000X magnification |
|
|
Resolution in a compound light microscope |
"Resolution" the ability of the lenses to distinguish two points In a compound microscope, the wavelength of the light waves that illuminate the specimen limits the resolution. The wavelength of visible light ranges from about 400 to 700 nanometers. The best compound microscopes cannot reslove parts of a specimen that are closer together than about 200 nanometers. |
|
|
Parfocaling an a compound light microscope objective lens |
"Parfocal" refers to objectives that can be changed with minimal or no refocusing. 4X and 10X objective lens' do not have adjustable settings |
|
|
Types of Microscopes Simple microscope |
Has only one lens |
|
|
Types of Microscopes Compound Light microscopy |
-Uses visible light to observe specimens -Resolution is the ability of lenses to distinguish two points -A microscope with a resolving power of 0.4 nm can distinguish between two points greater or equal to 0.4 nm -Shorter wavelengths of light provide greater resolution -The refractive index is a measure of the lightbending ability of a medium -The light may bend in air so much that it misses the small high-magnification lens -Immersion oil is used to keep light from bending |
|
|
Types of Microscopes Brightfield Illumination |
-dark objects are visible against a bright background -light reflected off the specimen does not enter the objective lens |
|
|
Types of Microscopes Darkfield Illumination |
-light objects are visible against a dark background -light reflected off specimen enters the objective lens |
|
|
Types of Microscopes
Phase-Contrast Microscopy |
|
|
|
Types of Microscopes Fluorescence Microscopy |
|
|
|
Types of Microscopes Electron Microscopy |
|
|
|
Types of Microscopes Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) |
|
|
|
The microscope you will use in this lab is called a _____________microscope. |
The microscope you will use in this lab is called a Brightfield compound microscope. |
|
|
What is the most common differential staining procedure in Microbiology? |
Gram Stain |
|
|
What is a Gram Stain? |
|
|
|
What is a Gram + positive stain? |
|
|
|
What is a Gram - negative stain? |
|
|
|
What are the 4 reagents in a Gram Stain? |
|
|
|
What is the main component in the Bacteria Wall? |
Peptidoglycan |
|
|
What is the purpose of Mordant? |
To make the stain look better (primer) and to stick to the slide. |
|
|
What is Acid-fast staining? |
|
|
|
What is the cell wall of an Acid-fast stain bacteria made up of? |
An impermeable, wax-like lipid called Mycolic Acid |
|
|
What is the shape of a bacillus bacteria? |
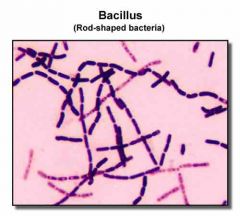
Bacillus = Rod shape |
|
|
What is the shape of the coccus bacteria? |
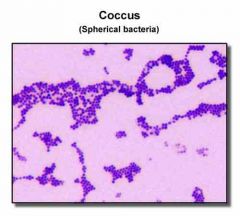
Coccus = Spherical/round |
|
|
What is the shape of staph bacteria? |
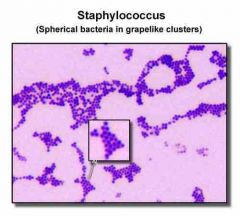
Staph = Clusters |
|
|
What is the shape of the strep bacteria? |
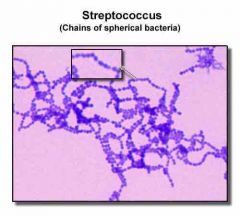
Strep= chain |
|
|
What is the spiral bacteria shape? |
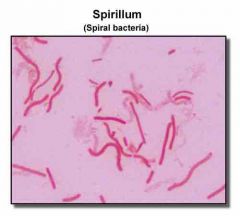
Spiral= Spirillum,Vibrio, Spirochete |
|
|
What are pairs shape bacteria? |
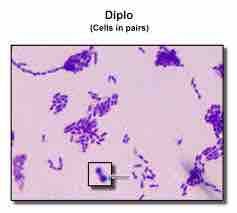
Pairs shape bacteria = Diplococci,Diplobacilli |
|
|
What is BSL 1? |
|
|
|
What is BSL 2? |
|
|
|
What is BSL 3? |
|
|
|
What is BSL 4? |
|
|
|
What BSL is the lab that we work in? |
BSL 2 |

