![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Vibrio characteristics |
• G- Curved rod, comma shaped • Motile • Aerobic • Non-spore • Non-capsulated (except non-O1 cholerae, parahaemolyticus and vulnificus) • Oxidase positive • Late lactose fermenter |
|
|
Salt requirements of vibrio |
Halophiles: • Can't grow in absence of salt • Can grow in upto 7-10% NaCl • Parahaemolyticus and vulnificus Non-halophiles: • Can grow in absence of salt • Best growth in 1% salt • Cholerae |
|
|
Serotypes of cholerae |
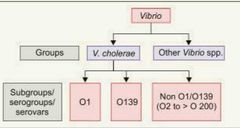
• O1 caused major epidemics |
|
|
Vibrio cholerae O1 - classification |
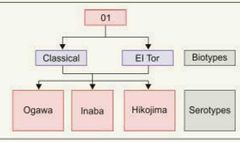
|
|
|
Infective dose of V. cholerae |
Large (≈10^8) as sensitive to gastric acid |
|
|
Mechanism of cholera toxin |
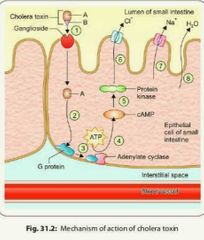
• B is a pentamer • Bound to GM1 ganglioside |
|
|
El Tor biotype of V. cholerae |
• Produces a Haemolysin • Resistant to polymyxin B |
|
|
Pathogenesis of shigella |
Bacteria enter the intestinal epithelial M cells → Cross basolateral membrane → Shig in submucosa → Phagocytosed (induced phagocytosis)→ Escape phagosome → Multiplication and spread into adjacent cells → Release of cytokines by infected cells → Inflammatory response → Microabscesses in the terminal ileum, large gut → Necrosis, ulceration, bleeding |
|
|
Shigella properties |
• G- Non spore forming rods • Non motile • Non lactose fermenting (except sonnei, which is late lactose fermenter) • Produce no gas from fermenting glucose • Do not produce H2S |
|
|
TCBS agar |
• Thiosulphate Citrate Bile Sucrose • Selective for vibrio • Yellow colony against dark green background of the agar |

