![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How is TB transmitted?
|
TB transmitted via respiratory droplets.
|
|
|
What does a positive Mantoux or time test indicate?
|
A positive Mantoux or tine test indicates TB infected the person at some time.
|
|
|
How has TB treatment changed?
|
TB treatment now requires antibacterial susceptibility testing to find effective drugs. Treatment is usually with triple antibiotic therap for six months to two years.
|
|
|
Describe the pseudomembrane caused by diphtheria.
|
The pseudomembrane, which forms in the pharynx, can cause asphyxiation. It should not be removed because of the risk of bleeding to death.
|
|
|
What is unusual about the morphology of Bordetella pertussis?
|
Bordetella pertussis is a coccobacillus
|
|
|
Who is most susceptible to pertussis?
|
Young children are most susceptible to pertussis.
|
|
|
How is pertussis recognized?
|
Pertussis can be recognized by the paroxysmal sound when coughing stops long enough for inspiration/
|
|
|
What does a paroxysm cause?
|
A paroxysm causes the whooping sound that occurs when coughing must stop for oxygen replacement by a stressful inspiration.
|
|
|
What two systems are used to classify the streptococci?
|
Two systems used to classify the streptococci are Lancefield's C carbohydrate grouping (A,B,C, etc) and by hemolysis type.
|
|
|
What are the common, significant sites of human infection by the streptococci?
|
The common, significant sites of human streptococcal infection are throat, oral cavities, vagina, and intestines.
|
|
|
In what relatively new site is group B strep (Strep agalactiae) found today?
|
Group B strep (Strep. agalactiae) is now found in the human vaginal tract.
|
|
|
Which people are at risk for which diseases from group B strep?
|
Newborns are at risk for septicemia and meningitis from group B strep.
|
|
|
What color will viridans strep produce on blood agar? What particular dz does viridans strep cause?
|
Viridans strep will produce a greenish tinge on blood agar. Viridans strep causes subacute endocarditis.
|
|
|
What chemical component of the cell wall is used to differentiate the above streptococci?
|
C carbohydrate is used to diff. streptococci
|
|
|
What relation does the pneumococcal (Strep. pneumoniae) capsule have to virulence?
|
Virulence: only encapsulated strains are virulent
|
|
|
relation of pneumonococcal capsule to number of time an indiv can acquire pneumococcal pneumonia
|
ninety times because they are ninety serovars
|
|
|
What are the epidemiology and pathology of the pneumococcus?
|
Pneumococcus is spread from human to human. Infections cause a pus-like exudate and fluid accumulation in the lungs. X rays and rusty sputum help in dx. Death by drowning occurs, since the lungs fill with fluid
|
|
|
How should infection with the pneumococcus be prevented?
|
Infection with the pneumococcus can be prevented with Pneumovax (vaccine), but immunity lasts only five years. Booster shots are recommended if no hypersensitivity develops
|
|
|
Two unusual characteristics about Mycoplasma cell envelopes
|
Two unusual characteristics about Mycoplasma cell envelopes are that the cell has no cell wall (peptidoglycan layer) and membranes that contain sterols.
|
|
|
Describe how to diagnose the disease caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
|
The best diagnosis for Mycoplasma pneumoniae is to observe increasing titers of cold agglutinins that cause RBC agglutination at refrigerator temps.
|
|
|
Describe the source, symptoms, and at risk individuals for legionellosis. On what does Legionella pneumophila usually feed?
|
Sources for legionellosis are aerosols from lakes, streams, and cooling towers. The symptoms include respiratory distress. Individuals at risk are heavy smokers and drinkers. Legionella pneumophilia usually feed on amoebae.
|
|
|
How do contacts of meningitis pts protect themselves?
|
Health care workers and family contacts are at risk to acquire meningitis from patients and need prophylactic treatment with rifampin.
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of meningitis?
|
The most common cause is Hemophilus influenza. The organism was initially isolated from a flu patient, hence the influenza misnomer in the name. This gram-neg, pleomorphic, rod-shaped, aerobic organism requires carbon dioxide and some vitamins to grow. Untreated H. influenzae is 90 percent fatal, and, even with immediate treatment, one third of all pts have permanent mental damage.
|
|
|
How soon does treatment of meningococcal meningitis need to start?
|
Treatment of meningococcal meningitis needs to start stat.
|
|
|
How are C. pneumoniae cultured?
|
C. pneumoniae cannot be grown on bacterial media but must be grown inside of human cells in culture. They cannot produce their own ATP and must acquire it from the host cell; hence, they are obligate intracellular pathogens.
|
|
|
Practice sketching and labeling the five layers of the cell envelope of Streptococcus pyogenes (group A strep)
|
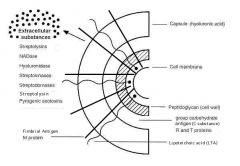
|
|
|
What virulence activities are associated with each of these layers? What virulence activities are associated with the major toxins?
|
C carbohydrate prevents lysozyme from lysing the cells; the M protein, which displays ninety types, is an attachment factor and antiphagocytic; the hyaluronic acid capsule masks bacteria, since it is also a human polysaccharide; and streptolysins damage the membrane of heart cells and white blood cells (WBCs),
|

