![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lipids are
-nonpolar -bipolar -polar -hyperpolar |
Nonpolar
|
|
|
Lipids are a class of biomolecules whose only common feature is
|
that they are NOT soluble in water
|
|
|
What are the important functions of lipids
|
-structural component of MEMBRANES
-ENERY STORAGE -PROTECTIVE coating -metabolic regulation (warmth) |
|
|
What are fatty acids?
|
long-chain monocarboxylic (mono = 1) acids that are the major components of fats and oils
Basically long hydrocarbon chains with a carbonyl group |
|
|
What are three major characteristics of fatty acids?
-solubility -arrangement -bonding |
INSOLUBLE in water (like all lipids)
Ussually made up of EVEN number of carbons in a STRAIGHT chain. May or May not include double bonds |
|
|
If a fatty acid chain includes double bonds it is called
|
UNSATURATED
|
|
|
If a fatty acid chain contains several double bonds it is termed
|
POLY unsaturated
|
|
|
If a fatty acid has no double bonds it is then called
|
SATURATED
|
|
|
Lipds are distinguished in to TWO categories. What are they?
|
Saponifiable and non-saponifiable lipids
|
|
|
Name the 5 examples of saponifiable lipids
|
Waxes
Triglycerides Phosphoglycerides Sphingolypids Glycolipids |
|
|
Name the 2 examples of non-saponifiable lipids
|
Steroids and Terpenes (TARPAN, lol)
|
|
|
Waxes are...
|
esters of fatty acids and long-chain alcohols
|
|
|
What is the purpose of waxes
|
protective coatings for hair, skin, and feathers, and to protect plants from dehydration and insects
|
|
|
Triglycerides, which are also known as triglycerols, are
|
esters of glycerol and three fatty acids
|
|
|
Glycerols are classified as monoglycerols, diglycerols or triglycerols according to WHAT?
|
the number of fatty acids they have attached to the glycerol group.
|
|
|
Fats are ________ at room temperature and are obtained usually from
________ sources |
SOLIDS; ANIMAL
|
|
|
Oils are ________ at room temperature and are obtained usually from _______ sources
|
liquid; PLANT
|
|
|
WHAT CONDITIONS ARE REQUIRED FOR THE "HYDROLYSIS" OF TRIGLYCERIDES TO TAKE PLACE?
|
3 moles of water +
H+ or lipase |
|
|
What are the two PRODUCTS we get in the process of "HYDROLYSIS" of tricerides?
|
GLYCEROL and THREE fatty acids
|
|
|
in the "HYDROLYSIS" of triglycerides, which bond is cleaved?
|
The bond between the Carbonyl Carbon and its neighboring oxygen.
|
|
|
HYDROLYSIS of triglycerides
|
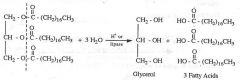
Name the reaction
|
|
|
"SAPONIFICATION" of triglycerides
|
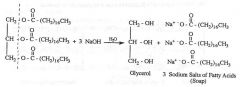
Name the reaction
|
|
|
What are the products in "SAPONIFICATION" of triglycerides?
|
Glycerol and 3 SALTs of fatty acids
|
|
|
What conditions are required for the saponification of triglycerides?
|
a BASE (KOH, LiOH, NaOH) and Water
|
|
|
What simple property is at play in the "cleaning action of soap"?
|
Like dissolves like
|
|
|
In the cleaning action of soap, what are the characteristics of the heads and tails of soap molecules?
|
Soap molecules have polar heads (hydrophyllic) and non-polar tails (hydrophobic)
|
|
|
what part of the soap molecule is responsible for the removal of oil and dirt from the skin?
|
The TAILS of the soap since they are NONPOLAR as is dirt and oil
|
|
|
Emulsions that are formed can be broken down into smaller bodies called __________ as a result of scrubbing.
|
Micelles
|
|
|
Hydrogenation of Triglycerides
|
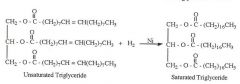
Name the reaction
|
|
|
What catalyst is required to HYDROGENATE triglycerides?
|
Ni, Pt, Pd (one of these)
|
|
|
In the food pyramid where do fats and oils sit? Why?
|
On the top. Because they should be used sparingly to prevent artheriosclerosis
|
|
|
1 gram of fat or oil
|
9 calories
|
|
|
1 gram of carbohydrates or proteins
|
4 calories
|
|
|
Lipids have a _____ energy content
|
HIGH
|
|
|
Unused nutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids) are converted into small ____________ that are deposited in _____________
|
GLOBULES OF FAT; ADIPOSE TISSUE
|
|
|
The energy storage of ___________is long-term, unlike the energy storage of __________, which is short-term
|
ADIPOSE TISSUE; GLYCOGEN
|
|
|
Percent fat (% fat) =
|
(fat calories/total calories) × 100
|
|
|
Fat calories =
|
number of grams of fat listed on the label × (9 calories/1 gram of fat)
|
|
|
Phosphoglycerides have two fatty acids: a ____________ and an _________________
|
PHOSPHATE GROUP; AMINO ALCOHOL
|
|
|
Phosphoglycerudes are found in
|
cell membranes
|
|
|
The fluid mosaic model says that a cell membrane has a double layer of phospholipids, which is called the ____________
|
lipid bilayer
|
|
|
The center of this layer has ________ hydrocarbon tails
The outer surface has the polar phosphate and amino alcohol groups |
nonpolar on the inside and polar surface (much like soap)
|
|
|
TOUGH QUESTION!
Sphingolipids contain |
the amino alcohol sphingosine, instead of glycerol, one fatty acid, a phosphate group, and an amino alcohol
Unlike most saponifiable lipids, they have an amide bond instead of an ester bond |
|
|
Sphingolipids are found in
|
the brain and nerve tissue
|
|
|
Glycolipids contain
|
sphingosine, one fatty acid, and a monosaccharide (usually galactose or glucose)
|
|
|
Glycolipids are found in
|
the brain and in the myelin of neurons
|
|
|
__________ have a fused-ring structure that is called the steroid nucleus
|
Steroids
|
|
|
_____________ is the most common type of steroid
|
Cholesterol
|
|
|
Cholesterol is essential for the production of
|
hormones, vitamin D and bile acids
|
|
|
Where is cholesterol found in the body?
|
brain, nerve tissue, myelin, cellular membranes and the liver
|
|
|
What are the TWO sources of Cholesterol in the body?
|
Those synthesized by the body from fats
AND Those consumed in animal products |
|
|
________ are found in essential oils and flavorings, chlorophyll, and the visual pigments of the retina
|
terpene
|
|
|
Vitamin _____ is a Terpene
|
A
|

