![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
241 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are yeasts, appearance
|
unicellular, budding, sexual or asexual reproduction, colonies slimy or mucoid, much like bacteria
|
|
|
what are molds, appearance
|
filamentous, long chains of cells called hyphae, mass of hyphae called mycelium, molds are downy, fluffy, cottony
|
|
|
what is a mycelium
|
mass of hyphae
|
|
|
what are conidia
|
spores
|
|
|
in dimorphic species, what temp are mycelial forms around
|
<or=30 C
|
|
|
in dimorphic species, what temp are yeast forms or yeast-like forms around
|
>35C
|
|
|
name dimorphic fungi (7)
|
Histoplasma capsulatum
Blastomyces dermatidis Coccidiodes immitis Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Sporothrix schenckii Black molds Penicillium marneffei |
|
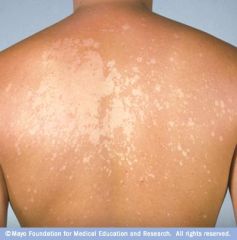
fungal
|
tinea versicolor- example of Superficial or Cutaneous Mycoses
|
|
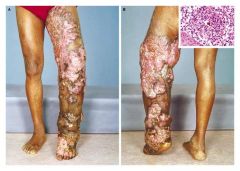
fungal
|
chromoblastomycoses: example of subcutaneous Mycoses
|
|
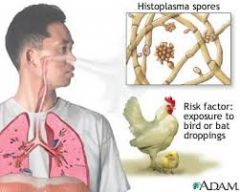
histoplasmosis
|
for review
|
|
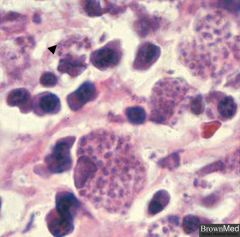
dimorphic
|
histoplasmosis
|
|

dimorphic fungus
|
histoplasmosis on gms
|
|
|
where endemic: histoplasmosis
|
ohio river valley
|
|
|
where found: histoplasmosis
|
Bird and bat droppings in soil, caves, ohio river valley
|
|
|
dimorphic appearance of histoplasmsois and life course in human
|
thermally dimorphic: in the environment it grows as a brownish mycelium
inhaled microconidia convert into yeasts in alveolar macrophages go through lymphatics - walled off and calcified in immunocompetent host; in immunocompromised have disseminated dz |
|
|
frequent agar plate for use of evaluating fungi
|
Sabouraud's dextrose agar or Sab glucose agar
|
|
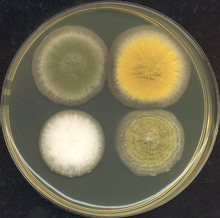
what fungus
|
aspergillus
|
|
|
what special containers are needed for fungi
|
basically anything
|
|
|
what is the value of adding chloramphenicol to SAB plate
|
inhibits bacterial growth and helps isolate slower growing fungi
|
|

what kind of plate might this be
|
SAB
|
|
|
Selective SAB with choro and cycloheximide alternative names
|
Mycosel/Mycobiotic
|
|
|
use of Mycosel/Mycobiotic plates
|
dermatophytes
|
|
|
use of Selective SAB with choro and cycloheximide
|
dermatophytes
|
|
|
Blood brain heart infusion agar with or without
antibiotics |
useful for looking for systemic fungi
|
|
|
why add cyclohexamide to an agar
|
suppresses saprophytic molds (molds that live on decaying organic matter) to allow for growth of slower growing systemic molds
|
|
|
****what does cyclohexamide also suppress (besides its intended saprophytic molds) (5)
|
Trichosporon beigelii
Candida tropicalis Cryptococcus neoformans Yeast of Blastomyces Yeast of Histoplasma "cyclone TraCCYY" missed the boat |
|

what kind of plate is this, what's it looking for
|
systemic fungi
|
|
|
old fashioned way to identify that a fungus truly dimorphic (now done molecularly)
|
- usually transferring mold to yeast (but could go the other way)
plate from SAB to blood infusion and v/v and go into cold, rm temp, back and forth for weeks to convert |
|
|
what is the basic flow of how to identify a fungus
|
1. Direct preparation
2. Inoculate media/ incubate at 30*C for 4 wk – best to grow mycelial phase of dimorphics 3. Observe for yeast or mold growth 4. Do proper tests for identification a. Mold – observe microscopically using Lactophenol cotton blue b. Yeast – do manual or automated chemical tests |
|
|
what are the three direct preparation steps to ID a fungus
|
Gram stain
Calcofluor white stain Impression smears – GMS or PAS |
|
|
why do we Inoculate media and incubate at 30*C for 4 wk –
|
best to grow mycelial phase of dimorphics
|
|
|
when evaluating molds and doing final step of ID after isolation, what do you use
|
Mold – observe microscopically using Lactophenol
cotton blue |
|
|
what is a lactophenol cotton blue
|
phenol, which will kill any live organisms
lactic acid which preserves fungal structures cotton blue which stains the chitin in the fungal cell walls. |
|
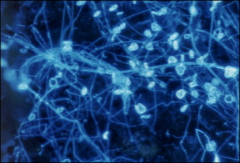
what kind of test is this
|
Calcofluor white - designed to replace KOH, special product that enables yeast or hyphae to fluoresce
|
|
|
when is a KOH test performed
|
to distinguish between dermatophytes and Candida albicans symptoms (vs. no fungi)
|
|
|
what are the three categories of dermatophytes
|
Trichophyton (found in skin, nail, and hair infections), Epidermophyton (skin and nail infections), and Microsporum (skin and hair infections)
|
|
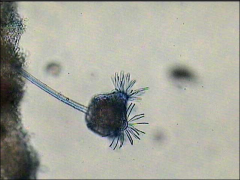
what kind of test is this and what is it designed to look for
|
lactophenol cotton blue
to look for molds (great for myelicum) |
|
|
defunct test for fungi
|
Exoantigen immunodiffusion tests
|
|
|
DNA probe test - where are they most useful
|
to confirm dimorphics
|
|
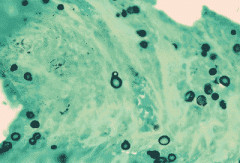
what
|
blastomycoses
|
|
|
association Mucicarmine
|
crytococcus neoformans - muco polysaccharide capsule
|
|
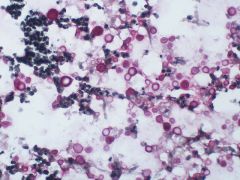
fungi
|
cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
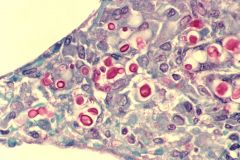
fungus
|
cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
|
are grams stains better for yeast or mycelial forms
|
yeast more than mycelial fungi
|
|
|
where is histoplasmosis capsulatum found
|
eastern half us
mexico caves Bat guano and bird droppings (Starlings) |
|
|
what are the sx of histoplasma capsulatum
|
Chronic progressive pulmonary,
cutaneous/mucocutaneous, Chronic systemic (RES system) or acute fulminating systemic disease (fatal) |
|
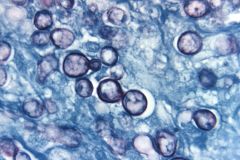
what
|
hhistoplasma capusulatum variant duboisii
|
|
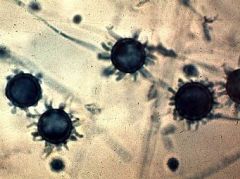
fungus - spore form
|
histoplasma capusulatum
|
|
|
what is special about the Histoplasma capsulatum var. duboisi
|
found in Africa
more cutaneous and bone manifestations |
|
|
what serologic tests might be mildly useful for histoplasma capsulatum
|
Complement fixation test - only good if immune system
Immune diffusion – H and M bands |
|
|
if can't culture, how detect histoplasma capsulatum
|
Direct antigen detection in urine (eia for ag in urine); Disseminated and chronic pulmonary disease, can work in immunosuppressed too
|
|
|
how do you culture histoplasma capsulatum
|
at 30*C; SLOW!! 2 – 8 weeks
|
|
|
appearance of histoplasma capsulatum on SAB plate
|
White to brown mycelium , cottony
|
|
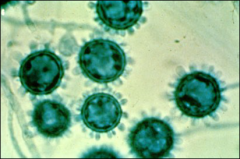
what
|
histoplasma capsulatum
mold phase tuberculated macroconidia that are large and round (8 – 16 uM) and small microconidia (Microconidia are infectious particle) |
|
|
what is a histoplasma capsulatum look alike fungus
|
Sepedonium
not dimorphic macroconidia same but no microconidia |
|
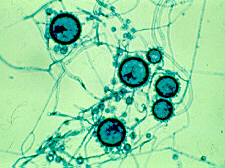
what
|
histoplasma - macro and microconidia
|
|
|
what does histoplasma capsulatum look like at 35C in lab
|
small yeast, round to oval,
always consistent in size and shape (2 -4 uM) narrow neck in budding |
|
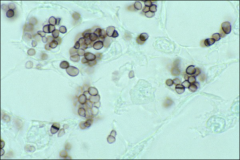
what
|
2-4uM histoplasma, consistent size and shape, narrow neck budding
|
|
|
histopathology of histoplasmosis (3)
|
- caseating and noncaseating granulomatous inflammation
- calcified lesions - Acute disease in the RES system with intracellular budding yeast forms (2 – 4 mM) |
|
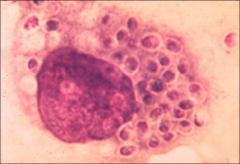
what
|
intracellular yeast forms (2-4um) of histoplasma
|
|
|
cf histo and cryptococcus in morphology
|
histoplasma - consistent in size and shape
cryptococcus all over the place in size |
|
|
does histoplasma capsulatum have a capsule
|
not a true capsule like cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
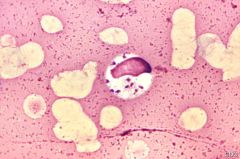
what
|
Leishimania - protozoan parasite; kinetoplast, transmitted by sand fly
|
|
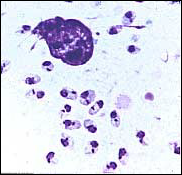
what
|
leishmania small, round bodies 2–4 μm in diameter with indistinct cytoplasm, a nucleus, and a small, rod-shaped kinetoplast. (contrast to histoplasma which is 2-4 um but without kinetoplast)
|
|
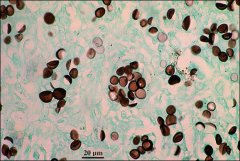
what
|
Histoplasma capsulatum var duboisi
8-10 um |
|
|
what should you think of if you see narrow based budding, 8-10um uniformly sized yeast, tuberculate conidia
|
Histoplasma capsulatum var duboisi
8-10 um |
|
|
where is blastomycosis dermatitidis endemic
|
eastern USA (esp southeastern)
|
|
|
clinical fx of blastomycosis
|
- pulmonary
- skin -bone |
|
|
growth of blastomycosis
|
Culture at 30*C
Takes 2 – 3 weeks to grow |
|
|
on plates
|
Fluffy white – buff colored prickly
|
|
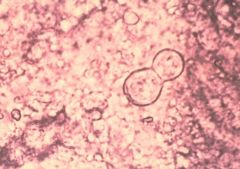
what
|
broad based budding- Large mother yeast cells averaging 8 – 20 uM or larger.Round to oval
Thick, double contoured double refractile cell walls Single broad based buds |
|
|
what
|
blastomycosis -note multiple nuclei
|
|
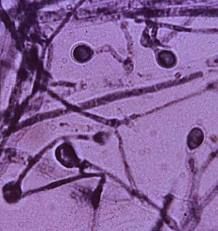
what
|
Pear shaped conidia like lollipops
blastomycosis |
|
|
Pear shaped conidia like lollipops
|
blastomycosis
|
|

what
|
blastomycosis, Large mother yeast cells averaging 8 – 20 uM or larger.Round to oval
Thick, double contoured double refractile cell walls Single broad based buds |
|
|
blastomycosis Look alike fungus --
|
Chrysosporium spp.
|
|
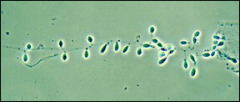
what
|
Chrysosporium spp. - not dimorphic, grows in 3-4 days (not weeks) but supposed to be look alike to blastomycosis, grows at 30 and 37
|
|
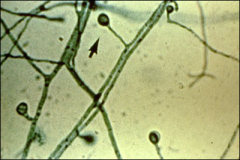
what
|
blastomycosis - pear shaped, lollipop, at 30 C
|
|
|
fx of blastomycosis on histopathology
|
Mixed pyogenic and granulomatousinflammation
Microabscesses Broad based budding yeast cells |
|
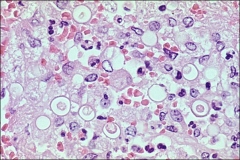
what
|
blastomycosis - rather obscure but notice thick double contoured wall, with "retraction" internal to that. in this the center is somewhat degraded
|
|
|
where is coccidiodes immitis found
|
Found in SW USA, Mexico – areas known as the
Sonoran life zone (cooler part of desert) – desert sands |
|
|
how get coccidiodies
|
inhalation of desert sand
|
|
|
alternative names for coccidiodes
|
Valley fever, desert rheumatism, valley bumps
|
|
|
clinical types of infections: coccidiodes
|
Six types of infections:
1) asymptomatic 2-3) pulmonary - focal or diffuse 4) cutaneous 5)meningitis 6)disseminated |
|
|
those at risk for disseminated coccidiodes (3 groups)
|
Higher incidence of disseminated in HIV
darker skinned ethnic groups pregnancy |
|
|
growth of coccidiodes
|
Culture at 30*C; Takes 2 – 3 days to grow
|
|
|
appearance on SAB plate: coccidiodes
|
White wooly mold
|
|
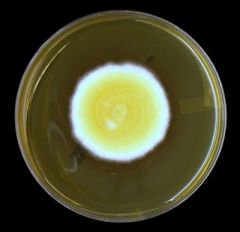
what on SAB
|
blastomycosis dermatidis
|
|
|
word of caution about coccidiodes
|
Very infectious to laboratory personnel
|
|
|
description of coccidiodes hyphal form
|
Septated hyphae with chains of thick walled
barrel shaped arthroconidia with dead cells in between |
|
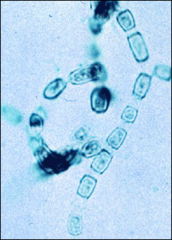
what
|
coccidiodes immitis (cause of cocciomycosis)
|
|
|
Which fungal stain binds to cellulose and chitin present in fungal cell walls, causing fluorescence under ultraviolet light
|
calcofluor white
|
|
|
correct ratio of India ink:CSF that should be placed on a slide
|
1:1
|
|
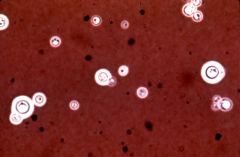
prganism that demonstrates budding yeast cells with wide capsules in an India ink preparation of spinal fluid is probably _____
|
cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
|
best test for cryptococcus neoformans in CSF
|
Latex bead antigen agglutination test of the CSF
|
|
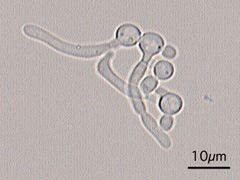
formation of germ tubes is s/o
|
candida albicans
|
|
|
what is birdseed agar for
|
Cryptococcus neoformans is the only yeast that produces brown colonies (due to melanin production) on birdseed agar
|
|
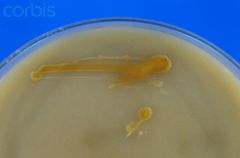
what
|
cryptococcus neoformans - brown colonies on birdseed agar
|
|
|
phenol oxidase positive
|
cryptococcus
|
|
|
what fungal organism can be associated with catheter-related sepsis
|
Malassezia furfur
|
|
|
fx of Malassezia furfur
|
requires lipids from olive oil for growth, and is a small yeast with a wide bud
|
|
|
what agar is useful at detecting mixed yeast populations
|
Chromogenic agar (best at 35-37)
|
|
|
what candida species doesn't produce germ tubes (good neg ctl for germ tube studies
|
Candida tropicalis
|
|
|
look alike to coccidiodes
|
Look alike fungus = Malbranchea species
|
|
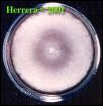
what
|
White wooly mold
coccidiodes |
|
|
interesting point about dimorphism in coccidiodes
|
not dimorphic in lab (same at 30 as 37) but in humans, dimorphic
|
|
|
histopathology of coccidiodes
|
Thick walled spherules (10 – 80 uM) with
endospores All stages of development and fragmented spherules Granulomatous inflammation with caseation |
|
|
two dz that you need to distinguish from coccidiodes
|
Rhinosporidium seeberi spherules – larger – 100 – 300 uM in size
Myospherulosis other things make spherules |
|
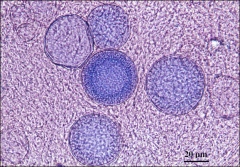
what
|
coccidiodes spherules with endospores
|
|
|
what
|
coccidiodes
|
|
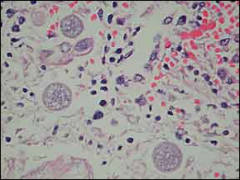
what
|
coccidiodes
|
|
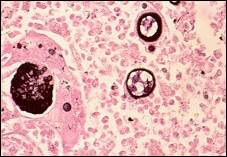
what
|
coccidiodes
|
|
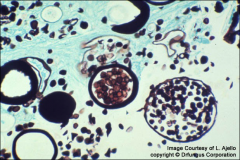
what
|
rhinosporidium (bigger) 100 – 300 vs. 10 – 80 uM of coccidiodes- also usually found in oral/nasal (not in lung or deep tissue like coccidiodes)
|
|
|
what is myospherulosis
|
fungi-like spherules composed of erythrocytes damaged by endogenous and exogenous fat
|
|
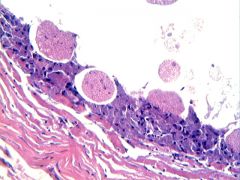
what
|
myospherulosis
|
|
|
what is another name for paracoccidioses brasiliensis
|
south american blastomycosis
|
|
|
sx of paracoccidiodes
|
Pulmonary – primary disease
Can disseminate – muco-cutaneous, lymphatics, CNS, adrenals, GI Hallmark – facial involvement - nasal |
|
|
paracoccidiodes culture
|
30C kinda looks like blastomycosis but won't have to worry about that
Culture @ 37*C Slow (3- 4 weeks) waxy coral-like yeast ***Large yeast (10 – 20 uM – up to 60uM) with multiple daughter buds “Mariner’s wheel” |
|
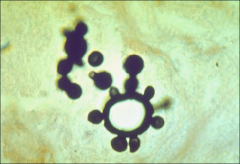
what
|
mariner's wheel - multiple budding yeast
paracoccidiodes |
|
|
histopathology of paracoccidiodes
|
Mixed granulomatous and pyogenic inflammation
Paracoccidiodomas as old coin lesions With polarized light – see maltese cross formation Observe Mariner’s wheel yeast cell – multiply budding large yeast |
|
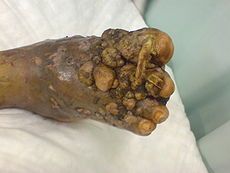
what
|
madura foot - known as mycetoma
three sx Swollen lesions usu on extremities Draining sinuses Sulfur granules traumatic implantation (from soil) |
|
|
98% of mycetomas are caused by what
|
bacteria! gram + filamentous
Nocardia: brasiliensis and N. asteroides Streptomyces spp Actinomadura Actinomyces israelii (anaerobic bacteria) |
|
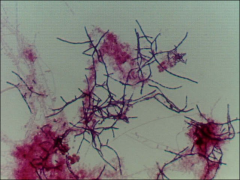
what
|
nocardia
|
|
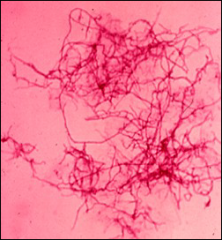
partial acid fast stain - bug and chemicals of stain
|
nocardia
Positive Carbol Fuchsin (like usual AFB) but decolorizes with H2So4 (instead of HCL like most AFB) Potassium permangenate (?) |
|
|
what stains will nocardia be negative for that you might think to try
|
its a partial acid fast organism and thus is negative with HCL-using stains like ziehl-nielson, kenyon or rhdamine-rhodamine (?)
|
|
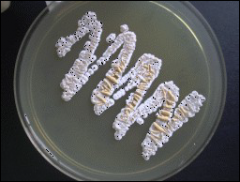
what
|
nocardia
3 – 5 days Dry Crumbly Musty smell |
|
|
what is a eumycotic mycetoma
|
traumatic transplantation
black molds: Pseudallescheria boydii Maduerella Curvularia Exophiala others |
|
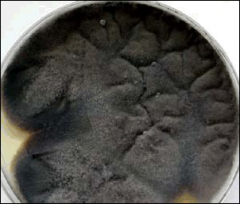
what
|
black mold: black on reverse too
|
|
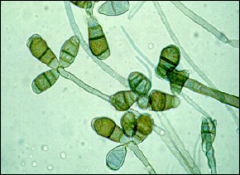
what
|
curvularia
|
|
|
what is chromoblastomycosis
|
Wart like lesions
Sclerotic bodies in tissue Growth of dematiacious fungi ex.Fonsecaea, Phialophora, Cladosporium, Exophiala, and Rhinocladiella |
|
|
madura foot vs. chromoblastomycosis
|
look really similar at end stage - chromoblastomycosis is supposed to be more warty
|
|
|
three patterns of sporulation of dematiceous fungi
|
Rhinocladiella – like sporulation
Phialophora like sporulation Cladosporium like sporulation |
|
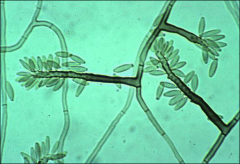
what
|
Rhinocladiella – like sporulation
reminds me of pine branches |
|
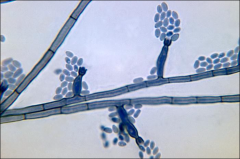
what
|
Phialophora like sporulation
looks like blackberries |
|
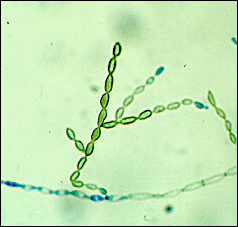
what
|
Cladosporium like sporulation
maybe like forsythia? worry about this one chromoblastomycosis to brain |
|
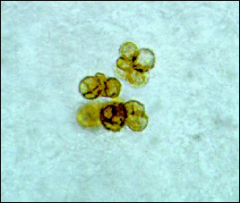
what
|
sclerotic body, means chromoblastomycosis, copper penny
|
|
|
diagnostic feature in chromoblastomycosis
|
sclerotic body
|
|
|
diagnostic feature in mycetoma
|
sulfur granules
|
|
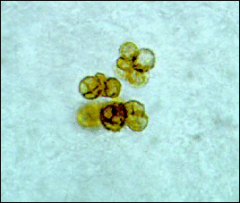
what
|
sclerotic body
|
|
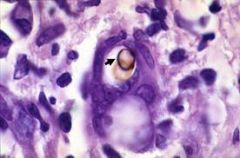
what
|
sclerotic body
|
|
|
name 3 subcutaneous fungal infections
|
mycetoma
chromoblastomycosis sporotrichiosis |
|
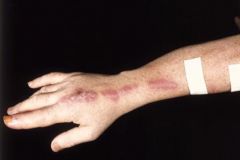
what
|
sportotrichiosis
Initial skin lesion w/wo ulceration Lympho-cutaneous spread (LN enlargement)– bone – systemic Pulmonary - CNS (inhaled) |
|
|
explain lab growth patterns of sporothrix
|
Dimorphic dematiacious mold
- 30*C rapid growth (3 -5 days) - turns brown to black over time - septate hyphae with conidia in daisy wheel - At 37*C small oval yeast cells, elongated 2 – 5 uM, cigar bodies |
|
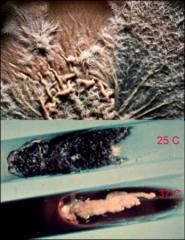
what
|
sporothrix yeast at 37, black mold at 25
|
|
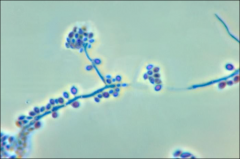
what
|
daisy-like arrangement sporothrix
|
|
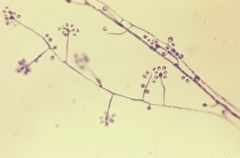
what
|
sporothrix - daisy like
|
|
|
what does sporothrix look like on histology
|
Pyogenic – to – granulomatous inflammation
hard to find yeast in tissue Asteroid body known as Splendore Hoeppli phenomenon |
|
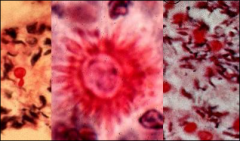
what are you likely to get in tissue for sporothrix
|
splendore-hepaly - no yeast in tissue, but IF found, cigar (ovoid, elongated yeast)
|
|
|
where do you see rhinosporidosis, sx
|
Water and fish disease in India, Brazil, etc
Chronic granulomatous infection of mucous membranes, mass lesions Endospores can be mucicarmine positive remember really big spherulo |
|
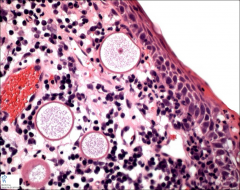
nasal
|
rhinosporidiosis - note larger spherules than coccidiodes
|
|
|
what is unique about candida
|
Endogenous pathogen
|
|
|
fungus associated with catheter
related infections in children |
Candida parapsilosis
|
|
|
association with Candida parapsilosis
|
catheter
related infections in children Parapsilosis, plastic, puer/puella |
|
|
most common candida species
|
c. albicans
|
|
|
what three candida species may be resistant to fluconazole
|
Candida glabrata, kruseii, and tropicalis
|
|
|
growth characteristics of Candida in lab
|
Rapid growth = 24 – 48 hours
Bacterial like colony – pasty white Budding yeast – oval @ 7 uM in size and form pseudohyphae (look like sausage links) |
|
|
which candida does not form pseudohyphae
|
Candida (Torulopsis) glabrata is @ 4 uM in
size and does NOT form any pseudohyphae (half the size) - tiny yeast |
|
|
tiny yeast (2)
|
histo and C. glabrata
|
|
|
two tests to id C albicans
|
1) germ tube +
2) Produce chlamydospores on cornmeal agar |
|
|
what other candida is germ tube positive and how distinguish from C. albicans
|
Candida stellatoidea also germ tube positive
but C. stell sucrose positive, while C. albicans is sucrose negative |
|

which bug(s) is/are this
|
candida albicans (sucrose -) or c. stellatoidea (sucrose+)
|
|
|
germ tube test - how long incubate
|
4 hours - if longer, get false positives
incub in plasma |
|
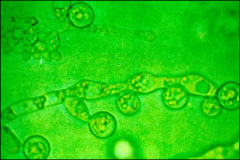
what
|
Positive for Chlamydospores = C. albicans
cornmeal agar, resting spore (protective spore) terminal chlamydospore Incubation at 30*C for @ 48 hours – observe microscopically |
|
|
on histopath for Candida glabrata
|
smaller yeast cells and no pseudohyphae - extracellular
(differentiate from histoplasma) |
|
|
histopath for candida
|
Pyogenic to granulomatous
Usually observe yeast cells, pseudohyphae and/or hyphae appearing structures |
|
|
what is tinea versicolor caused by
|
Malassezia furfur
|
|
|
common disease with malezzeia furfur
|
Skin: macules, papules, patches,
plaques on chest back and shoulders with either hypo or hyper pigmentation |
|
|
what is a bad form of Malessezia furfur
|
Fungemia in neonates on IV lipid feeding in central lines
|
|
|
growth characteristic for Malessezia furfur
|
Lipophilic yeast – required for growth
Small budding yeast 2 – 4 uM with collarette add virgin olive oil to it |
|
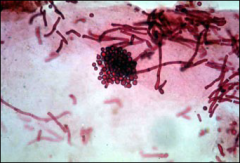
what
|
M. furfur, spaghetti and meatballs
|
|
|
dermatophytes, tineas, ringworms (hair, skin, nails)
|
Microsporum
Epidermophyton Trichophyton |
|
|
how to dx dermatophytes
|
clinical, KOH prep
|
|
what
|
koh, test
-skin scraping -add Koh (dissolve skin, nail, hair) +/- heat - coverslip and see |
|
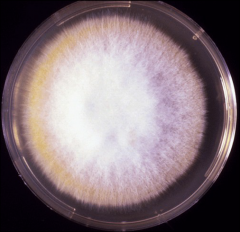
what
|
microsporum canis
@ 30*C, one week note: white with yellow edge creeping out |
|
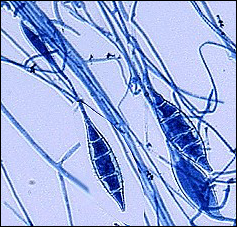
what
|
microsporum canis
Microsporum canis - dog/cat ringworm Tuberculate macroconidia – few micro +hyaline hyphae |
|
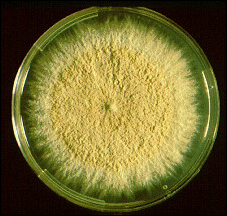
what
|
Microsporum gypseum colony @ 30*C at one
week only beige ? |
|
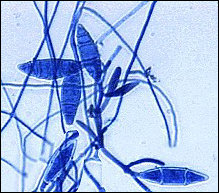
what
|
Microsporium gypseum - soil
|
|
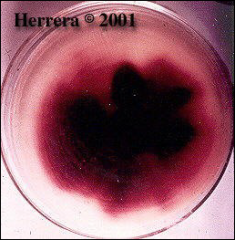
what
|
Trychophyton rubrum colony – red diffusible pigment
on REVERSE |
|
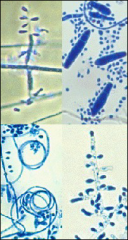
what
|
numerous MICROconidia - lots of shapes, pencil shaped Macroconidia
|
|
|
main cause tinea capitis ring worm in children
|
Trichophyton tonsurans -
|
|
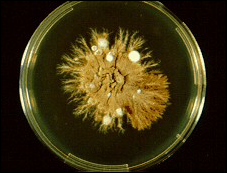
what
|
Epidermophyton floccosum - khaki green color colonies
|
|
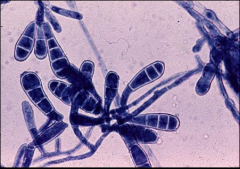
what
|
Epidermophyton floccosum
Beaver tail spores – no microconidia |
|
|
where find cryptococcus neoformans
|
Ubiquitous saprophytic yeast assoc. with pigeon, chicken or turkey droppings
inhale it Disease – CNS, blood - can disseminate (meningitis) |
|
|
who is most associated with getting cryptococcus neoformans
|
immunocompromised host - HIV
|
|
|
cryptococcus growth characteristics in lab
|
Irregular sized (2 – 20uM) yeast cells**** round
Polysaccharide capsule*** India ink – negative staining method*** Cryptococcal antigen test – Ag in CSF and blood Daughter cells attached by narrow thread Great variability in size and shape Grows well on all agars – mucoid colonies due to capsule formation Urease + Inositol + |
|
|
what population is crypto not in
|
kids
|
|
|
two chemical tests to know for cryptococcus neoformans
|
Urease + Inositol +
|
|
|
only yeast inositol+
|
crytococcus
|
|
|
source of cryptococcus
|
poor pigeon
|
|
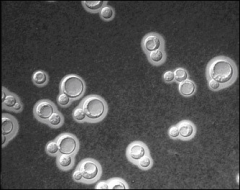
phase contrast who
|
round, variably sized
cryptococcus neoformans |
|
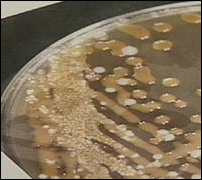
what
|
cryptococcus
Mucoid beige |
|
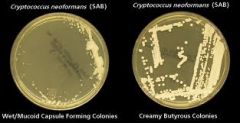
what
|
cryptococcus
|
|
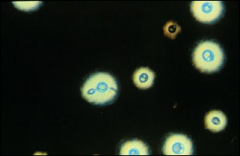
what test, what bug
|
india ink, negative (no) staining of capsule on cryptococcus, can get false haloes on lymphs so ideally get buddng cell
|
|
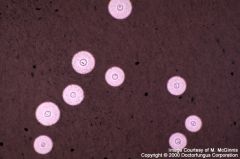
what
|
cryptococcus on india ink
|
|

what
|
slant where pink is positive for urease, yellow is negative
cryptococcus is urease + |
|
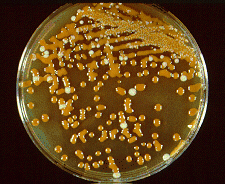
what
|
birdseed agar, chocolate brown colonies = cryptococcus
the background white on this are candida the only yeast to turn brown on birdseed agar is cryptococcus |
|
|
opportunistic fungal pathogens
|
Filamentous molds, septate, usu branching
Hyalohyphomycetes – hyaline (clear) Phaeohyphomycetes – black or dematiaceous Saprophytes in soil, plants, nature |
|
|
most common Hyaline Fungi
|
hundreds
Aspergillus, Penicillium, Fusarium, Paecilomyces, Trichosporon, Geotrichum, Scopulariopsis, Acremonium, |
|
|
aspergillus
|
Hyaline
Septate Branching at 45 degree angle |
|
|
sx/clinical aspergillus
|
Vasoinvasive, thrombosis, infarctions
Supperative inflammation |
|
|
Main look alike for aspergillus
|
Pseudallescheria boydii
|
|
|
most common three aspergillus
|
Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspergillus flavus Aspergillus niger |
|
|
how long for aspergillus spp to grow
|
Grow in 48 – 72 hours
|
|
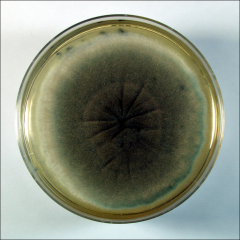
what
|
aspergillus fumigatus
green carpet |
|
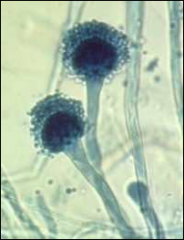
what
|
aspergillus fumagatus
30, green colony, spores are "head up" like a broom |
|

what
|
aspergillus flavus
|
|
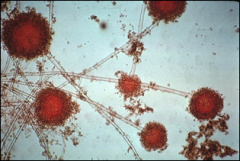
what
|
aspergillus flavus
sunburst |
|
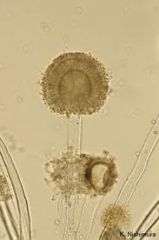
what
|
aspergillus flavus
|
|
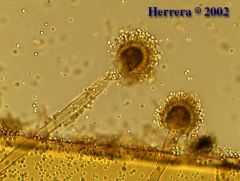
what
|
aspergillus flavus
|
|
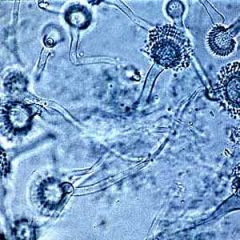
what
|
aspergillus fumagatus - like mop
|
|
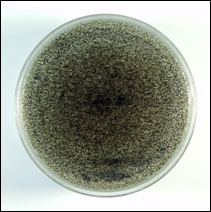
what
|
aspergillus niger - salt and pepper
|
|
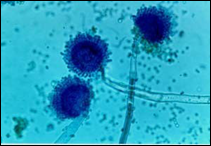
what
|
aspergillus niger - see black retained on lactophenol cotton blue; head goes all the way around
|
|
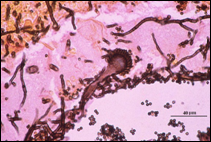
what
|
aspergillus
open cavity to have fruiting body fruiting head and dichotamous branching Branching at 45* angle, septate hyphae |
|
|
define dichotamous
|
continous
|
|
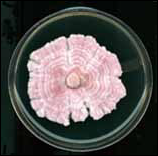
what
|
Fusarium species – Fucshia color
|
|
|
clinical fx of fusiarium
|
Associated with kerititis and disseminated
Infection in BMT |
|
|
what population should you associated with fusarium
|
BMT population
|
|
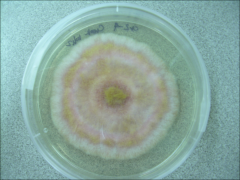
what
|
Fusarium
|
|
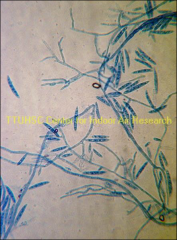
what
|
Fusarium
banana boat |
|
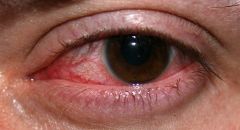
what fungus is associated
|
fusarium - keratitis
moisture - humid |
|

what
|
penicillium
|
|
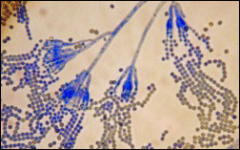
what
|
bony hand, broom
penicillium (not aspergillus - more like mop) |
|
|
can penicillium cause disease
|
yes, skin, nail, disseminated
|
|
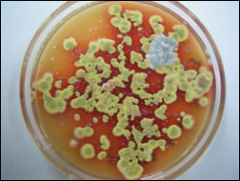
what
|
Red diffusible pigment of P.marneffei
|
|
|
only species of Penicillium that is almost always pathogenic
|
P.marneffei
|
|
|
two fungi with red diffusable pigment
|
P.marneffei and T. rubrum (but Penicillium is green but T. rubrum is white)
|
|
|
p. marneffei in clinical settings (2)
|
- southeast asia, skin infections
- lung, AIDs |
|
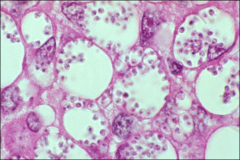
what
|
p. marneffei
|
|
|
what is only penicillium, dimorphic
|
p. marneffei yeast like in tissue, hyphal at 30
|
|
|
three black molds that can disseminate
|
Phaeohyphomycosis
Eymycotic mycetoma Chromoblastomycosis Phaeohyphomycosis |
|
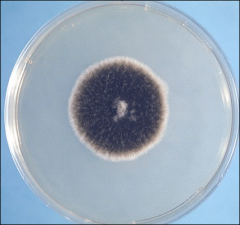
what
|
alternaria
|
|

what
|
hand grenade
alternaria |
|
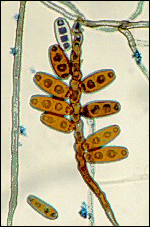
what
|
bipolaris- bad actor
sinus, or innocuous lesion in leg then can just march on |
|
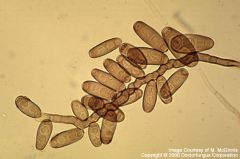
what
|
bipolaris
|
|
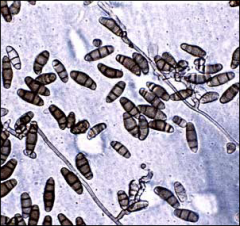
what
|
curvularia
|
|
|
alternative name for Pseudallescheria boydii
|
Teleomorph Scedosporium apiospermum
|
|
|
what is Pseudallescheria boydii
|
like aspergillus in tissue (not in lab), vasoinvasive
|
|
|
three plate pushers
|
Absidia, rhizopus and mucor - grow so fast (within 24 hours) can push the lid off the plate
|
|
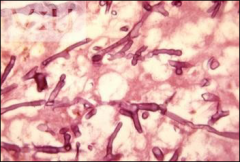
what
|
zygomyces
90* angle branching, aseptate, ribbon like, SACS weak - so need to mince not grind |
|
|
need to differentiate between absidia and rhizopus
|
based off where sac is... still not clear... for review
|
|
|
diabetic with rhinocerebral involvement
|
mucor
|

