![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
157 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
monomorphic encapsulated yeast responsible for meningitis in immunocompromised patients
|
cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
|
gram-positive cocci that is the MCC of adult meningitis
|
s. pneumoniae
|
|
|
what is the only test able to detect HIV infection in newborns?
|
PCR
|
|
|
in relation to HIV, what does RT-PCR test for and what is its usefulness?
|
"-circulating viral RNA
|
|
|
what serologic test is used for initial screening of HIV?
|
ELISA or latex particle agglutination
|
|
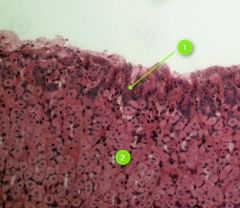
what serologic test is used for CONFIRMATION of HIV infection?
|
western blot -or- immunofluorescence
|
|
|
what test is used to detect HIV virus in blood (AKA the viral load)?
|
RT-PCR
|
|
|
what test is used to detect HIV infection in newborns?
|
PCR
|
|
|
what is tested as an early marker of HIV infection?
|
p24 antigen
|
|
|
what is tested to evaluate progression of HIV disease?
|
CD4:CD8 T-cell ratio
|
|
|
transduction
|
delivery of bacterial genes from one bacterium to another via a virus vector (phage)
|
|
|
what is specialized transduction?
|
mech of transfer of DNA that results from an error in life cycle of temperate virus (ex virus that infects w/o lysing cells)
|
|
|
how and where do temperate phages introduce their genomic DNA?
|
"-into the bacterial chromosome @ a SPECIFIC site
|
|
|
which genes are mostly likely to be transferred by specialized tranduction?
|
those closest to insertion site of phage
|
|
|
a gene closest to oriT on a bacterial genetic map would be transferred during which event?
|
conjugation of the bacterial cell (an Hfr cell) with an F- cell
|
|
|
a gene on a bacterial genetic map that is close to the IS (insertion sequence) would be transferred during which event?
|
specialized tranduction with a temperate (lysogenic) phage
|
|
|
how does specialized transduction differ from generalized transduction?
|
"specialized=""exision error""
|
|
|
pseudomonas aeruginosa is responsible for which infections?
|
"-secondary wound infections/septicemia (burn patients)
|
|
|
a burn pt develops septicemia and erythematous vesicles around burned areas that become hemorrhagic, necrotic, & ulcerated. what is this condition, the causative agent, and the product that is responsible for the formation of these lesions?
|
"-ecthyma gangrenosum asst'd w/ Pseudomonas septicemia
|
|
|
functions of Pseudomonas capsule during infection
|
"-adherence to epithelial cells
|
|
|
function of endotoxin (LPS) and location
|
"LOCATION: outer membrane gram - bact
|
|
|
function of pili
|
binding to epi cells
|
|
|
what is pyocyanin & its function?
|
"blue pigment produced by P. aeruginosa
|
|
|
how do major types of viral genomes make mRNA for protein synthesis?
|
|
|
|
what is the antibiotic property of vancomycin?
|
binds D-ALA-D-ALA that is vital for synth of peptidoglycan peptide bridges
|
|
|
how do vancomycin-resistant enterococci b/cm resistant?
|
utilize D-lactic acid in their peptide bonds instead of D-ALA-D-ALA
|
|
|
what is a common mode of resistance for aminoglycosides, chloramphenicol, and sulfonamides?
|
enzymatic deactivation: most commonly chemical modifications like acetylation, adeylation, & phosphorylation
|
|
|
which drugs undergo enzymatic deactivation during bacterial resistance?
|
aminoglycosides, chloramphenicol, and sulfonamides
|
|
|
how does penicillin resistance occur?
|
alteration of affinity or number of penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) in cell membrane
|
|
|
beta lactamase is a bacterial enzyme that inactivates which drugs with antibiotic resistance?
|
penicillins & cephalosporins
|
|
|
which drugs are affected by bacterial resistance via decreased ribosomal binding of antibiotic?
|
"protein synthesis inhibiting antibiotics:
|
|
|
gram + cocci on bile esculin agar ID what?
|
group D streptococci
|
|
|
how is vancomycin resistance acquired?
|
plasmids
|
|
|
how does the vancomycin resistance gene work?
|
"-encodes a ligase that produces a cell-wall pentapetide that terminates in D-ALA-D-LAC (instead of D-ALA-D-ALA)
|
|
|
what causes acute bacterial endocarditis?
|
S. aureus
|
|
|
what is the organism that is gram +, catalase positive, coagulase positive cocci in grapelike clusters
|
S. aureus
|
|
|
acute bacterial endocarditis is most commonly found in which types of patients?
|
intravenous drug users
|
|
|
which areas is most commonly affected by acute bacterial endocarditis?
|
tricuspid valve
|
|
|
in infectious mononucleosis the EBV virus infects which cells via what receptor? are these cells found on blood film?
|
"b lymphocytes via CD21 receptor
|
|
|
what are Downey cells and which infection are they seen with?
|
"-infectious mononucleosis
|
|
|
what is a resistance transfer factor?
|
bacterial plasmid that encodes drug-resistance genes & is capable of mediating its own tranfers to another bacterium during conjugation
|
|
|
how do resistance transfer factors accumulate multiple drug-resistant genes?
|
accumulating transposons carrying the drug-resistant genes
|
|
|
what are transposons?
|
mobile genetic elements that are capable of movement within bacterial cells
|
|
|
what do resistance transfer factors contain that aid in its transfer to other bacteria?
|
tra operon
|
|
|
what are the flanking sequences in the DNA of transposon, how do they insert themselves into the new location, what are the new flanking sequences in the new location created by?
|
"-indirect repeats that are complentary & antiparallel to each other
|
|
|
what are introns? who does not possess introns?
|
"repetitive, non-transcribed segments of DNA
|
|
|
what are responsible for formation of multiple drug-resistant plasmids?
|
mobile segments of DNA called transposons
|
|
|
what are insertion sequences? what are they composed of ? where are they found? how do they work?
|
"-points of bacteriophage insertion
|
|
|
gram +, coagulase - species are characterized as being
|
"novobiocin susceptible
|
|
|
which species is novobiocin susceptible? which is resistant?
|
"**on our office's STAPH retreat, there was NO StRES**
|
|
|
how can staph epidermidis be introduced into a pt?
|
"-catheter placement
|
|
|
what does bacitracin resistance distinguish between?
|
"*B-BRAS*
|
|
|
what does catalase production distiguish between?
|
"Staphylococcus (cat +)
|
|
|
what 2 medically important organisms with IV catheter infection does coagulase production occur?
|
"Staph. Aureus
|
|
|
what does optochin resistance differentiate between?
|
"the major pathogenic alpha-hemolytic streptococci
|
|
|
what do the clininal manifestations of fever, HA, & nuchal rigidity + CSF findings of ↑ neutrophils, ↑ prot, ↓ glu) suggest & what are the likely microorganisms?
|
"acute pyogenic (bacterial) meningitis
|
|
|
what is the most important pathogenic mech of S pneumoniae & its function? what else does it possess as a pathogenic mech?
|
"*polysaccharide capsule-protects against phagocytosis
|
|
|
which organisms have cytolysins?
|
"clostridium perfringens
|
|
|
what is the most common cause of meningtits in older pts?
|
S. pneumoniae
|
|
|
an HIV pt's blood was cultured and on EM this bacterium showed a envelope with this basic structure. what color does the gram stain show?
|
"this is a GRAM - bacteria
|
|
|
bacillary angiomatosis is found in which type of patient and what is the responsible organism?
|
"CAT SCRATCH FEVER-caused by bartonella henselae
|
|
|
what should you suspect in immunosuppressed pts with fungal meningitis?
|
cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
|
what are some distinguishing characteristics of cryptococcus neoformans?
|
"-budding encapsulated yeast
|
|
|
what should you think of in a pt who is an IVDU with vegetations on the tricuspid valve? most likely organism?
|
"infective endocarditis
|
|
|
what organism may cause infective endocarditis in a severly immuno comp pt?
|
fungal organisms (ex Cadida albicans)
|
|
|
which normal commensal organisms in the oral cavity may cause infective endocarditis?
|
"""HACEK"" group:
|
|
|
which organisms cause endocarditis in recipients of prosthetic valves?
|
"Coag - staph like
|
|
|
which organisms cause endocarditis in previously abnorm valves (damaged from RF) or with congenitally abnorm valves?
|
viridans strep
|
|
|
microorganisms that commonly cause bronchitis in smokers?
|
"H influenzae
|
|
|
what type of org is H influenzae?
|
"encapsulated
|
|
|
which organism causing bronchitis in smokers does not gram stain well?
|
legionella
|
|
|
which organism causing bronchitis in smokers is a gram - cocci
|
moraxella
|
|
|
"what causes erythema infectiosum or ""5th disease""?"
|
parvovirus B19
|
|
|
what does exposing a pregnant woman to erythema infectiosum in her 1st trimester lead to?
|
"fetus with:
|
|
|
what is the organism asst'd w/ erythema infectiosum, transmission, pathogenesis, sx's?
|
"ORGANISM: parvovirus B19
|
|
|
what does exposure to varicella during pregnancy cause?
|
"congenital varicella syndrome:
|
|
|
congenital rubella syndrome causes
|
"patent ductus arteriosus
|
|
|
Schuffner dots on blood film are asst'd with what?
|
Plasmodium vivax & P. ovale
|
|
|
maltese cross formation in red blood cells, ixodes tick transmits, malaria-like symptoms
|
babesia microti
|
|
|
plasmodium that cause relapses following recovery from primary infection & reason for relapse
|
"P. vivax
|
|
|
plasmodium ID-d with Schuffner dots on blood film that is found in the northern hemisphere
|
P. vivax
|
|
|
what is floppy baby syndrome, cause?
|
"reversible flaccid paralysis in children under 1 yo
|
|
|
what molecules are unique to bacterial spores & what is the function both and individual funciton?
|
"dipicolinic acid & calcium dipicolinate
|
|
|
pathophys of this presentation?"
|
"PNEUMOCYSTIS JIROVECI
|
|
|
asst'd organism with ecthyma gangrenosum, toxin type and mech, primary target
|
"-Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
what organism causes cystercosis and neurocysticercosis? how is it acquired? which types of hosts are involved? what is the progression of the dz?
|
"ORG: larval cysts of tapeworm Taenia solium
|
|
|
which toxin has similar action to Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin and what are the target cells?
|
"diphtheria toxin
|
|
|
toxin type and effect for cholera toxin
|
> adenylate cyclase activity by ribosylation of GTP-binding prot
|
|
|
toxin type and effect for clostridium perfringens
|
"alpha toxin
|
|
|
toxin type and effect for anthrax toxin:
|
"-adenylate cyclase
|
|
|
toxin type and effect for botulinum toxin
|
"neurotoxin
|
|
|
toxin type and effect for E coli labile toxin
|
similar to cholera toxin: > adenylate cyclase activity by ribosylation of GTP-binding prot
|
|
|
toxin type and effect for pertussis toxin
|
"ribosylating Gi
|
|
|
toxin type and effect for shigatoxin
|
< prot synth by inhibiting 60S ribosomal SU
|
|
|
toxin type and effect for strep erythrogenic toxins
|
"similar to diphtheria toxin (neurotoxin)
|
|
|
toxin type and effect for tetanus toxin
|
"neurotoxin
|
|
|
MC parasitic infection in US, age it is usually acquired, progression
|
"Toxoplasma gondii
|
|
|
what is the organism MC responsible for PSEUDOAPPENDICITIS in the US and how is it transmitted?
|
"Yersinia enterocolitica
|
|
|
Abscess formations in CP"
|
Staph aureus
|
|
|
Maj clinical features due to toxemia from this organism"
|
diphtheria bacilli (Corynebacterium diphtheriae)
|
|
|
bronchitis, bronchiolitis & pneumonia (adults)"
|
H. influenza
|
|
|
Sometimes implicated in subacute bacterial endocarditis (not asst'd w/ tonsillar abscesses)"
|
strep salivarius
|
|
|
MCC of pharyngitis"
|
strep pyogenes
|
|
|
Tx w/ fluoroquinolones"
|
"Proteus mirabilis
|
|
|
organism attribute most important in pathogenesis & its function"
|
"Neisseria gonorrhoeae
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
what occurs when 2 bacteria w/ different antibiotic resistances are cultured together & how?
|
"transfer of genes
|
|
|
suspect what in pt with gastroenteritis following ingestion of raw osters? how are these organism described?
|
"Vibrio vulnificus
|
|
|
what are erythromycin & theophylline used for? why can they not be used together?
|
"ERYTHROMYCIN=URI, potent inhibitor of CYP450 isoenz's
|
|
|
cell type diagnostic for HPV
|
koilocytes
|
|
|
micro finding diagnostic for herpesviruses
|
Cowdry-type inclusions
|
|
|
micro finding diagnostic for smallpox virus
|
Guarnieri bodies
|
|
|
micro finding diagnostic for rabies virus
|
Negri bodies
|
|
|
micro finding diagnostic for cytomegalovirus
|
Owl's-eye inclusions
|
|
|
RF's for pigment stones:
|
"chronic hemolytic anemias
|
|
|
Lg intestinal fluke that causes abdom pain, diarrhea, intestinal mucosal abscesses
|
Fasciolopsis buski
|
|
|
lung fluke that causes cough, bronchiectasis & hemoptysis
|
Paragonimus westermani
|
|
|
blood fluke that infects pelvic veins & may cause bladder dz (incl cancer)
|
Schistosoma haematobium
|
|
|
Beef intestinal tapeworm that may cause intestinal obstruction
|
Taenia saginata
|
|
|
"Gram + anaerobic rod that can cause cervicofacial (""lumpy jaw""), female reproductive or gastrointestinal mycetomas w/ sulfur granules"
|
Actinomyces israelii
|
|
|
Organism asst'd w/ female pt w/ IUD
|
Actinomyces israelii
|
|
|
contains cytoxin-asst'd gene A (CagA) & type III secretory system
|
H. pylori
|
|
|
asst'd w/ gastric/peptic ulcer, chronic gastritis, gastric lymphoma
|
H. pylori
|
|
|
EBV linked to which types of cancer?
|
"Burkitt lymphoma
|
|
|
HBV-C & B linked to which types of cancer?
|
primary hepatocellular carcinoma
|
|
|
HPV linked to which types of cancer?
|
cervical
|
|
|
3 distinct syndromes asst'd w/ this virus"
|
"PARVOVIRUSES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
coxsackie viruses cause
|
"USUALLY: coldlike illness
|
|
|
echoviruses infect which organ systems?
|
"GI
|
|
|
hepadnavirus causes
|
Hep B
|
|
|
herpesviruses cause
|
"HSV1 & 2
|
|
|
mumps causes
|
"parotitis
|
|
|
ssRNA"
|
mumps
|
|
|
virus that produces multinucleated giants cells (AKA syncytia)
|
mumps
|
|
|
why are antibodies against mumps ineffective?
|
"syncytia formation-->virus is not exposed outside of cell
|
|
|
what is a common complication of measles infection? what is found in a sputum sample?
|
"giant-cell pneumonia
|
|
|
name the dz's caused by e coli & their pathogenesis
|
|
|
|
inhibition by bacitracin"
|
Strep pyogenes
|
|
|
most likely cause of glomerulonephritis following sore throat
|
Strep pyogenes
|
|
|
organism causing pharyngitis followed by RF
|
strep pyogenes
|
|
|
lysed by bile"
|
strep pneumoniae
|
|
|
not lysed by bile"
|
strep mutans
|
|
|
grows on 40% bile & 6.5% NaCl"
|
enterococcus faecalis
|
|
|
CAMP +"
|
strep agalactiae
|
|
|
malignant transformation of HPV is related to ?
|
early proteins E6 & E7 that leads to inactivation of tumor-suppressor genes p53 & pRb
|
|
|
& characteristic cells"
|
"HPV
|
|
|
Name & asst'd organism
|
"A. Cowdry inclusion body; HSV
|
|
|
Tx is sulfadiazine & pyrimethamine"
|
toxoplasmosis
|
|
|
MCC ring-enhancing lesions in AIDS
|
"primary brain lymphoma
|
|
|
-<2yo; young adults-elderly"
|
|
|
|
-tx"
|
|
|
|
how does herpes zoster arise? in which pts does it typically present? what can it progress to?
|
"-reactivation of dormant varicella zoster virus
|
|
|
MCC lobar pneumonia in adults; characteristics; treatment
|
"Strep pneumoniae
|
|
|
what antibiotic has limited absorption when taken with iron &/or calcium? which OTC drugs should be avoided with this specific drug type?
|
"quinolones (ofloxacin)
|
|
|
group D strep whose cell wall contains glycerol teichoic acid & is asst'd w/ colon cancer & endocarditis
|
Strep bovis
|
|
|
#1 cause of neonatal meningitis & septicemia"
|
S. agalactiae
|

