![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Connective and supportive tissue arrise from which of the following: endoderm, mesoderm, or ectoderm
|
mesoderm
|
|
|
The basic 4 functions of connective tissue include
|
structural support
defense mechanism delivery/storage of nutrients repair |
|
|
Structurally connective tissue cells are (close/far apart) and separated by lots of ____
|
far apart separated by lots of intercellular material
|
|
|
What are the four main components of connective tissue that make up the ECM (extracellular matrix)
|
Cells (fixed or mobile)
Fibers (3 types) Ground Substance Tissue Fluid |
|
|
Do the connective tissue cells usually have a basement membrane?
|
No, CT cells are usually lacking a basement membrane
|
|
|
What are the main components of CT's ground substance?
|
proteoglycans, glycoproteins, fiber precursor molecules
|
|
|
Name three examples of fixed (or resident) connective tissue cells
|
Fibroblast/ Fibrocyte
Macrophage (from monocytes) Mast cell Pericyte Adipocyte Mesenchymal cells |
|
|
Name three examples of mobile (or transient) cells
|
plasma cells
lymphocyte polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells--- neutrophils Eosinophil Basophil macrophages (can be both? or the ones not from monocytes?) |
|
|
What is the major resident cell found in ordinary (NOT cartilage or bone) connective tissue cells? What is this cell types main role?
|
Fibroblasts: responsible for
synthesizing the matrix which is made of many different proteoglycans and fibers whose synthesis is quite involved. In c.t., you usually see only the nucleus of the fibroblast |
|
|
What are some distinguishing characteristics of the fibroblast nucleus? Distinguish b/w active and nonactive firbroblasts:
|
The nucleus of the fibroblast is ‘football shaped’
and, in the most active fibroblasts, vesicular with a nucleolus. Inactive fibroblasts are known as ‘fibrocytes,’ and their nuclei are darker and more flattened |
|
|
Fibroblast function to synthesize mainly
|
elastin and collagen
|
|
|
A Macrophage is part of what system
|
the mononucear phagocyte system MPS
|
|
|
Macrophages perform two main roles
|
phagocytosis and antigen presentation
|
|
|
Describe the nucleus and cytoplams of the macrophage cell
|
round or indented, vesicular and usually abundant cytoplasm
|
|
|
Mast cells are involved in ____responses and produce___and ____
|
allergic responses and wound repair, producing heparin, histamine
|
|
|
Describe how you could distinguish a mast cell and what stain it is positive for
|
round cell, granulated cytoplasm that are positive staining with toluidine blue
|
|
|
Mast cell mediators are important for( increasing/ decreasing )vascular permeability and inducing bronchiole (constriction or relaxation)
|
increasing permeability and constricting bronchiole
|
|
|
What are pericytes? Where are they located? What type of nucleus
|
stem cells for small blood vessels (mesodermally derived tissues) located along capillaries and venules
vesicular nucleus |
|
|
Name three locations where fixed macrophages (MPS cells) can be found
|
in the lymph nodes (which have both free and fixed)
In bone marrow In the spleen (which has both free and fixed) |
|
|
Name the Monomuclear Phagocyte System (MPS) cells found in these organs:
connective tissue liver lung bone serous cavities |
connective tissue- histiocyte
liver-Kupffer cell lung- alveolar macrophage bone- osteoclasts serous cavities- leural and peritoneal macrophages |
|
|
How do you distinguish lymphocytes?
|
seen in c.t. as small, dark, round nuclei (as is usually the case, you only
see the nucleus in c.t.). |
|
|
Can you tell the difference b/w
|
You cannot tell the difference between these when you look at an
H&E stained section |
|
|
What are the two broad classes of lymphocytes
|
T lymphocytes (thymus derived; participate
in ‘cell mediated’ reactions) and B lymphocytes (bone marrow derived; participate in ‘humoral’ or antibody mediated reactions). |
|
|
Describe the plasma cell cytoplasm and nucleus:
|
cytoplasm is abundant basophilic, round
nucleus is cart wheel like and eccentrically positioned with clumps of chromatin making the cartwheel |
|
|
What is the role of plasma cells and what are they the activated from of?
|
They secrete a lot of antibody and develop from activated B cells
|
|
|
Plasma cells and Mast cells are the exception to the general rule of idnetifying connective tissue cells because
|
you can see more than their nucleus (granules in mast cells and cytoplasm of plasma cells)
|
|
|
Why is the cytoplasm of plasm cells visible
|
It is very darkly basophilic since there is a lot of RER (for protein synthesis)
|
|
|
Neutrophils are also known as
|
heterophils, PMNs or polymorphononuclear cells
|
|
|
Describe the appearance of Neutrophils in H&E
|
multi-lobulated, small, dark nuclei.
|
|
|
What are the neutrophils role in cells
|
they participate in inflammatory defense reactions and are capable of phagocytosis of small particles
|
|
|
What does the cytoplasm of PMNs/ neutrophils contain?
|
eosinophilic granules
|
|
|
Eosinophils
|
visible red color
bilobed nuclei; since they have reddish granules you can sometimes see the cytoplasm. |
|
|
Basophils
|
visible blue color
semi segmented/ bi-lobed nuclei |
|
|
What is the main fiber type found in most supporting tissues
|
collagen (most abundant protein in the human body)
|
|
|
How many types of collagen are found in connective/supportive tissue
|
Type I, II, III, IV, VII
|
|
|
Type I collagen is found in ____
and is/ is not visible wiht light microscope |
Fibrous supporting tissue (dermis of skin, tendons, ligaments and bone, can range from loose to dense)
Can be seen with LM |
|
|
Type II collagen is found in _____and consits of____
|
hyaline cartilage adn consists of fine fibrils which are dispersed around ground substance
|
|
|
Type III collagen makes up the fiber type known as _____. This is found
|
Reticulin. Forms the reticular supporting meshwork of highly cellular tissue like liver, bone marrow and lymphoid organ
|
|
|
Type IV collagen is unique in that it does not form ____but rather a ____and important constituent of ____
|
does not form fibrils, more meshlike structure and constituent of basement membrane
|
|
|
Type VII collagen
|
forms anchoring fibrils that link to basement membrane
|
|
|
Elastin is synthesized by ____, is arranged in ______, and found in _____ where it confers stretching and elastic recoil
|
synthesized by fibroblasts, arranged in fibers and or discontinuous sheets, found in skin, lung, and blood vessels
|
|
|
Type I collagen is produced by
|
mature fibroblasts
|
|
|
A silver stain is required to see Type____ collagen which are considered to be____philic
|
retcular fibers/ type III collagen
argyrophilic |
|
|
Type III (reticular CT ) collagen is found in
|
hemopoietic and lymphatic organs
|
|
|
How can you distinguish Elastic Fibers in H&E
|
stain brighter pink than collagen and are more branched or wavy
shinier than smooth muscle |
|
|
Elastin is synthesized by ____, is arranged in ______, and found in _____ where it confers stretching and elastic recoil
|
synthesized by fibroblasts, arranged in fibers and or discontinuous sheets, found in skin, lung, and blood vessels
|
|
|
Name four functions of the ground substance
|
fills space b/w cells and fibers
-acts as a physical barrier -acts as modulator for cell functions such as growth -Contain/house proteoglycans (GAGs) |
|
|
Type I collagen is produced by
|
mature fibroblasts
|
|
|
What is a GAG?
|
tthe main CHO compent of proteoglycans
glycosaminoglycans A polysaccharide which contains amino sugars example: chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, keratan sulfate (most are basic/highly sulfated ) Exception is the acid gag hyaluronate (or hyaluronic acid) |
|
|
A silver stain is required to see Type____ collagen which are considered to be____philic
|
retcular fibers/ type III collagen
argyrophilic |
|
|
THe most common GAG of connective tissue is
|
Hyaluronic Acid (unsulfated) important in cartilage
|
|
|
Type III (reticular CT ) collagen is found in
|
hemopoietic and lymphatic organs
|
|
|
Other glycoproteins (besides GAGs) that can be found in the ground substance include
|
fibronectin, chondronectin, laminin
|
|
|
How can you distinguish Elastic Fibers in H&E
|
stain brighter pink than collagen and are more branched or wavy
shinier than smooth muscle |
|
|
How does the interstitial fluid get around the cells to make up the ECM
|
blood vessels travel in the connective tissue and the fluid leaves the circulatory system and flows around the cell, maintained by hydrostatic and colloid osmotic pressure
|
|
|
Name four functions of the ground substance
|
fills space b/w cells and fibers
-acts as a physical barrier -acts as modulator for cell functions such as growth -Contain/house proteoglycans (GAGs) |
|
|
What is a GAG?
|
tthe main CHO compent of proteoglycans
glycosaminoglycans A polysaccharide which contains amino sugars example: chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, keratan sulfate (most are basic/highly sulfated ) Exception is the acid gag hyaluronate (or hyaluronic acid) |
|
|
THe most common GAG of connective tissue is
|
Hyaluronic Acid (unsulfated) important in cartilage
|
|
|
Other glycoproteins (besides GAGs) that can be found in the ground substance include
|
fibronectin, chondronectin, laminin
|
|
|
How does the interstitial fluid get around the cells to make up the ECM
|
blood vessels travel in the connective tissue and the fluid leaves the circulatory system and flows around the cell, maintained by hydrostatic and colloid osmotic pressure
|
|
|
Most GAGs are (positive/negatively) charged and the expection is ____which is not as large as a (-/+) charged GAG and also not
|
Negatively charged
exept Hyaluronic acid which has much less of a - charge and is nonsulfanated |
|
|
The Cartilage ECM contains proteoglycan aggregates and the _______makes the cartilage resilient and compressible
|
negatively charged hydrated GAGS
|
|
|
Mesenchymal CT is only found in the _______
|
embryo
|
|
|
What are the mesenchymal cells present in adults (stem cells)
|
Pericytes and Satelite cells
|
|
|
What is the shape of pericytes and/or satelite cells
|
spindle-shaped with a large vesicular nucleus
|
|
|
What is the most abundant connective tissue found in the body
|
loose irregular CT
|
|
|
Loose Irregular CT conaints ___fiber types in a _____arrangement and can be described as a strong/delicate/ rigid/flexible) tissue
Examples of Loose Irregular CT |
all fiber types (collagen most obvious and abundant)
Loose arrangement -delicate and flexible Superficial fascia, mesenteries, lamina propria of gut |
|
|
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue is found where and more ___than loose irregular
|
found in dermis, organ capsules, capsule of adrenal gland, and has fibers more densely packed
|
|
|
Dense Regular CT is arranged _____ and has ____cells flattened b/w the fibers
Examples of Dense Regular CT includes |
Fiber arranged in a regular, parallel manner, contains fibrocytes (mature fibroblasts)
ex: Tendons, ligaments, and aponeuroses, eye (sclera and cornea) |
|
|
Does dense regular CT have a rich or poor blood supply and innervation
|
poor blood supply
|
|
|
Dense Regular Elastic CT tends to be more___ and similar to dense regular except for ___fibers. Examples include
|
more wavy, has elastin fibers
Found in nuchal ligament and aorta |
|
|
In adipose tissue the main cell you would see on a H&E slide would be a(an)____
|
adipocyte
|
|
|
How would you describe the arrangement of adipose tissue
|
cells arranged singly, in clusters or in masses.
Adipocytes have a basal lamina**** |
|
|
Brown adipose tissue is associated with and can be distinguished by
|
active energy metabolism
rich in mitochondria and capillaries with relatively large nucleus |
|
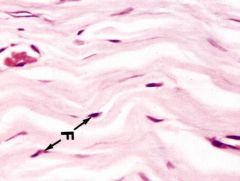
F = ?
|
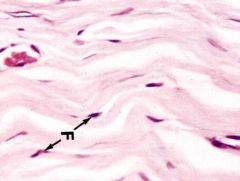
Fibroblast
|
|
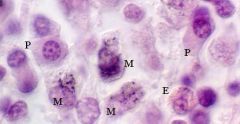
macrophage
|
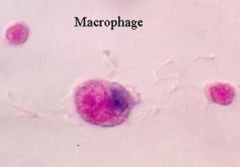
marcrophage
|
|
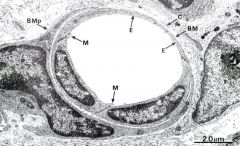
pericyte (holding capillary cell/ surrounding it)
|
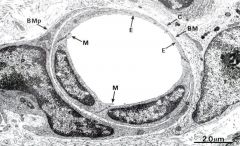
|
|
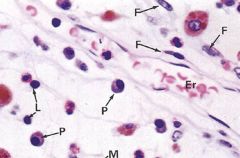
plasma and lymphocyte
|
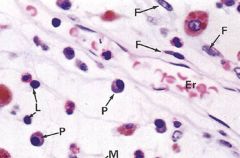
plasma and lymphocyte cell
|

