![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Capping
|
. |
|
|
|
Alternate RNA splicing |
Exons of the RNA (1° transcript) are spliced together with out the introns |
|
|
|
Poly-adenlation |
addition of 200 AMP |
|
|
|
mRNA |
1 transcript +cap + spliced +ploy-adenylation |
|
|
|
eIF4G |
eIF4G + CAP = initiation of translation |
eukaryotic initiation factor |
|
|
Glycosylation |
oligosaccharides are added |
|
|
|
NANA |
N-acetyl neuraminic acid / sialic acid terminal sugar |
- charge, -surface area charge, added at the golgi |
|
|
Protein structure |
1 - a.a. sequence 2 - localized folding - αhelix βpleated sheet 3 - Hbonds 4 - multiple subunits - disulphide bonds |
|
|
|
Protein domain |
part of a protein that has its own 3° structure |
|
|
|
Protein family |
related evolutionarily similar 1°, 2°, 3°, structure and function |
evolution occurs when gene is duplicated, and one evolves |
|
|
Protein Superfamily |
Related evolutionarily similar 2°, 3°, structure |
MFS, ABC, Ig |
|
|
Electrophoresis |
Agarose = DNA fragments SDS-PAGE = proteins |
by size and weight |
|
|
SDS-PAGE |
sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
-charged detergent, denatures and coats proteins |
|
|
DTT |
dithiothreitol |
breaks disulfide bonds |
|
|
SDS + DTT |
denatures proteins, separates subunits, uniform charge |
|
|
|
Ligand |
specific extracellular signaling molecules |
binds to a specific site on a receptor, changes expression of genes |
|
|
Cytokines |
protein signaling moecule that regulate duration and intensity of immune response |
synthesized and secreted by leukocytes |
|
|
Interleukins |
secreted by leukocytes |
|
|
|
chemokines |
chemoattractant cytokine that attracts phagocytes and lymphocytes |
aid in adhesion |
|
|
Interferons |
interfere with viral replication, binds to interferon receptors |
|
|
|
Antigen |
substance that can be recognized by the adaptive immune sys. as foreign |
|
|
|
Hematopoiesis |
differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells into blood cells |
|
|
|
Immunocompetent |
immature lymphocytes that mature in primary lymph organs |
|
|
|
B cells |
bone marrow |
|
|
|
T cells |
Thymus |
|
|
|
Secondary lymph organs |
traps antigen, holds lots of B and T cells, prodces adaptive immune response (to eliminate antigen) |
lymph nodes spleen mucosa associated lymph tissue |
|
|
MALT |
antigens on mucosal surfaces in lungs, digestive tract, rogenital sys. |
mucosa-associated lymph tissue: peyers patches, tonsils, appendix |
|
|
Microfold (M) cells |
epithelial cells in peyers patches folds, and pockets full of B&T & dendritic, macrophage cells, |
|
|
|
Transcytosis |
endocytise antigen from intestinal lumen and released into pocket of M cells |
adaptive immune respone to antigen |
|
|
Lymphatic circulation |
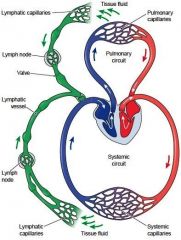
|
|
|
|
Extravasation |
movement of leukocytes from unruptures blood vessels into tissues |
normal or in response to signal |
|
|
Extravasation Steps; |
1) Rolling adhesions 2) Tight bingding 3) Diapedesis 4) Migration |
differs in the proteins being used |
|
|
Neutrophils |
engulf bacteria and destroy circulate in blood |
first phagocyte to arrive in tissue
|
|
|
Rolling adhesion |
endothelium expresses adhesion molecules |
selectin CXCL8 |
|
|
Selectin |
binds weakly to the surface, slows the rolling of cells |
|
|
|
CXCL8 |
chemokine on surface, binds to neutrophils receptor CXCL8R |
produced by macrophage in response to infection |
|
|
Tight binding |
binding of CXCL8 causes conformational change, in neutrophil surface protein, integrin |
integrin binds tightly to ICAM of blood vessels endothelium |
|
|
Integrin |
attaching the cell cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix |
|
|
|
ICAM |
Ig-superfamily cell adhesion molecule
|
|
|
|
Diapedesis |
the passage of blood cells through the intact walls of the capillaries |
|
|
|
Migration |
up a gradient of chemoattractants (CXCL8/C5a) to the site of infection |
movement from one place to another
|
|
|
Innate immunity |
wide range of pathogens 1st line: (prevents colonization and entering tissues) mechanical, chemical |
2nd line: (adaptive immunity) alternative/lectin pathways, phagocytes inflammation |
|
|
Skin |
Physical: dead epithelial cells w keratin |
Chemical: NaCl lowers aw, lysozyme (lyses peptidoglycan of gram+), sebaceous glands sectrete sebum (fatty acis lower pH) |
|
|
Mucous membranes |
glycoproteins over epithelial Physical: traps particles turbulent air flow tears, saliva |
Chemical: lysozyme lactoferrin antimicrobial peptides - defensins |
|
|
Defensins |
+charged peptides (30 a.a. w/ disulfide bonds) disrupt -charged cell membrane |
gives lysozyme access to peptidoglycan |
|
|
2nd line defense |
complement system phagocytes inflammation |
|
|
|
Adaptive immunity |
classical complement sys. phagocytes/lymphocytes eliminates infection recognize infections |
|
|
|
Complement sys. |
produce C3 converase |
|
|
|
Alternative Pathway |
bindint to carbohydate on pathogen surfaces |
|
|
|
LectinPathway |
lectins bind to carbohydrates |
|
|
|
C3 convertase |
C3 -> C3a + C3b |
|
|
|
C5 convertase |
C5 -> C5a + C5b |
|
|
|
MAC |
membrane attack complex |
|
|
|
Opsonin |
binds to pathogen cells and phagoctes |
|
|
|
Anaphylatoxin |
. |
|
|
|
Vasodialation |
. |
|
|
|
Edema |
. |
|
|
|
Mast cells |
. |
|
|
|
Defensins |
+charged peptides (30 a.a. w/ disulfide bonds) disrupt -charged cell membrane |
gives lysozyme access to peptidoglycan |
|
|
Macrophage |
mature monocytes |
|

