![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
heterotroph (definition) |
organisms that use organic molecules as carbon sources which often also serves as energy source |
|
|
autotroph (definition) |
organisms that use carbon dioxide as their sole or principal carbon source |
|
|
phototrophs (definition) |
use light as an energy source |
|
|
chemotrophs (definition) |
obtain energy from the oxidation of chemical compounds |
|
|
lithotrops (definition) |
use reduced inorganic substances |
|
|
organotrophs |
obtain electrons from organic compounds |
|
|
despite diversity of energy, electron, and carbon sources used by organisms, they all have the same 3 basic needs which are... |
1. ATP as energy currency 2. reducing power to supply electrons for chemical reactions 3. precursor metabolites for biosynthesis |
|
|
most respiration involves the use of a ________ |
electron transport chain |
|
|
aerobic respiration (definition) |
final electron acceptor is oxygen |
|
|
anaerobic respiration (definition) |
final electron acceptor is a different exogenous acceptor such as NO3, SO4, CO2, Fe, or SeO4 |
|
|
as ______ pass through the ______ to the final electron acceptor, a _______ is generated and used to synthesize ______ |
electrons, electron transport chain, proton motive force (PMF), ATP |
|
|
aerobic respiration can be divided into 3 steps |
1. glycolysis 2. TCA cycle 3. electron transport chain with oxygen as the final electron acceptor |
|
|
many different energy sources are funneled into common _______ pathways |
degradative |
|
|
most pathways generate _______ or ________ of the pathways used in glucose metabolism |
glucose, intermediates |
|
|
fewer pathways greatly _______ metabolic efficiency |
increases |
|
|
only 4 ____ molecules are synthesized directly from _______ of _______ to ______ |
ATP, oxidation, glucose, CO2 |
|
|
most ____ is made when _____ and _____ (formed as glucose is degraded) are ________ in the _______ |
ATP, NADH, FADH, oxidized, electron transport chain |
|
|
the mitochondrial _________ is a series of _______ carriers, operating together to transfer ________ from _______ and ______ to a terminal ________ acceptor, _____ |
electron transport chain, electron, electrons, NADH, FADH, electron, O2 |
|
|
electrons flow from carriers with more _______ reduction potentials (E0) to carriers with more ________ E0 |
negative, positive |
|
|
ETC - redox pairs each pair is ______ and then _______ |
reduced, reoxidized |
|
|
ETC - redox pairs carriers are constantly ______ |
recycled |
|
|
ETC - redox pairs the difference in _______ of electron carriers, NADH and O2, is _______ resulting in the release of a great deal of ______ |
reduction potentials, large, energy |
|
|
_____ creates the proton motive force |
electron transport chain |
|
|
bacterial and archael ETC are located |
in the plasma membrane |
|
|
difference between mitochondrial ETC and bacterial and archael ETC (4 points) |
1. different electron carriers 2. may be branched 3. may be shorter 4. may have lower P/O ratio |
|
|
oxidative phosphorylation (definition) |
the process by which ATP is synthesized as the result of electron transport driven by the oxidation of a chemical energy source |
|
|
proton motive force (PMF) drives ______ |
ATP synthesis |
|
|
diffusion of _____ back across the membrane (_____ the gradient) drives the formation of _____ |
protons, down, ATP |
|
|
ATP synthase uses the ______ down gradient to _____ ATP synthesis |
proton motive force, catalyze |
|
|
ATP synthase functions like a _______ |
rotary engine (conformational changes) |
|
|
dissimilatory nitrate reduction uses ______ as the terminal electron acceptor, making it ______ to the cell for ______ or _______ |
nitrate, unavailable, assimilation, uptake |
|
|
denitrification (definition) |
the reduction of nitrate to nitrogen gas |
|
|
denitrification in soil causes _______ |
loss of soil fertility |
|
|
what is the order of energy yield from highest to lowest for these electron acceptors? |
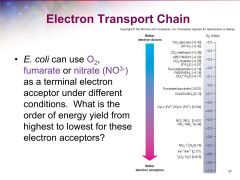
|
|
|
chemoorganotrophic fueling processes: aerobic respiration 1. mechanism 2. what is going in? 3. what is coming out? |
1. organic energy and electron source > electrons > ETC > O2 also... organic energy and electron source > electrons > ETC > PMF > OxPhos > ATP 2. what is going in? - electrons 3. what is coming out? - oxygen and ATP |
|
|
chemoorganotrophic fueling processes: anaerobic respiration 1. mechanism 2. what is going in? 3. what is coming out? |
1. organic energy and electron source > electrons > ETC > SO4, NO3, CO2, fumarate, etc. also... organic energy and electron source > electrons > ETC > PMF > OxPhos > ATP 2. what is going in? - electrons 3. what is coming out? - SO4, NO3, CO2, fumarate, etc. and ATP |
|
|
glycolysis 1. in 2. out 3. what is the cell getting out of this reaction? |
1. IN: glucose, 2 ATP, 2 NAD, 2 phosphate, 2 ADP 2. OUT: pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH 3. energy, the first step in cellular respiration |
|
|
TCA cycle 1. in 2. out 3. what is the cell getting out of this reaction? |
1. IN: acetyl Co-A (from pyruvate in step 2 of cellular respiration), oxaloacetate 2. OUT: 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH, 2 CO2, regenerated oxaloacetate 3. energy, step 3 in cellular respiration |
|
|
oxidative phosphorylation is made up of a) the electron transport chain 1. in 2. out 3. what is the cell getting out of this reaction? b) chemiosmosis 1. in 2. out 3. what is the cell getting out of this reaction |
a) the ETC 1. electrons on the electron carriers NADH and FADH 2. NAD, FAD, H2O, ATP 3. regenerate electron carriers and creates a proton gradient (PMF) b) chemiosmosis: the process in which energy from a proton gradient is used to make ATP 1. ADP 2. ATP 3. 30-32 ATP per 1 glucose molecule |

