![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
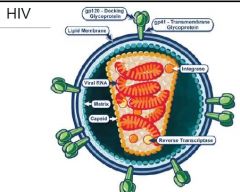
HIV. Name the 3 main protiens associated
|
|
|
|
HIV. Describe the following proteins
1. gp120 2. gp41 3. p24 (gag) 4. p17 5. pol |
gp120 → docking glycoprotien
gp41 → Transmembrane protein p24 → Capsid protein p17 → matrix protein pol → Reverse Transcriptase |
|
|
HIV binds to on
`1. T cells (2) 2. Macrophages (2) |
1. CXCR4 & CD4
2. CCR5 & CD4 |
|
|
HIV 4 stages of Infection
1. Pneumonic 2. During what phase does replication occur? Where? |
Four Fs
Flulike (acute) Felling Fine (latent) Falling Count Final Crisis 2. Latent phase in Lymph Nodes |
|
|
For HIV Infection, with the following CD4 counts, think of what BUG
1. CD4 < 400 2. CD4 < 200 (3) 3. CD4 <100 (3) 4. CD4 < 50 (3) |
1. C. albicans (oral)
2. JC virus, Cryptosporidium spp. & Pneumocystis jirovecci 3. C. a;bicans (Esophageal), Histoplasma capsulatum & Toxoplasma gondii 4. Cryptococcus neofromans, CMV (retiniti) MAC |
|
|
For HIV, name the SYSTEMIC Clinical Presentation & Findings/Labs for:
1. Histoplasma capsulatum (4 & 2) |
1. Low-Grade feverm Cough, hepatosplenomegaly & Tongue Ulcer
2. Oval yeast cells w/in Macrophages & CD4<400 |
|
|
For HIV, name the DERMATOLOGIC Clinical Presentation & Findings/Labs for:
1. C. albicans- (2 & 3) 2. Bartonella genselae (2 & 1) |
1a. Thrush & Fluffy White Cottage-Cheese lesions
1b. Pseudohyphae. CD4<400 → oral & CD4 <100 → Esophageal 2a. Superficial vascular proliferation & Bacillary angiomatosis 2b. Neutrophilic inflammation on biopsy |
|
|
For HIV, name the GASTROINTESTINAL Clinical Presentation & Findings/Labs for:
1. Cryptosporidium spp (2 & 2) |
1a. CHRONIC & WATERY diarrhea
1b. CD4 <200 & Acid-Fast cysts |
|
|
For HIV, name the NEUROLOGIC Clinical Presentation & Findings/Labs for:
1. JC virus reactivation (2 & 2) 2. Toxoplasma gondii (1 & 2) 3. Cryptococcus neoformans (2 & 3) 4. CMV (1 & 3) 5. Directly associated w/ HIV (1 & 1) |
1a. PML & Encephalopathy
1b. CD4 < 200, reactivation of latent virus & demyelination 2a. Abscesses 2b. CD4 < 100 & Ring enhancing lesions on IMAGING 3a Encephalitis & Meningitis 3b. CD4 < 50 & India Ink Stain → Yeast w/ narrow based budding & large capsule 4a. Retinitis 4b. CD4 < 50, Cotton Wool spots on fundoscopic exam & Esophagitis 5a. Dementia 5b. rule out Other causes |
|
|
For HIV, name the ONCOLOGIC Clinical Presentation & Findings/Labs for:
1. HHV-8 (2 & 2) 2. EBV (2 & 2) 3. May be associated w/ HBV (2 & 2) 4. Often associated w/ EBV (1 & 3) 5 HPV (1 & 2) |
1a Karposi Sarcoma & Superficial NEOPLASTIC proliferation of vasculature
1b, LYMPHOCYTIC inflammation on biopsy 2a. Hairy leukoplakia 2b. Lateral tongue 3a. NHL, large cell type 3b. Oropharynx w/ Waldeyer's ring 4a. Primary CNS lymphoma 4b. Focal or Mulriple (differentiate vs. toxoplasmosis) 5a Squamous cell carcinoma 5b Anus (MSM) & Cervix (females) |
|
|
For HIV, name the RESPIRATORY Clinical Presentation & Findings/Labs for:
1. CMV (1 & 2) 2. Aspergillus fumigatus (3 & 1) 3. Pneumocystis jiroveci (1 & 1) 4. MAC (avium & intraceukkulare) (1 & 1) |
1a. Interstitial pneumoniae & 1b. 1b. Owl's eye intranuclear inclusion bodies o BIOPSY
2a. Invasive asoergillosis 2b. Pleuritic pain, Hemoptysis & Infilitrate on Imaging 3a. Pneumoniae 3b .CD4 < 200 4a Tuberculosis like disease 4b. CD4 < 40 |
|
|
HIV in the USA
1. #? 2. Letter? |
1. HIV-1
2. HIV - B |
|
|
HIV
1. Family 2. Nucleic Acid 3. Baltimore Class |
1. retrovirus
2. 2 copires of +ss RNA w/ Reverse Transcriptase 3. Group VI |
|
|
For Retroviruses, name the characterestics & examples associated w/
1. Oncovirinae B 2. Oncovirinae C 3. Oncovirinae D 4. Lentivirinae 5. Spumavirinae 6. Endogenous viruses |

|
|
|
Retroviruses
1. Simple Retrovirusus encode what genes (3) 2. COMPLEX (5) 3. Lentiviruses associated w/ (2) |
1. Gag, Pol & Env
2. tat, rev, nef, vif & vpu 3. Neurological & Immunosupressive disease |
|
|
Retrovirusus. Encode for
1. gag (froup specific antigen) (2) 2. Pol: polymerase (3) 3. Env: envelope (1) |
1. Core & Capsid protiens
2. Reverse Transcriptase, Protease & intergrase 3. Glycoproteins |
|
|
Retroviruses
1. 2 copies of (+) RNa are 2. Provirus is formed by? 3. Intergrated into? by? 4. What are viral m RNA |
1. non-infectious
2. Reverse Transcripatse 3. Host genome, by intergrase 4. non-structural 7 structura proteins |
|
|
HIV. Characterestics
1. 2 copies of 2. Orfs 3. Proteins |
1. Genome
2. 9 3. 15 |
|
|
HIV.
1. Name the 3 main genes 2. 4 accessory genes 3. Name the regulatory genes & role |
1. Gag, Pol & Env
2. vif, vpr, vpu & nef 3. TAT→ Transactivating protein → Regulates cellular genes REV→ RNA splicing & Exporting to Cytoplasm |
|
|
Name the SEVEN steps in the HIV life cycle
|
1. Fusion
2. Entry 3. Viral DNA via RT 4. Viral DNA:transport to nucleus, intergration 5. New vRNA → genomic RNA, viral proteisn 6. New vRNA + proteins move to cell surface→ new, immature, HIV virus 7. Virus matures by protease releasing HIV proteins |
|
|
HIV what is required for
1. Budding & Fusion 2. Formation of viral DNA 3. Transport into the nucleus membrane & addition into genome 4. Transcription (Provirus → mRNA) 5. Required for assembly |
1. CD4 receptor w/ CCR5 or CXCR4
2. Reverse transcription 3. Intergrase 4. Host RNA polymerase 5. HIV protease |
|
|
HIV
1. When you from the ds DNA, type of interaction 2. Linked by 3. ds DNA is |
1. Kissing interaction
2. Dimer linkage 3. Is variant, d/t lack of proof reading |
|
|
HIV
1. transmission (2) 2. Vehicle (3) 3. Survival outside host |
1. Sexual contact & Needles
2. Blood, Semen & Vaginal Fluid\ 3. Rate |
|
|
HIV epi for Children <15 yrs & total, describe
1. People living w/ HIV 2. Newly infected 3. AIDS deaths |
1. 34.2 mill, 3.4 mil
2. 2.5 mil, 330, 000 3. 1.7 mil, 230, 000 |
|
|
HIV Epi
1. Spiked in the? 2. Since? d/t? 3. Which is the only region in the world to show a DECREASE in life expectancy, despite the introduction of ARVT 4. 3 countries with highest mortality 5. In adults 15 & older, of new HIV, almost 48% are? 6. 42% |
1. 90s
2. Decreasing d/t ARVT 3. CENTRAL africa 4. Bostwana, Zimbabwe & Swaziland 5. Women 6. 15-24 yrs old |
|
|
HIV Pathogenesis
1. MAJOR DETERMINANT (2) 2. Has also been found in what cells |
1. Tropism for CD8+ T-cells & Macrophages
2. Multipotent Hematopoietic Stem & Progenitor Cells |
|
|
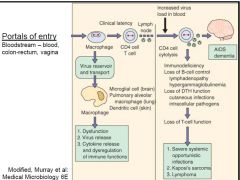
Desribe HIV pathogensis
1. Portal of Entry 2. Macrophage involvment 3. CD4 + T Cells |
|
|
|
HIV
1. Portals of entry 2. Virus resevoir 3. Clinical latency before 4. Clinical effects of macrophage (3) 5. CD4 + T cell lysis effects(5) 6. In brain 7. Loss of T cell function leads to |
1. blood, Colon-Rectum & Vagina
2. Macrophages 3. Invovlement of CD$ T cell 4. Dysfunction, Virus Release & Dysregulation of Immune functions (via cytokines 5. Lymphadenopathy, Loss of DTH fxn, Cutaneous infetions, Intracellular pathogens & Hyper-Ig-emia 6. Dementia 7. Severe systemic Opportunistic Infections, Karposi's sarcoma & Lymphoma |
|
|
AIDS when
|
1. CD4+T cells drop below a certain level, where oppurtunistic infections & Tumours occur
|
|
|
HIV Pathogenesis
1. Enters body via (2) 2. Carry virus to? Resulting in infection of 3. Resivour |
1. Macrophages & Dendrites
2. LN → CD4+ T cell infection 3. MACROPHAGES |
|
|
HIV-Pathogenesis
Mo Immune Evastion (5) |
1. Antigenic variation
2. Carb MASKING of target EPITOPEs 3. Comfirmational changes by ENVELOPe to MASK targets 4. Downregulation of host HLA 5. Latency in T-cells & APC |
|
|
HIV Encephalopathy & Dimentia
1. Inlcusion bodies (3) 2. Spread of virus via |
1. Macrophages & Mircoglia → Synctia
2. Cell → Cell 3. |
|
|
HIV diagnosis
1. Screening test (2) 2. Confirmatory test 3. Sample of (3) |
1. ELISA & antigen test vs. p24
2. Western Blot 3. Serum specimenes (from Venipuncture & Finger stick), Oral fluid, Urine & Fi |
|
|
HIV Treatement, Prevention & Control
1. Universal testing for 2. Prevention (2) 3. Trhearpy begins at what time 4. HAART contains (3) 5. Contains 6. Therapy length |
1. Prenatal
2. Condoms & Once daily pil 3. CD4+ Tcells < 350 4. Protease inhibitor & 2 nucleoside RT inhibitors 5. RNA level below ASSAY DETECTION limits 6. LIFE LONG |
|
|
HIV patients w/o THERAPY
Progression 1. 80% 2. 5-10% 3/ 10-15% |
1. Typical → 7-10Yrs
2. Rapid → w/in 2 years 3. NON →7-10+yrs (CD$ count high |
|
|
Course of HIV progression
1. Clinical Latency = 2. If HIV test 3. |
1. Winrdow Period
|
|
|
Final Stage of HIV infection
1. What has happened 2. Indicators of AIDS (3) |
1. Virus has weakened the immune system, so can not defend vs infection
2. 1 or More specific infections, Certain cancers &/or very low # of Tcells |
|
|
Name the FIVE starges of AIDS progression
|
1. Acute Infection
2. Strong anit-HIV immune defense 3. A latent resevoir 4. loss of CD4+ T cells & Immune response 5. Onset of AIDS |
|
|
Strep. pneumoniae in HIV
0. Key 1. Colonizes oropharynx via 2. Spread via (2) 3. Stimulate Local Inflammatory response via (3) 4. Evade phagocytic Killing |
0 Most common bacterial infection
1. Surface Protein Adhesins 2. Pneumolysin & IgA protease 3. Teichoic acid, Peptidoglycan Frags & Pneumolysisn 4. PLS Capsule |
|
|
MAC
1. Are (2) 2. Infection when CD4 coutn < 3. Causes what dieasese (3) 4. In patients w/ aids 5. Describe symptoms invovled (6) |
1. Mycobacterium avium & Intracellulare
2. <50 3. Asymptomatic colonization, Localised pulmonary disease & Solitary nodule 4. Disseminated disease (Tuberculosis like) 5. Night Sweats, Weight Loss, Abdominal Pain, Fatigue, Diarrhea & Anemia |
|
|
MAC infections
1. Immunocompetent 2. Advanced ADIS 3. In children |
1. Pulmonary MAC
2. Disseminated MAC 3. MAC lymphadenitits |
|
|
AIDS & Tuberculosis are
1. Leading cause among people living w/ AIDS 2. Greatest risk factor for TB |
0. TWIN EPIDEMICS
1. TB 2. AIDS |
|
|
Salmonella & AIDS
1. Salmonellosis More common in |
1. HIV+>AIDS
|
|
|
Bartonella henselae
1. Type of bacteria 2. Bacillary Angiomastosis 3. Infection of 4. Key HISTORY 5. Histo 6. On biopsy (vs. Karposi) |
1. Gram-ve, non enteric rod
2. Superfical Vascular Proliferative disease (Purplish, bright red) 3. Skin, LN, Liver or Spleen 4. Cat scratch 5. Stellate non-casseating granuloma 6. Neutrophil inflammation (vs. Lymphocyte) |
|
|
HIV & Hepatititis more like to develop
Why? |
1. Liver toxicity from meication
2. HAART metabolized in liver |
|
|
CMV (HHV-5)
0. Most common 1. Member of what family 2. Established latent infection in 3. Baltimore |
0. VIRAL cause of Congenital defects
1. Betaherpesviridinae (largest genome) 2. Mononuclear lymphocytes 7 Stromal cells 3. ClassI |
|
|
CMV & AIDS
1. Organs (3) 2. Lung causes 3. Diagnostic for lun 4. Eyes causes? @ CD4+ level 5. Diagnostic for Eye |
1. Lung, Eye & GIT
2. interstitial pneumoniae 3. OWL EYE inclusion bodies 4. Retinititis <50 5. Cotton Wool spots on Fundoscopy |
|
|
HHV-1 & -2 & AIDS
1. HIV increases 2. Severe symptoms include (2) 3. Who is at risk for Disseminated, Life threatening disease (2) |
1. Infection more, sever, longer
2. Blindness & Brain damage 3. immunicompromised & Neonates |
|
|
HPV & AIDS
1. Especially pronve to infection 2. Lead to what tumour 3. Females 4. MSM |
1. HIV +
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma 3. Cervical 4. Anal |
|
|
JC Virus & AIDS
1. JC virus causes 2. Symptoms (4) 3. Gross Brain (2) 4. CD4+ levels |
1. Progressive Multifocal LUKOENCEPHALOPATHY
2. Speech problesm, ONE SIDED: weakness, vision loss & numbness 3. Granularity white matter (vs. MS) 4. <200 |
|
|
KSHV (HHV-8) & AIDS
1. Most frequently 2. Tumor of 3. Biodpy 4. Clinical Presentation 5. Can affect |
1. Detected TUMOR in AIDS patients
2. Blood vessel wall (Superfical Neoplastic Proliferation of Vasculature) 2. LYMPHOCYTEs 3. Pink, Red, PURPLE lesions on skin & mouth 4. GIT & Lungs |
|
|
Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
1. Originates 2. MOST commonly found in patients (3) 3. Viral Infections which ↑ risk 4. Often found on? with |
1. Lympocytes
2. Inherited immunodefeciency, Autoimmune Disese & HIV 3. HTLV-1, Hep C & EBV 4. Oropharynx (Waldeyer'r Ring) |
|
|
Candida Albicans & HIV
1 Leading to onset of 2. On microscopy 3. CD4+ levels < 400 4. CD4+ levels <100 |
1. Candida pneumoniae
2. Pseudohyphae 3. Oral Thrush 4. Esophageal Thrush |
|
|
Cryptococcal Neoformans & HIV
1. In environment found (3) 2. CD4+ levels 3. Affects CNS 4. Stain? Shows? 5. Able to grow |
1. Soil, Bat droppings or bird
2. <100 (1st aid <50) 3. MENINGITIS 4. India Ink Halo & Large Capsule 5. Yeast @ 37⁰c |
|
|
Pneumocystis jirovecii
1. CD4+ 2. Causes 3. Reduced infection viA |
1. <200
2. Pneumoniae 3. ARVT |
|
|
Toxoplasmii gondii & AIDS
1. tyoe of organism (bartonella) 2. Spread by primarily 3. Or eating Raw 4. CD4+ 5. Causes (2) |
1. Parastive (vs. Non-enteric -ve rod)
2. Cats 3. Prok, Lamb & Venison 4. <100 5. Encephalitis & Abscess |
|
|
Cryptosporidiosis & AIDS
1. Ingestion of 2. CD4+ 3. Symptom 4. Disease w/ therapy is 5. Found in stool |
1. Contaminated Food & Water
2. <200 3. Chronic Watery diarrgea 4. refactory 5. Acid Fast cysts |

