![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define cartilage and the components that make up cartilage
|
def= a dense supportive connective tissue
consists of cells (chondrocytes), fibers, and ground substance |
|
|
Fibers + ground substance make up the
|
ECM = extracellular matrix
|
|
|
Cartilage is vascular/ avascular
|
avascular, no capillary bed
|
|
|
Three types of cartilage
|
hyaline, fibrocartilage, elastic cartilage
|
|
|
name examples of hyaline cartilage
|
developing bones, growth pate, articular surfaces, respiratory tract
|
|
|
fibrocartilage can be found in
|
intravertebral disks, cardiac skeleton, wher some tendons and muscle attach to bone
|
|
|
elastic cartilage can be found in the
|
epiglottis, pinna (part of your outer ear)
|
|
|
chondrocytes
|
mature cells w/in spaces in the cartilage ECM
-can be single or in isogenous groups maintain cartilage |
|
|
Chondroblasts
def- differentiated from- produce- appearance- life cycle- |
cells that produce cartilage
mesenchymal cartilage matrix rounded wiht basophili cytoplasm become chondrocytes once they are surrounded by ECM |
|
|
Lacuna
|
space in the ECM occupied by the chondrocyte
|
|
|
What is a valuable clue for identifying cartilage tissue
|
lacunae
|
|
|
Chondrocytes do or do not communicate with one another
|
Do not communicate, are isolated
|
|
|
Ground substance constituents include
|
Proteoglycan aggregates containing GAGs
Hyaluronic acid in small amounts |
|
|
Ground substance has an affinity for _____. Proteoglycans absorb ____x their dry wt in interstitial fluid
|
affinity for water
50x |
|
|
___charge of GAGs adn proteoglycans aids in resiliency of the tissue (repelling each other)
|
Negative charge
|
|
|
How do chondrocytes get their needed nutrients?
|
Chondrocytes depend on diffusion of nutrients and waste products through the extracellular matrix. Cartilage is avascular and chondrocytes do not contact one another
|
|
|
Describe the characteristic of the ECM and how this is intertwined wiht proteoglycan aggregates
|
The extracellular matrix is sponge-like. The proteoglycan aggregates hold extracellular fluid which can be squeezed in and out of the cartilage
|
|
|
Perichondrium is what type of connective tissue
|
dense irregular CT surrounding cartilage in some places
|
|
|
The ____layer of the perichondrium is chondrogenic. The ____layer is typical fibrous connective tissue
|
inner layer is chondrogenic (cells of inner layer are chondroblasts resembling fibroblasts)
outer layer is typical fibrous CT |
|
|
________is NOT present on articular cartilage
|
perichondrium
|
|
|
Perichondrium is not identifiable around ______b/c _____is always found with dense connective tissue
|
fibrocartilage
|
|
|
Peri means
|
around
|
|
|
What are the two types of way cartilage can grow
|
appositional or interstitial
|
|
|
Describe appositional growth
|
new cartilage is deposited on the surface of existing cartilage under the perichondrium.
Chondroblasts in the inner layer of the perichondrium become trapped by their own products to become chondrocytes. |
|
|
Describe interstitial growth
|
the cartilage tissue can expand from within the tissue.
Chondrocytes within the cartilage can also divide and produce more cartilage. |
|
|
isogenous groups indicate____growth
Result from division of _____ Seen as clusters of _____ |
Interstitial
chondrocytes in lacunae 2 or more lacunae in close proximity |
|
|
Hyaline cartilage
-ECM contains what type of fibers -has ____staining ground substance |
fine collagen fibers (type II)-bot resolvable with LM
ECM has glassy (homogeneous) appearance Basophilic ground substance |
|
|
How are chondrocytes found/ organized/ arranged in hyaline cartilage?
|
Chondrocytes occur singly or in clusters (isogenous groups) and are randomly arranged in hyaline cartilage (with the exception of the zones of the growth plate of growing bone, and the zones of articular cartilage).
|
|
|
Articular cartilage is a specialized type of _____cartilage to reduce friction
|
hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
Elastic cartilage is found places where flexibility is needed
|
Epiglottis
External ear Eustacian (auditory) tube |
|
|
what would differentiate hyaline cartilage of the trachea from elastic cartilage of the epiglottis, when stained with hematoxylin and eosin and viewed with a light microscope?
|
Difference in the consistency of the extracellular matrix.
(presence of elastic fibers in ECM) |
|
|
Fibrocartilage has an abundance of ___fibers
|
large collagen
|
|
|
What is the most abundantly found cartilage in the body
|
Hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
Will see fibrocartilage develop in
|
tendons and ligaments and some intervertebral disks
|
|
|
How would you describe the cells of fibrocartilage
|
rounded cells in lacunae, arranged in rows b/w colagen fibers
|
|
|
How can you distinguish fibrocartilage form dense regular collagenous CT?
|
look for round cells in lacunae to indentify fibrocartilage
|
|
|
Can find fibrocartilage in __tissues
Look for ____pattern |
pubis symphysis
cardiac skeleton intervertebral disk cardiac skeleton herringbone |
|
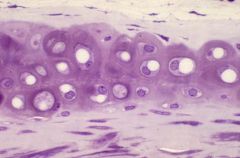
hyaline
|
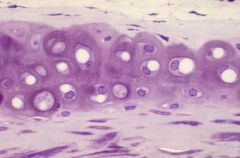
Hyaline
|
|
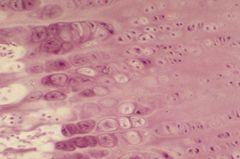
The space containing a cartilage cell is called a ___
|
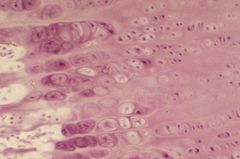
lacunae
|
|
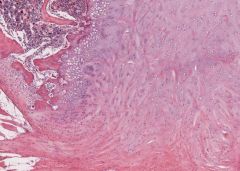
fibrocartilage
|
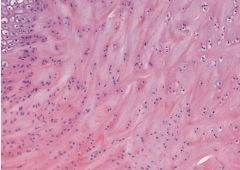
zoomed in
|
|
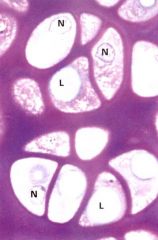
lacunae
|
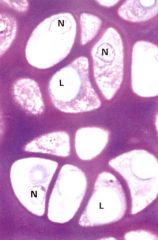
lacunae
|
|
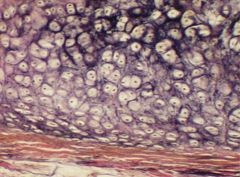
isogenous groups
|
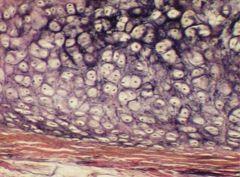
isogenous groups- cells bound together
|
|
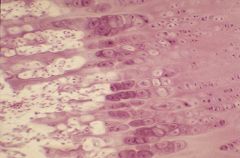
identify this tissue section
|
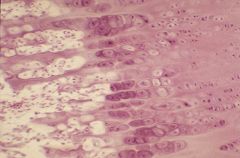
growth plate
|
|
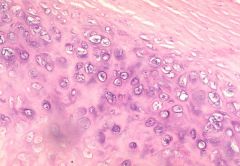
Find the perichondrium
|
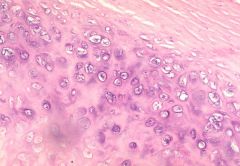
upper right hand corner of slide
|
|
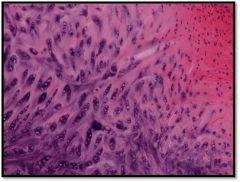
darker stained fibrocartilage
|
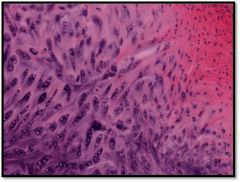
darker stained fibrocartilage
|

