![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the most virulent pathogens that affect human beings.
They are classified into two genera |
Marburg virus and Ebola virus
|
|
|
Ebola virus genome
|
, linear, nonsegmented, negative-stranded RNA.
Noninfectious, complementary to viral mRNA Transcribed into subgenomic mRNAs encoding 7 structural proteins. |
|
|
Where does the ebola virus replicate?
|
cytoplasm
|
|
|
Ebola viruses cause
|
severe haemorrhagic fever which leads to multisystem dysfunction.
incubation period 4-10 days. |
|
|
Ebola disease is characterized by
|
pharyngitis, nausea, and severe vomiting of blood and production of blood stools.
If fatal, death occurs 6-9 days after onset of the clinical disease. All sick individuals have circulating viral antigen. Mortality rate is up to 90%. |
|
|
High risk patients for Ebola are
|
traveled into areas where hemorrhagic fever occurred recently.
been in contact with with body fluids from a person with hemorrhagic fever. worked in a laboratory environment handling the viruses. |
|
|
The most lethal ebola strain to humans
|
Zaire ebolavirus
|
|
|
Ebola virus reservoir
|
Fruit bats
|
|
|
How does Ebola virus causes viral replication?
|
Ebola VP 35 inhibits activation of PKR protein which induces the viral replication
|
|
|
Detection of Ebola virus is via
|
ELISA, RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry.
|
|
|
Ebola tx
|
No vaccine or antiviral drugs are available to control filovirus infections.
Treatment is limited to the supportive measure. Antibody-containg serum and interferon therapies have been tried in patients with filovirus infection. Infected patients should be quarantined and contaminant animals should be sacrificed. Handling of this family of viruses or contaminated materials requires biosafety level 4 facilities. |
|
|
Bunyaviruses are typically spread by
|
mosquitoes, ticks, or flies. However, the hantaviruses are the exception where they are carried by rodents.
|
|
|
Bunyaviruses are the causative agents of
|
encephalitis and hemorrhagic fevers.
The viruses are classified as biohazard level 3 or 4 pathogens. |
|
|
Bunyaviruses genome
|
enveloped, segmented, negative-stranded RNA viruses.
Viral particles are roughly spherical and 90-120 nm in diameter. Viruses encode structural and non-structural proteins |
|
|
Unique features of bunyaviruses:
|
Share common morphology and basic components
Virion is enveloped with three (L, M, S) negative-sense RNA genome strands. Organized in a nucleocapsid, but virion has no matrix protein |
|
|
bunyaviruses replicate in
|
cytoplasm.
Virus can infect humans and arthropods. Virus in arthropod can be transmitted to its eggs. |
|
|
bunyaviruses are transmitted by
|
bite of an infected arthropod
California encephalitis group is transmitted by Aedes mosquito |
|
|
Aedes mosquito characteristics
|
Aedes mosquitoes are daytime feeders and live in forest
Aedes mosquitoes lay eggs in small pools of water trapped in places such as trees and tires. Virus is able to pass into ovary and infect arthropod eggs, allowing virus to survive during winter. |
|
|
People at risk of bunyaviruses
|
People in the habitat of the arthropod vector (e.g., campers, forest rangers and woodsmen for California encephalitis virus).
|
|
|
bunyaviruses Geography/Season
|
Disease incidence correlates with vector distribution (more common in summer).
|
|
|
Initial viremia by bunyaviruses causes
|
flu-like symptoms
|
|
|
Establishment of secondary bunyavirus viremia may allow virus access to specific target tissues
|
Particular target tissue determines the nature of disease
May include central nervous system, vascular endothelium, or other organs (hemorrhagic fevers/encaphalitis). |
|
|
Immune response to bunyavirus
|
Antibody is important in controlling viremia.
Interferon and cell-mediated immunity may prevent the outgrowth of infection |
|
|
Encephalitis is caused by
|
La Crosse virus
|
|
|
Hemorrhagic necrosis caused by
|
Rift Valley fever virus
|
|
|
pathogenesis of rift and la crosse virus
|
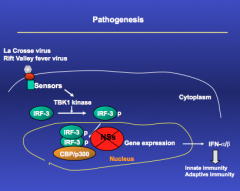
|
|
|
how to detect bunyaviruses
|
Enzyme-linked immunoasorbent assay (ELISA) may detect antigen in clinical specimens from patents with viremia.
The reverse-transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test can be used to detect viral nuclei acids. Virus-neutralization assays can be used to indentify the virus. Assays for immunoglobulin (Ig) M are useful in the documentation of acute infection and IgG analysis is used to document recent infection. |
|
|
bunyaviruses tx
|
No specific therapy is available for infections of Bunyaviruses.
Human disease is prevented by interruption of the contact between humans and the vector. Arthropod vectors are controlled by eliminating the growth conditions for the vector. Rodent control minimizes the transmission of many viruses, especially hantaviruses. |
|
|
Arenaviruses
genome |
enveloped virion with two circular, negative-sense RNA genome segments (L, S). Virion appears sandy because of ribosomes that are packaged in particle.
S genome segment is ambisense (both positive and negative sense) |
|
|
Arenavirus infections are
|
are zoonoses, establishing persistent infections in rodents.
Pathogenesis of arenavirus infections is largely attributed to T-cell immunopathogenesis. |
|
|
Arenaviruses can infect macrophages and may cause release of
|
mediators of cell and vascular damage.
|
|
|
Arenaviruses Tissue destruction is exacerbated by
|
T cell mediated immune responses.
Virus infects specific rodents and is endemic to rodents habitat (mainly tropics). |
|
|
Humans become infected with arena virus through
|
inhalation of aerosolized urine and feces, or through contaminated foods.
|
|
|
An arenavirus infection is usually diagnosed on the basis of
|
serological findings. These virus are too dangerous for routine isolation.
|
|
|
Ribovirin has limited activity against
|
arenaviruses and supportive therapy is all that is available for patients with arenavirus infections.
These rodent-borne infection can be prevented by limiting contact with the vector. |

