![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
118 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Key differences between Animals and Fungi?
|
-Ergosterol in membrane instead of Cholesterol
-have a Cell Wall made of chitin, glucan, and mannan |
|
|
Type of nutritional organism Fungi are?
|
Heterotrophs = cannot synthesize their own nutrients, but assimilate nutrients from surroundings
|
|
|
How is being a heterotroph imporant in the way Fungi cause disease in humans?
|
Fungi secrete enzymes that digest the substrate..aka our tissue (amylase, lipase, cellulase, proteinase)
|
|
|
2 morphological forms of fungi?
|
Yeasts
Filaments |
|
|
Filaments are long, hollow structures filled with __1__ and often divided by __2__
|
1. cytoplasm
2. cross-walls |
|
|
Filaments are larger than __1__, they can break apart and each fragment can __2__. The filament form allows for __3__
|
1. macrophages
2. start a new colony 3. tissue penetration |
|
|
Yeasts are __1__-cellular and divide by __2__
|
1. uni
2. fission (budding) |
|
|
Host defense against filaments:
Host defense against yeast: |
Oxidative burst
Phagocytosis |
|
|
Pathogenic Fungi:
-some have the ability to grow at __1__ degrees. -Some have a __2__ which protects them from immune system -__3__ allows them deep penetration of the lung where systemic infection can start |
1. 37' C
2. polysaccharide capsule 3. small spore size |
|
|
Interaction with _______ may predispose fungi to be parasites of higher animals
|
soil amoebae
|
|
|
4 major groups of fungi
|
Ascomycetes
Basidiomycetes Zygomycetes Imperfect fungi |
|
|
The four groups are differentiated based on _________
|
their spore types
|
|
|
List some examples of Asexual spores
|
Arthrospore
Chlamydospore Fusarium conidia Alternaria conidia Neurospora conidia |
|
|
Asexual spores have these characteristics
|
-vary in size from a few microns to hundreds of microns
-often very Hydrophobic -some have mucilage |
|
|
What stage of fungal life cycle is most relevant to allergy sufferers?
|
Spores are often allergenic
-dead spores maintain allergenicity |
|
|
Most numerous spores in the air we breath?
|
Conidia, but also smut spores and ascospores
|
|
|
Type of Hypersensitivity caused by spores?
|
Type I: spore binds to IgE on Mast cells
|
|
|
4 most common environmental fungi
|
Aspergillus
Alternaria Cladosporium Penicillium *their spores are common indoors and outdoors* |
|
|
Spores are common after _______ events
Spores are not common in these environments: _____ |
rain
desert/arid |
|
|
Some ______ infections can be related to fungal presence
|
sinus
*Eosinophilic Fungal Rhinosinusitis *difficult to tell if fungi are growing in sinus or incidental |
|
|
Where are typical locations of fungi indoors?
|
Moisture places
-shower -water ducts -furnace filters -house plants |
|
|
Household item that can kill fungi
|
bleach
|
|
|
Most common fungal toxins and most significant public health risk associated with fungi
|
Mycotoxins in grain
|
|
|
-Estimated # of different mycotoxins: __1__
-Toxin also common in __2__ -__3__ poisoning is much less common than mycotoxin exposure |
1. 300-400
2. nuts 3. mushroom |
|
|
Aflatoxin is from grains and nuts infected by ________
|
Aspergillus
|
|
|
Explain how Aflatoxin is activated
|
It is metabolized to its active form in the Liver
|
|
|
What can complicate Aflatoxin ingestion?
|
HBV + Aflatoxin exposure have higher incidences of LIVER CANCER
|
|
|
Alkaloid mycotoxins include these 3
|
1. Clavicepes infected rye -> Lysergic Acid (LSD)
2. St. Anthony's fire = hallucinations, cramps 3. Neurotoxins in infected grains |
|
|
Fumonisin mycotoxins come from __1__ infected __2__
-It is associated with __3__ CA. -causes disease in __4__ |
1. Fusarium
2. Wheat 3. Esophageal 4. farm animals |
|
|
Example of a Fumonisin mycotoxin
|
Vomitoxin
*produced by Fusarium |
|
|
Fungus that causes "sick building syndrome"
|
Stachybotrys Chartrum
|
|
|
Stachybotrys Chartum mycotoxins
Concentration of infected material that can contain a lethal dose |
Trichothecenes
Satratoxin F, G, and H 100-1000 cm'2 |
|
|
People in contaminated buildings have elevated titers of antibodies to:
-S. Chartum: __1__ -Satratoxin: __2__ |
1. IgA, IgM, IgE
2. IgG *Stachybotrys is relatively uncommon compared to enviromental Alternarium, Cladosporium, Aspergillus |
|
|
Gliotoxin is produced by these 2 fungi
|
Aspergillus
Gliocladium |
|
|
3 properties of Gliotoxin
Gliotoxin mechanism? |
1. highly toxic
2. immunomodulatory 3. stimulates apoptosis Mechanism: inhibits nuclear factor kappa B |
|
|
Are most cases of Mushroom poisoning lethal or non-lethal?
|
Non-lethal
|
|
|
What is the most common symptom of Mushroom poisoning?
|
Vomiting
|
|
|
Amanita toxins are __1__ polypeptides which inhibit __2__
|
1. cyclic
2. RNA Polymerase |
|
|
Amanita toxins can lead to death within __1__ days without a __2__ transplant
|
1. 6
2. liver |
|
|
Ibotenic Acid toxin is produced by __1__ and causes these symptoms: __2__
|
1. Amanita muscaria
2. nausea, vomiting, confusion, visual distortion |
|
|
Psilocybin causes these clinical effects
|
Hallucinations or Perceptual distortions
|
|
|
Why are Anti-fungal therepies limited?
|
Fungi are closer to animals than bacteria are
-many drugs that kill fungi are bad for people as well |
|
|
Most anti-fungal therapies depend on the presence of ________ in the fungal membrane
|
Ergosterol
|
|
|
Fungi use __1__ in their membranes
Animals use __2__ in their membranes |
1. Ergosterol
2. Cholesterol |
|
|
List the pathway to Ergosterol synthesis
|
Squalene --> Lanosterol --> Ergosterol
|
|
|
2 antifungal classes that target Squalene Epoxidase
|
Thiocarbamates
Allylamines |
|
|
Thiocarbamates and Allylamines are effective against __1__ but less so against __2__
|
1. Dermatophytes
2. yeast |
|
|
Squalene accumulation can be ______ to the fungi
|
toxic
|
|
|
List 4 Allylamines
|
Terbinafine
Naftifine Amorolfine Butenafine *all end in FINE |
|
|
Lamisil is also known as _________
What is it effective against? |
Terbinafine
Oral or Topical -effective against molds, dermatophytes, some candida yeasts |
|
|
What is the 1st commited step in Ergosterol synthesis?
|
Squalene
|
|
|
Terbinafine is marketed to __1__ because of higher frequency of __2__ infections
|
1. Athletes
2. toenail/foot |
|
|
Terbinafine (lamisil):
-__1__ due to squalene accumulation. -1/2 life is __2__ following oral administration -take orally for __3__ -topical OTC for __4__ or _5_ |
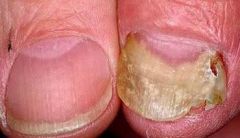
1. FUNGICIDAL
2. 4.6 hours 3. Onychomycosis (nail infection) 4. ringworm or athletes foot |
|
|
Oral Terbinafine has reduced clearance in patients with __1__ or __2__ impairment
|
1. liver
2. kidney |
|
|
Terbinafine has a ______ times higher affinity for fungal squalene epoxidase than for human
|
4000
|
|
|
Azoles bind to _____ and inhibit __________
|
P450 (14DM)
Lanosterol Demethylase (14 alpha-demethylation of lanosterol) *newer Azoles have a higher specificity for fungal enzyme while older azoles cross react with human P450's |
|
|
Fluconazole trade name
|
Diflucan
|
|
|
__________ biochemistry is markedly effected by reduction in renal fxn
|
Fluconazole
|
|
|
Fluconazole (Diflucan):
-half life: __1__ -effective against __2__ |
1. 30 days
2. yeasts, widely used for serious fungal infections |
|
|
Fluconazole: fungistatic or fungicidal?
|
Fungistatic
*need immune system to clear organisms |
|
|
Type of Fluconazole formulations available?
|
Oral or IV
|
|
|
Antifungal drug that penetrates into all body fluids
|
Fluconazole
|
|
|
Fluconazole is marketed for _________ infections
|
Vulvovaginal candidiasis
|
|
|
Fluconazole:
-__1__% is excreted in urine unchanged -prophylactic in __2__ |
1. 80%
2. HIV and transplant recipients |
|
|
Itraconazole formulations available
|
Oral or IV
|
|
|
_______ Itraconazole is unpredictable
|
Oral
-best with food |
|
|
Itraconazole inhibits a broad range of fungi except __1__ and __2__
|
Fusarium
Zygomycetes |
|
|
Itraconazole trade name
|
Sporanox
|
|
|
Property of Itraconazole
|
Lipophilic = accumulates in nails and fatty tissue
|
|
|
Solution or IV Itraconazole are used for some systemic infections especially in _________
|
IC'ed patients
|
|
|
Antifungal that is contraindicated in patients with Heart or Liver Disease
|
Itraconazole
|
|
|
40% of Itraconazole is excreted as _________ in urine
|
inactive metabolites
|
|
|
Issue with Itraconazole
|
serious drug interactions
|
|
|
Voriconazole trade name:
It is marketed for: |
Vfend
Aspergillosis |
|
|
Voriconazole is fungistatic to these fungi
|
Candida
Aspergillus Cryptococcus Blastomyces Coccidioides Histoplasma Fusarium Penicillium |
|
|
Voriconazole is not effective against ________
|
Zygomycetes
|
|
|
Voriconazole half-life is ________
|
Dose dependent, enzyme saturation
|
|
|
Survival rate of 71% in patients with solid organ tranplants on __1__, compared to 58% with __2__
|
1. Voriconazole
2. Amphotericin B |
|
|
Rifampicin is contraindicated with this antifungal drug
|
Voriconazole
|
|
|
Side effects of Voriconazole (2)
|
Visual disturbances
Hepatic issues |
|
|
____% of Voriconazole is excreted as metabolites in the urine
|
80%
-<2% is unchanged |
|
|
This new azole drug is broadly active but cross resistance with Itraconazole or Fluconazole.
It has a stronger inhibition of P450 target than Itraconazole |
Posaconazole (Noxafil)
|
|
|
Posaconazole trade name
|
Noxafil
|
|
|
New azole drug with similar activity to Fluconazole and Voriconazole and Itraconazole
|
Ravuconazole
|
|
|
Class of Antifungals that disrupt fungal membrane by forming pores
|
Polyene antibiotics (macrolides)
|
|
|
Are polyene antibiotics fungistatic or fungicidal?
|
Fungicidal
|
|
|
2 polyene antibiotics
|
1. Amphotericin B
2. Nystatin |
|
|
Nystatin was developed from ______.
There are new _____ formulations |
soil Actinomycete
Liposomal |
|
|
Topical Nystatin is used for: 1
Nystatin lozenges are used for: 2 Oral Nystatin for: 3 |
1. Cutaneous candidiasis
2. Oropharyngeal candidiasis (thrush) 3. vulvovaginal candidiasis |
|
|
Is nystatin resistance common or uncommon?
What is Nystatin not useful for? |
uncommon
Systemic infections |
|
|
Nystatin is not presently useful for ________ treatment
|
systemic
|
|
|
Amphotericin B: fungicidal or fungistatic?
|
Fungicidal
|
|
|
Amphotericin B has broad range activity except against __1__ and __2__
|
1. Fusarium
2. Malassezia |
|
|
Amphotericin B resistance is uncommon but can be clinically relevant in _______
|
Candida
|
|
|
Amphotericin B plasma half-life: _1_
Elimination half-life: _2_ |
1. 24 hours
2. 15 days |
|
|
What is the first line of defense for Systemic and Opportunistic infections?
|
Amphotericin B
|
|
|
Serious side effects of Amphotericin include _______
|
nephrotoxicity
-lipid and liposomal formulations help with this |
|
|
Most treatments with Amphotericin B require _____ administration
|
IV
*oral absorption is very low |
|
|
Cerebral infections may require _______ administration of Amphotericin B
|
intrathecal
|
|
|
Amphotericin B is sometimes administered in combo with _______
|
Flucytosine for Cryptococcal meningitis
|
|
|
Dosing of Amphotericin B is based on _______
|
cumulative dose
-.3 to 1.5 mg/kg over 1-4 hrs |
|
|
Amphotericin B accumulates in these 3 parts of the body
|
Spleen
Liver Lung |
|
|
Lipid formulation of Amphotericin B = 1
Liposomal formulation = 2 |
1. Abelcet
2. Ambisome -for pediatric administration |
|
|
Griseofulvin is indicated for: __1__
-half life = _2_ -cheap and is used for: _3_ -side effects: _4_ -currently clinical trials are looks at efficacy vs. __5__ |
1. Dermatophytes
2. 9-24 hrs 3. tinea capitis 4. Headache, rash, confusion 5. Terbinafine |
|
|
Griseofulvin is isolated from ________
|
Penicillium
|
|
|
Griseofulvin disrupts _______
|
mitotic spindle = inhibits mitosis
|
|
|
Griseofulvin side effects
|
HEADACHE
rash confusion photosensitivity fatigue nausea peripheral neuropathy |
|
|
Echinocandins are inhibitors of ____________
|
cell wall synthesis
|
|
|
List 3 Echinocandins
|
Caspofungin
Anidulafungin Micafungin *all end in FUNGIN |
|
|
Echinocandins block synthesis of _________
Derivatives of the natural product ________ Produced by _______ |
1-3-beta glucan
pneumocandin Bo Glarea Iozoyensis |
|
|
Trade name of Caspofungin
|
Cancidas
|
|
|
What is Caspofungin?
|
An Echinocandin = inhibit glucan synthesis
|
|
|
Caspofungin properties
|
-poor oral bioavailability
-slow elimination (6-8 days) |
|
|
Caspofungin is prescribed for these 2 things
|
Aspergillosis
Candidemia *Glucan synthetase inhibitor |
|
|
Most serious toxin exposure is from contaminated _____
|
grain
|
|
|
Most common symptom of mushroom poisoning is ______
|
vomiting
|
|
|
Most therapies depend on targeting ________
|
Ergosterol containing membranes or inhibiting sterol synthesis
|
|
|
Organism in which Arthrospores are the infectious molecule
|
Coccidiomycosis
|

