![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Metabolism |
The sum of all energy transformation occurring within an organism and between the organism and it's environment |
|
|
|
Turbidity increase |
The greater number of cells present the more light reflect rather than transmits. |
Growth |
|
|
Turbidity decrease. |
Large colloidal will appear translucent if those large particles are broken down by hydrolysis exoenxymes into smaller crystalloid particles |
Hydrolysis |
|
|
HYDROLYSIS OF STARCH |
Coenzymes- amylase Hydrolysis Starch to sugar Iodine is added to medium Starch is present-purple Starch hydrolyzed to sugar no color change.
Agar plate, after incubation pour gram iodine.
Positive for amylase- no color change Negative for amylase - dark purple sound streak line.
Medium- agar Subtrate - starch Reagents - Iodine Positive-sugar
Iodine bind to starch |

|
|
|
Hydrolysis of gelatin |
Exoenzyme galatinese Hydrolysis of gelatin cause liquefy. Use of gelatin is accomplished by the enzyme gelatinase. Medium- gelatin Substrate- nutrient agar Reagents- none Nutrient agar tall tube Needle Positive liqidifed Negative - remains solid |

|
|
|
FERMENTATION OF CARBONHDRATES |
Product CO2 + pyruvic acid acidPh indicator-Phenol red Ph indicator-Phenol red
FERMENTATION BROTHS: EITHER SUCROSE,GLUCOSE,LACTOSE OR MANNITOL. Durham tube- inverted(use to collect gas)
|

|
|
|
REDUCTION OF NITRATE |
Presence of nitrite by adding sulfanilic acid and dimethyl-alpha-naphthylamine (DAN). NO COLOR CHANGE 1.Bacteria did not reduce to nitrate - N 2.Bacteria reduce nitrate to nitrite and further reduce nitrate to NH4. 3.Bacteria reduce nitrate to nitrite Further reduce nitrite to nitrogen If no color than add ZINC (catalyst) Nitrate broth After incubation add 5 drop sulfanilic and 3 DAN. nterpretation:• red after addition of reagents 1 and 2 : positive for nitrites• clear after addition of reagents 1 and 2 : add reagent 3 (zinc)• clear after addition of reagent 3 : positive for nitrite• red after addition of reagent 3 : negative for nitrites and nitrogen gas |

|
|
|
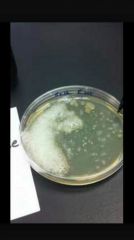
DETECTION OF CATALASE |
Used to differtiate aerobic and obligated aerobic bacteria. Anaerobic general lack the enzymes. Catalase enzymes neutralize the bacterial effects of hydrogen peroxide. |
|
|
|
Decarboxylases |
Decarboxylase broth tests for the production of the enzyme decarboxylase, which removes the carboxyl group from an amino acid. pH indicators bromcresol purple and cresol red. Bromcresol purple turns purple at an alkaline pH and turns yellow at an acidic pH. The three amino acids arginine lysine ornithine End product amino acid The decarboxylase test is useful for differentiating the Enterobacteriaceae. Oil layer on top |

|
|
|
HYDROLYSIS OF UREA |
Produces an exoenzyme UREASE Which can catalyze the breakdown of urea to AMMONIA and CARBON DIOXIDE GAS PHENOL RED into is included in the broth to test for the present of ammonia in the reaction. PH 6.9 RED (SLIGHT BASE) PH 6.9 - ABOVE HOTPINK (STRONG) PH6.9 LOWER YELLOW /GOLD (ACID) |

|
|
|
SIM REACTION SILFIDE/INDOLE/MOTILITY |
The sulfur reduction test is useful in differentiating enteric organisms. The indole test is a component of the IMViC series of tests, which is used for differentiating the Enterobacteriaceae. The motility test is useful for testing a wide variety of organisms. As a whole, the SIM test is primarily useful for differentiating Salmonella and Shigella Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Test -tests for enzyme cysteine desulfurase-bacteria with this enzyme can break down amino acid cysteine - growth medium- SIM medium agar Positive= black Negative= medium remains yellow or black line forms just below surface b. Indole Test -tests for enzyme tryptophanase- if bacteria has they can break down tryptophan - growth medium=SIM medium - Positive= pink strip -Negative= white strip (no change)Indole Test-note #22 (the middle strip) is the ONLY NEGATIVE =WHITE strip c.Motility Test += black or yellow with fuzzy growth - = yellow with 2d ribbon growth *note-when reading motility- ignore the little black line just below surface?Motility Test= Negative=2d Ribbon |
|
|
|
MR(METHYL RED)-VP (VOGES-PROSKAUER REACTION MR-VP |
aid in the identification of enteric gram-negative bacilli.ptimarily for ENTEROBACTERIACEAE. Voges-Proskauer TestA positive VP test is demonstrated by the development of a pink-red color on the surface of the medium 15 minutes to one hour after the addition of the reagents.A negative VP test is demonstrated by the appearance of a yellow color on the surface of the medium. Development of a copper-like color is also interpreted as negative.Methyl Red TestA positive MR test is demonstrated by the development of a stable red color on the surface of the medium after the addition of methyl red indicator.A negative MR test is demonstrated by the development of a yellow color on the surface of the medium. |

|
|
|
SIMMONS CITRATE TEST |
Use to determine carbon nd ammonium PH indicator bromthymol blue blue |

|
|
|
IMVIC test |
The IMViC tests are useful for differentiating the Enterobacteriaceae, especially when used alongside the urease test. When used alone, the IMViC tests are particularly useful for differentiating Escherichia coli, Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter cloacae, and Klebsiella pneumoniae (although colonial morphology and the presence of capsules can also be used to differentiate Klebsiella).The IMViC series includes four tests: Indole production (for which we use SIM medium)the methyl red testthe Voges-Proskauer testand citrate production |
|
|
|
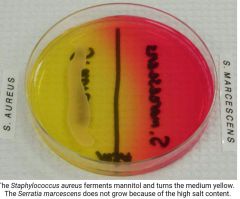
MANNITOL SALT |
Problem associated with staphylocci.importsnt to be able to separate staphylocci.importsnt from sttetocci.thr pathogenic strain of staphylococcus Aires is form in the NASPPHARYNX of between 30- 50 percent of population., the throat culture can easily be obtained. Agar contains mannitol (alcohol sugar ) PH INDICATOR Phenol red MSA also contains the sugar mannitol and the pH indicator phenol red. If an organism can ferment mannitol, an acidic byproduct is formed that will cause the phenol red in the agar to turn yellow. Most pathogenic staphylococci, such as Staphylococcus aureus, will ferment mannitol. Most non-pathogenic staphylococci will not ferment mannitol. |
|
|
|
COAGULASE PRODUCTIIN |
The coagulase test identifies whether an organism produces the exoenzyme coagulase, which causes the fibrin of blood plasma to clot. Organisms that produce catalase can form protective barriers of fibrin around themselves, making themselves highly resistant to phagocytosis, other immune responses, and some other antimicrobial agents The coagulase test is useful for differentiating potentially pathogenic Staphylococci such as Staphylococcus aureus from other Gram positive, catalase-positive cocci. |

Clot us postive No clot negative |
|
|
Red whitr |
Bkue |
|

