![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
121 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Perfect competition
|
occurs in an industry when the following four conditions are satisfied: Numerous small firms and customers, Homogeneity of a product, Freedom of entry and exit, Perfect information |
|
|
Price taker |
when a firm has no choice but to accept the price that has been determined in the market |
|
|
Short-Run equilibrium for Perfectly Competitive Firm
|
MC = MR = P |
|
|
Short-Run profit for Perfectly Competitive Firm
|
P>AC the firm will earn a profit; P |
|
|
Variable cost
|
a cost whose total amount changes when the quantity of output of the supplier changes |
|
|
Supply curve of the perfectly competitive firm
|
shows the different quantities of output that the firm would be willing to supply at different possible prices during some given period of time |
|
|
Supply curve of the perfectly competitive industry
|
shows the different quantities of output that the industry would supply at different possible prices during some given period of time |
|
|
Economic profit
|
equals net earnings, in the accountant's sense, minus the opportunity costs of capital and of any other inputs supplied by the firm's owner |
|
|
Long Run Equilibrium for Industry
|
P = MC = AC --> zero economic profit in long run |
|
|
Long-run supply curve for perfectly competitive industry
|
Equal to its long-run average cost curve |
|
|
Market |
A set of sellers and buyers whose activities affect the price of at which a particular commodity is sold |
|
|
Industry
|
Group of firms that supply a market for a particular commodity |
|
|
Market Structure
|
How the industry in a market is organized - There are 4 kinds: Perfect competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic competition, Oligopoly |
|
|
Different Kinds of Market Structure are Based on
|
-The number of firms in the industry |
|
|
The Perfectly Competitive Industry
-short run and long run for the industry |
SHORT RUN |
|
|
Pure monopoly
|
an industry in which there is only one supplier of a product for which there are no close substitutes and in which it is very difficult or impossible for another firm to coexist |
|
|
Barriers to entry
|
attributes of a market that make it more difficult or expensive for a new firm to open for business than it was for the firms already present in the market. 7 Examples: 1. Legal restrictions; 2. Patents; 3. Control of a Scarce Resource or Input; 4. Deliberately Erected Entry Barriers; 5. Large Sunk Costs (most important type of "naturally imposed" barrier to entry); 6. Technical Superiority; 7. Economies of Scale |
|
|
Patents |
a privilege granted to an inventor, whether an individual or a firm, that for a specified period of time prohibits anyone else from producing or using that invention without the permission of the holder of the patent |
|
|
Natural monopoly
|
an industry in which advantages of large-scale production make it possible for a single firm to produce the entire output of the market at a lower average cost than a number of firms each producing a smaller quantity |
|
|
Profit maximizing monopolist
|
1. Find the output at which MR equals MC to select the profit-maximizing output level. |
|
|
Monopoly profits
|
any excess of the profits earned persistently by a monopoly firm over and above those that would be earned if the industry were perfectly competitive |
|
|
Price discrimination
|
the sale of a given product at different prices to different customers of the firm when there are no differences in the costs of supplying these customers. Prices are also discriminatory if it costs more to supply one customer than another but they are charged the same price
|
|
|
Cartel |
a group of sellers of a product who have joined together to control its production, sales, and price in the hope of obtaining the advantages of monopoly |
|
|
Credible threat
|
a threat that does not harm the threatener if it is carried out. If a firm takes action to implement the threat, it becomes credible |
|
|
Dominant strategy
|
for one of the competitors in a game the strategy that will yield a higher payoff than any of the other strategies that are possible, no matter what choice of strategy is made by competitors |
|
|
Excess capacity theorem of monopolistic competition
|
Under monopolistic competition in the long run, the firm will tend to produce an output lower than that which minimizes its unit costs, and hence unit costs of the monopolistic competitor will be higher than necessary. Resulting Because the level of output that corresponds to minimum average cost is naturally considered to be the firm's optimal capacity. Thus, monopolistic competition tends to lead firms to have unused or wasted capacity |
|
|
Kinked demand curve
|
a demand curve that changes its slope abruptly at some level of output |
|
|
Maximin criterion
|
requires a player to select the strategy that yields the maximum payoff on the assumption that the opponent will do as much damage as it can |
|
|
Monopolistic competition
|
refers to a market in which products are heterogeneous but which is otherwise the same as a market that is perfectly competitive |
|
|
Nash equilibrium
|
results when each player adopts the strategy that gives the highest possible payoff if the rival sticks to the strategy it has chosen |
|
|
Oligopoly
|
a market dominated by a few sellers, at least several of which are large enough relative to the total market to be able to influence the market price. example: Apple, HTC and Galaxy; ATT, Sprint and Verizon |
|
|
Payoff matrix
|
shows how much each of two competitors (players) can expect to earn, depending on the strategic choices each of them makes |
|
|
Perfectly contestable market
|
when entry and exit are costless and unimpeded (not hindered) with Perfect Information present |
|
|
Price leadership
|
an arrangement in which one firm in the industry, in effect, makes pricing decisions for the entire group |
|
|
Price war
|
each competing firm is determined to sell at a price that is lower than the prices of its rivals, often regardless of whether that price covers the appropriate cost. Typically, in such a price war, Firm A cuts its price below Firm B's price; B retaliates by undercutting A; and so on until some of the competitor firms surrender and let themselves be undersold |
|
|
Repeated game
|
a game that is played a number of times |
|
|
Sales maximization
|
when a firm's objective seeks to adopt prices and output quantities that make its total revenue (the money value of its sales), rather than its profits, as large as possible. Set MR = 0 and find price on demand curve. |
|
|
Stick price
|
if the price does not change often, even when there is a moderate change in cost |
|
|
Zero-sum game
|
a game in which exactly the amount one competitor gains must be lost by other competitors |
|
|
agents
|
people hired to run a complex enterprise on behalf of the principals, those whose benefit the enterprise is supposed to serve.
|
|
|
excludable (excludability)
|
A commodity is _______ if someone who does not pay for it can be kept from enjoying it. |
|
|
beneficial externality
|
occurs when the consumption or production of a good causes a benefit to a third party. For example:When you consume education you get a private benefit. But there are also benefits to the rest of society. E.g you are able to educate other people and therefore they benefit as a result of your education. |
|
|
marginal private benefit (MPB)
|
Additional benefit enjoyed by a household (or business) in actually consuming (or producing) a good. |
|
|
marginal private cost (MPC)
|
Additional cost incurred by a household (or business) in actually consuming (or producing) a good. |
|
|
marginal social benefit (MSB)
|
the total benefit to society, from one extra unit of a good. The MSB = Marginal private benefit (MPB) + marginal external benefit (MXB) |
|
|
marginal social cost (MSC)
|
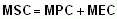
the total cost to society as a whole for producing one further unit, or taking one further action, in an economy. |
|
|
moral hazard
|
a situation in which one party gets involved in a risky event knowing that it is protected against the risk and the other party will incur the cost |
|
|
PPF (Production Possibility Frontier)
|
a curve depicting all maximum output possibilities for two goods, given a set of inputs consisting of resources and other factors. It assumes that all inputs are used efficiently. |
|
|
private good
|
a commodity that is purchased and used by one party and is not available to others (characterized by both "depletable" (significant decrease in abundance) and excludable.) |
|
|
public good
|
commodity or service whose benefits are not depleted by an additional user, even if people are unwilling to pay for the benefits. Examples: Beach or air |
|
|
rent seeking
|
the use of a company, organization or individual's resources to obtain economic gain; firms hope to obtain earnings without contributing to production |
|
|
stock option
|
contract that permits its owner to buy or sell a specified quantity of stocks of a corporation at a future date |
|
|
Ability-to-pay principle
|
economic progressive tax idea that people with greater ability to pay taxes should pay higher taxes |
|
|
Average Tax rate
|
- the ratio of taxes to income - The total amount of taxes paid by an individual or business divided by taxable income. This rate will vary based on the amount of income received during the taxable period - Paid taxes/taxable income = average tax rate. |
|
|
Benefits Principle
|
Taxation concept that those who benefit more from government expenditure should pay more taxes to support such expenditure. |
|
|
Burden of Tax
|
-The amount one would have to be given to be just as well off with the tax as without it. --The amount of income, property, or sales tax levied on an individual or business that varies depending on income level, jurisdiction, and current tax rates. Income tax burdens are typically satisfied by deductions from an individual's paycheck each time he or she is paid. Depending on the amount of allowances claimed by the individual, it may exceed the total amount of money deducted during the taxable period. |
|
|
Direct Taxes
|
taxes, such as income tax, that are levied on the income or profits of the person who pays it, rather than on goods or services. |
|
|
Excess Burden
|
- A tax to an individual which is the amount by which the burden of the tax exceeds the tax that is paid -one of the economic losses that society suffers as the result of taxes or subsidies |
|
|
Fiscal Federalism
|
-deals with the division of governmental functions and financial relations among levels of government. - The system of grants from one level of government to the next |
|
|
Horizontal Equity
|
-The notion that equally situated individuals should be taxed equally - Economic theory that states that individuals with similar income and assets should pay the same amount in taxes. |
|
|
Incidence of Tax
|
- The analysis of the effect of a particular tax on the distribution of economic welfare. - An allocation of the burden of the tax to specific individuals or groups |
|
|
Indirect Taxes
|
(such as sales tax, per unit tax, value added tax (VAT), or goods and services tax (GST)) is a tax collected by an intermediary (such as a retail store) from the person who bears the ultimate economic burden of the tax (such as the consumer) -Taxes levied on specific economic activities |
|
|
Marginal Tax Rate
|
- percentage of tax applied to your income for each additional dollar earned. |
|
|
Progressive Tax
|
One in which the average tax rate paid by an individual rises as the income rises |
|
|
Proportional Tax
|
One in which the average tax rate is the same at all income levels |
|
|
Regressive Tax
|
One in which the average tax rate falls as income rises |
|
|
Tax Deduction
|
- reduction of income that is able to be taxed, and is commonly a result of expenses, particularly those incurred to produce additional income - A sum of money that may be subtracted before the taxpayer computes his or her taxable income |
|
|
Tax Exempt
|
A particular source of income is____ if income from that source is not taxable |
|
|
Tax Loophole
|
A special provision in the tax code that reduces taxation below normal rates if certain conditions are met |
|
|
Tax Shifting
|
- a change in taxation that eliminates or reduces one or several taxes and establishes or increases others while keeping the overall revenue the same - When the economic Reactions to a tax cause prices and outputs in the economy to change, thereby shifting party of the burden of the tax onto others |
|
|
Vertical Equity
|
The notion that differently situated individuals should be taxed differently in a way that society deems to be fair |
|
|
capital
|
=Land + labor an inventory of plant and other productive resources hold by a business firm or some organization |
|
|
derived demand
|
a demand for a commodity, service, etc., that is a consequence of the demand for something else. |
|
|
economic profit
|
total revenue of a firm minus all of its costs |
|
|
economic rent
|
portion of the earnings of a factor of production that exceeds the minimum amount necessary to induce that factor to be supplied - any payment to a factor of production in excess of the cost needed to bring that factor into production |
|
|
entrepreneurship
|
act of starting new firms or introducing new products which involve risks that are necessary to seek out business opportunities managing/using land, labor and time to produce capital |
|
|
innovation
|
the act of putting the invention into practical use |
|
|
interest
|
- money paid regularly at a particular rate for the use of money lent, or for delaying the repayment of a debt. - payment for the use of funds employed in the production of capital |
|
|
invention
|
act of generating an idea for a new product or a new method for making an old product |
|
|
investment
|
flow of resources into the production of new capital |
|
|
marginal land
|
Any land that is exactly on the borderline between being used and not being used, and has little or no potential for profit, and often has poor soil or other undesirable characteristics |
|
|
marginal physical product (MPP)
|
the increase in output that results from a one-unit increase in the use of the input |
|
|
marginal revenue product (MRP)
|
additional sales value that a firm obtains by selling 1 additional good |
|
|
bilateral monopoly
|
market structure consisting of both a monopoly (a single seller) and a monopsony (a single buyer). Examples: 1. Governments and certain classes of defense contractors, and 2. marriage
|
|
|
collective bargaining
|
process of negotiation of wages and working conditions between a union and the firms |
|
|
human capital theory
|
theory that focuses on the expenditures (costs) made to increase productive capacity of workers, such as education - The accumulated knowledge and skills that make a workforce productive |
|
|
income effect
|
resulting rise of workers' purchasing power that enables them to afford more leisure |
|
|
innovative entrepreneur
|
someone who introduces a new product or a new process into the economy |
|
|
investment in human capital
|
any expenditure (cost) on an individual that increases their future earning power or productivity |
|
|
labor union
|
organization made up of a group of workers usually with the same specialization an organization intended to represent the collective interests of workers in negotiations with employers over wages, hours and working conditions. |
|
|
marginal revenue product of labor
|
increase in total revenue that results for each additional unit of labor |
|
|
monopsony
|
a market situation in which there is only one buyer Example: the purchase of workers' time in the labor market, such as in professional baseball |
|
|
substitution effect
|
-consumer choice theory that shows the effect of a change in the price of a good based upon the amount of that good demanded by a consumer - resulting incentive to work more because of higher wage |
|
|
Combat Discrimination
|
EEOC (Equal employment opportunity commission) - outlawed many forms of discrimination |
|
|
Combat Inequality
|
Personal Tax income Tax - takes larger share of income from rich |
|
|
Combatting Poverty
|
by Education, Welfare, Negative Income Tax |
|
|
Food Stamps
|
families are provided stamps with which to buy food. Size of benefit depends on income. |
|
|
Negative income tax
|
People below certain income level would be given payment from government. Guarantee = tax rate * break-level |
|
|
Poverty (2 ways)
|
Relative Poverty/Optimistic: falling below certain income makes you poor. once you pas the line you are not poor
Absolute Poverty/Pessimistic: Income below a certain level necessary to maintain a minimum standard of living e.g. enough money to buy the basic necessities of food, shelter and heat |
|
|
Poverty line
|
amount of income below which a family is considered "poor" set by society |
|
|
TANF
|
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families |
|
|
Discrimination
|
Behaving differently, usually unfairly, toward the members of a group
|
|
|
Discrimination Coefficient
|
a measure of the cost or disutility of prejudice; the monetary amount an employer is willing to pay to hire a preferred worker rather than a nonpreferred worker. |
|
|
earned-income tax credit (EITC)
|
a refundable tax credit for low- to moderate-income working individuals and couples, particularly those with children. The amount of EITC benefit depends on a recipient's income and number of children. |
|
|
entitlement programs
|
Government benefits that certain qualified individuals are entitled to by law, regardless of need. |
|
|
equality-efficiency trade-off
|
The decrease in economic efficiency that may come with a decrease in income inequality; the view that some income inequality is required to achieve economic efficiency. |
|
|
Income Inequality
|
imbalances in levels of income among individuals in the economy |
|
|
income mobility
|
Refers to the ease with which members of the workforce can move between levels of economic prosperity. |
|
|
Lorenzo curve
|
Graph showing how much the actual distribution of income differs from an equal distribution |
|
|
Medcaid
|
a federally funded and state-regulated plan designed to help people with low incomes to pay for health care |
|
|
Medicare
|
A program added to the Social Security system in 1965 that provides hospitalization insurance for the elderly and permits older Americans to purchase inexpensive coverage for doctor fees and other health expenses. |
|
|
noncash transfers
|
a government transfer payment in the form of goods and services rather than money, for example, food stamps, housing assistance, and job training; also called in-kind transfers |
|
|
Occupational Segregation
|
a pattern in which different groups of workers are separated into different occupations |
|
|
poverty rate
|
percentage of people whose income falls below the poverty line |
|
|
public assistance programs
|
Distributes public money to poor people: food stamps, medicaid, (Aid to Families with Dependent Children), Supplemental Security Income, and Job Opportunities & Basic Skills programs |
|
|
social insurance programs
|
government programs that pay benefits to retired and disabled workers, their families, and the unemployed, Mandatory; taxpayers pay into these programs; include social security, medicare, medicaid, unemployment, pay as you go system. |
|
|
social security
|
created old age pension for workers, joint federal state system of compensation for unemployed, and payment to widows, blind, deaf, and disabled |
|
|
Statistical Discrimination
|
the practice of making judgments about the quality of people, goods, or services based on the characteristics of the groups to which they belong |
|
|
Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)
|
Previously known as the Food Stamp program, the new name for the USDA program that is the primary food assistance program for low-income households |
|
|
Taste for Discrimination Model
|
A theory that views discrimination as a preference for which an employer is willing to pay. |
|
|
unemployment compensation
|
A system of government payments to people who are out of work and looking for a job |

