![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
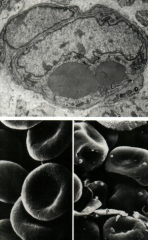
|
Erythrocytes (SEM) No nucleus
Note: Normal, biconcave RBCs (Left) Irregularly shaped RBCs of spherocytosis (Right) |
|
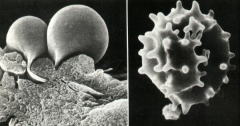
|
Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of RBCs
Note: Echinocytes - Transformed RBCs (Right) |
|
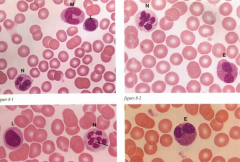
|
Top Left: Neutrophil (N), Monocyte (M), Lymphocyte (L) Top Right: Eosinophil (E), Neutrophil (N) Bottom Left: Lymphocyte (L), Neutrophil (N) Bottom Right: Eosinophil (E)
Function of Eosinophils: Parasitic infections - they have enzymes to fight infection - Peroxidases and oxidase enzymes fight infections
Function of Neutrophils: Phagocytosis
Primary function of Macrophages: Phagocytosis
|
|
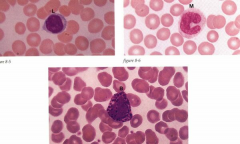
|
Lymphocyte (L), Monocyte (M), Basophil (B) (Found in blood)
Basophil function: Similar to mast cells, release histamine in response to allergic or parasitic reactions. Mast cells seen in connective tissue throughout body |
|
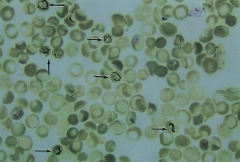
|
Reticulocytes |
|
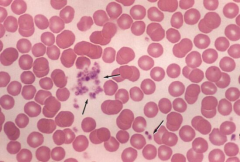
|
Platelets, process of platelet formation, blepping |
|
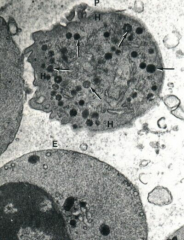
|
Platelet (SEM)
Note: Granules in the region called "granulomere" |
|
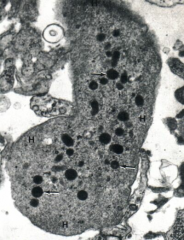
|
Platelet (SEM)
Note: Granule free peripheral region called "Hyalomere" (H) |
|
|
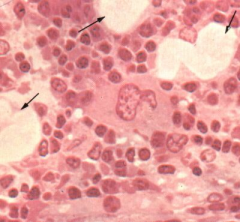
Hemopoiesis - Bone marrow (Andria note: Hamopoiesis is the growth/development of blood cells)
Function: Red, platelet, WBC, etc.
Erythropoiesis, leukopoiesis, hemopoiesis
Note: Megakaryocyte function - platelet production
Fat cells int he stroma (arrow) |
|
|
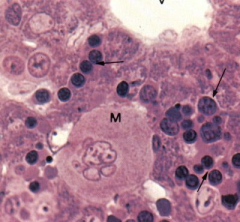
Hemopoiesis in the liver
Note: Hepatocytes (Vesicular nuclei), Central Vein (V), Hemopoietic elements (arrows), meakaryocyte (M) |
|
|
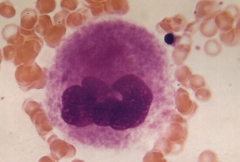
Megakaryocyte
Note: Multilobulated nucleus and granular appearing cytoplasm |
|
|
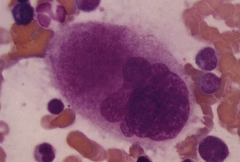
Mature megakaryocyte |
|
|
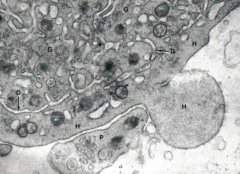
Platelet formation (SEM)
Note: Blebbing of the hyalomere (H) Demarcation vesicles (D)
|
|
|
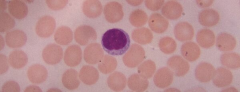
Lymphocyte (Peripheral blood) |
|
|
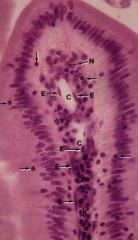
Lymphocyte in the epithelium and lamina propria of SI Villus (arrow)
Note: Lymphocytes (arrows) Central lacteal (lymphatic capillary) Endocytes (E) PMN (N) |
|
|
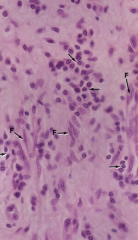
Lymphatic tissue in loose connective tissue
Note: Fibroblasts (F) Lymphocytes (arrow) |
|
|
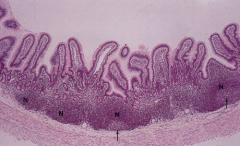
Peyer's patches in ileum. Function: immune function
Note: Nodular aggregates of lymphocytes (N) Germinal center (arrow) |
|
|
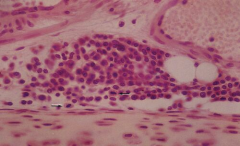
Nodular Aggregates of lymphocytes
Note: Cells in mitosis |
|
|
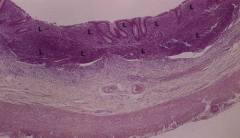
Appendix
Note: Abundant lymphocyte concentration (L) |
|
|
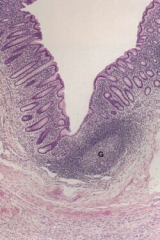
Large intestine showing a lymphatic nodule (collection of lymph nodes)
Note: Germinal center (G) |
|
|
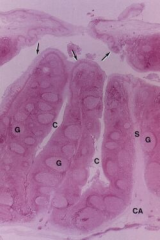
Palatine tonsil - Partially encapsulated lymphoid organ
Note: Stratified squamous epithelium (arrows) Crypts - Epithelial invaginations (C) Connective tissue of capsule (CA) |
|
|
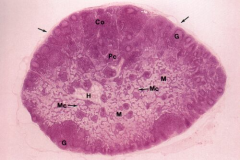
Lymphoid (whole)
Note: Cortex (Co), Paracortex (Pc), Medulla (M), Hilum (H), Capsule (arrows), Medullary cords of lymphocytes (Mc) |
|
|
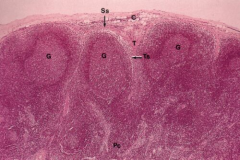
Lymph node - Cortex
Note: Subcapsular sinus (Ss), Capsule (C), Connective tissue trabecula (T), Germinal centers of secretive nodules of cortex (G), Trabecula sinus (Ts) |
|
|
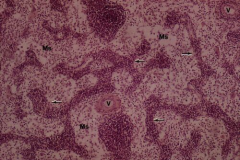
Lymph node
Note: Medullary sinuses (Ms), Blood vessels (V), Medullar cords of lymphocytes (arrow) |
|
|
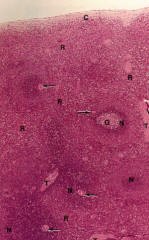
Spleen function: immune function and a minor reservoir for blood storage. Bacterial clearance occurs here
Note: Lymphatic nodules of red and white pulp (N), Germinal center (G), Central artery (arrow) |
|
|
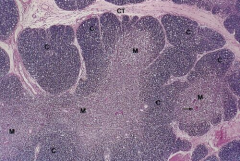
Thymus
Note: Hassall's corpuscle (arrow) Absence of nodules in - Cortex (C) and Medulla (M) |
|
|
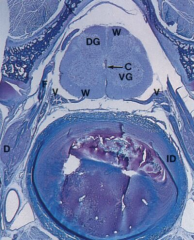
Spinal Cord and nerve fibers of dorsal roots (F) and ventral roots (V)
Note: White matter (W), Dorsal gray matter (DG), Ventral gray matter (VG), Dorsal root ganglion (D), Central canal (C), Inter vertebral disc (ID) |
|
|
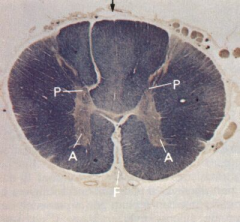
Spinal cord - Transverse section
Note: White matter (Peripheral), gray matter (Central H-form), Anterior horn (A), Posterior horn (P), Anterior median fissure (F), Posterior median septum (arrow) |
|
|
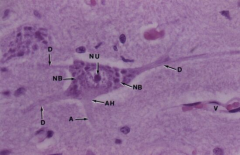
Motor Neuron
Note: Nucleolus (NI), Nissl Bodies (NB), Axon hillock (AH), Axon (A), Dendrites (D), Blood vessels (V) |
|
|
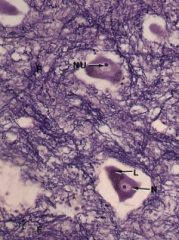
Ventral gray matter and motor neurons
Note: Nerve fibers (F), Nucleus (N), Nucleolus (NU), Lipofuscin (L) |
|
|
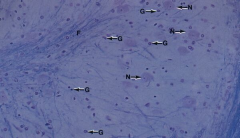
Neuronal cells (N) and Neuroglial cells (G) - Morphology |
|
|
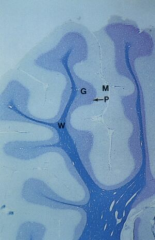
Cerebellum
Note: Molecular layer (M), Granular layer (G), Purkinje layer (P), White layer (W) |
|
|
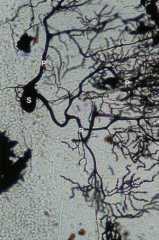
Cerebellum
Note: A typical Purkinje cells (S), highly branched cell process (P) |
|
|
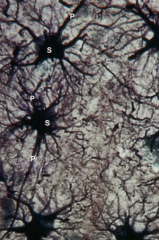
Protoplasmic astrocytes (Gray matter of spinal cord) / Mossy cells. Provide nutritional and structural support
Note: Cell body (soma) (S), Cell processes (P) |
|
|
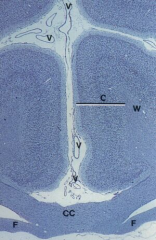
Cerebral cortex (C) (B-layers)
Note: White matter (W), Blood vessel (V), Corpus callosum (CC), fornix (F) |
|
|
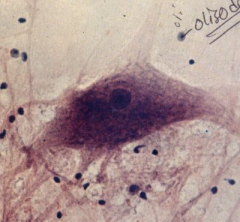
Anterior Horn (Motor) of spinal cord
Note: Oligodendrocytes (function - synthesize myelon, seen in CNS - in PNS, joan cells synthesize myelon) (CHECK IT), Multipolar neuron |
|
|
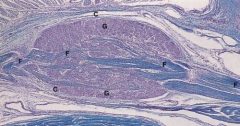
Pseudounipolar Neuron
Note: The single process leaving the perikaryon (arrow) |
|
|
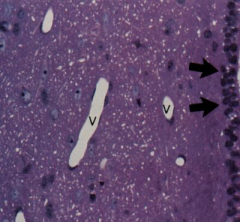
Ependymal cells lining the ventricle of the brain and spinal canal (fxn directional flow of CSF) (arrow)
Note: Simple cuboidal epithelium with apical cilia in capillaries (V) Nuclei of astrocytes Oligodendrocytes |
|
|
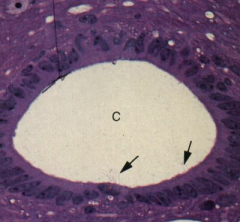
Epdnymal lining the central canal (C) of the spinal cord
Simplecolumnar epithelium with cilia (arrow) and microvilli |
|
|
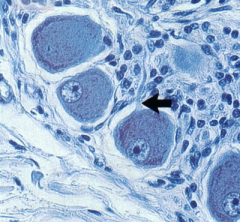
Dorsal root ganglion in PNS (sensory)
Note: Connective tissue capsule (C) Ganglion (G) Nerve fibers (F) |
|
|
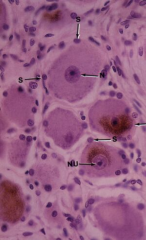
Dorsal root ganglion (sensory)
Note: Large ganglion cells Nucleus (N) Nucleolus (Nu) Satellite cells (S) Lipofuscin (L) |
|
|
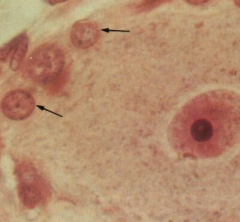
Synpathetic ganglion aka autonomic ganglion supporting cells of sympth ganglion
Note: Ganglion cell Satellite cells (arrow) fxn nutritional support |
|
|
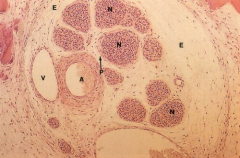
Periphereal nerve bundle
Note: Epineurium (E), perineurium (P), Nerve fascicle (N), Artery (A), Vein (V) |
|
|
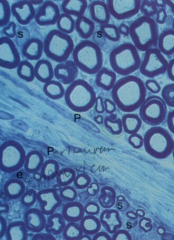
Myelinated nerve fibers
Note: Perineurium (P), Myelin sheath, Schwan cells (S), Endoneural nuclei |
|
|
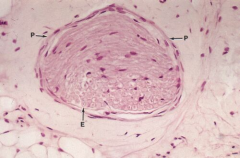
Solitary nerve fascicle
Note: Perineurium (P) Endoneurium of the nerve fiber (E) |
|
|
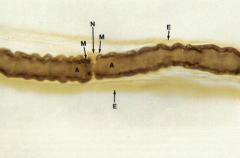
Myelinated nerve fiber with the node of Ranvier (fxn: saltitory, faster conduction) (N)
Note: Myelin sheath, Axon (A), Endoneurium of the node (E) |
|
|
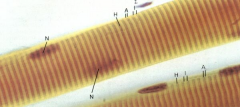
Skeletal muscle fibers, striated. It's a true synsechium (formed by fusion of multiple myoblasts) - Looks like one unit and functions as one unit
Note: Nuclei (N), Dark bands (A), Light bands (I), Central "H" bands (Light) |
|
|
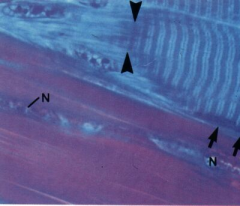
Musculo tendinous junction
Note: Connective tissue of endomysium Collagen bundles Nuclei of fibroblasts (Tenocytes) (N) |
|
|
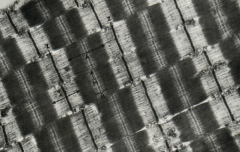
Electron Micrograph of myofibrils
Note: Dark bands (anisotropic) (A) Light 'H' bands with 'M' line (dark) Iosotropic light bands (I) with dark 'Z' lines (Sarcomere Z to Z) or Discs |
|
|
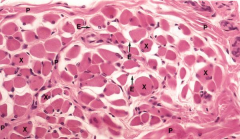
Skeletal muscle fascicle
Note: Perimysium (P), Endomysium (E) |
|

|
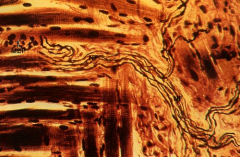
Sacrospinalis (Transverse section)
Note: Red (R) and White (W) fibers Intermediate fibers (I) |
|
|
Myoneural Junction Function: Conduct signal, releases acetylcholine to nicotinic receptor (Motor end plate)
Note: Motor ed plate (MEP), nerve fibers, skeletal muscle fibers |
|
|
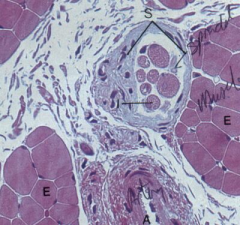
Neuromuscular Muscle spindle (S) Function: Proprioception
Note: Intrafusal fibers (I), Extrafusal fibers (E), Artery (A) |
|
|
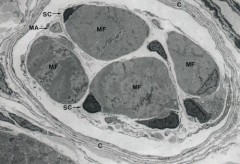
Electron micrograph of a muscle spindle
Note: Intrafusal muscle fibers (MF), Connective tissue capsule (C), Satellite cells of muscle fibers (SC), Myelinated axon (MA) |
|
|
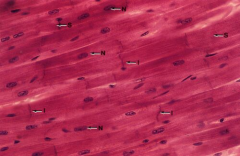
Cardiac muscle
Note: Central nuclei, intercalated disc |
|
|
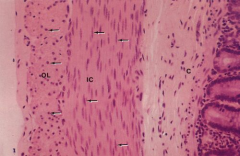
Intestinal smooth muscle (cross section)
Note: Inner circular layer (IC), outer longitudinal layer (OL), Connective tissue (C) |

