![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Capacity
|
maximum rate of output (no one best way to measure) (ability to hold, receive, store, or accommodate)
|
|
|
Design capacity
|
maximum output rate under ideal conditions (difficult to sustain)
|
|
|
effective capacity
|
maximum output rate under normal (realistic) conditions
|
|
|
capacity utilization rate
|
what's being used versus what's available
CUR - (capacity used) / (best operating rate) |
|
|
economies of scale
|
economic benefit of operating at a high volume (discounts for buying a lot)
|
|
|
economies of scope
|
ability to compete on flexibility
|
|
|
capacity strategy
|
decisions about the size of plant and equipment
|
|
|
capacity cushion (leading strategy)
|
prepare for the 'just in case', resources on staff to meet the demand should it arrive
|
|
|
demand cushion (lagging strategy)
|
fixed costs more easily covered; know demand is there; maintains high inventory or backlogs
|
|
|
capacity planning time - long range
|
greater than one year (brick and mortar)
|
|
|
capacity planning time - intermediate range
|
plans covering next 6 to 18 months (suppliers)
|
|
|
capacity planning time - short range
|
less than one month (overtime)
|
|
|
strategic capacity (capacity flexibility)
|
being able to have flexibility (facilities, equipment, labor force size); the ability to rapidly increase or decrease product levels of the ability to shift rapidly from one product or service to another
|
|
|
capacity focus
|
the idea that a production facility works best when it is concentrated on a limited set of production objectives
|
|
|
capacity flexibility - plant
|
quickly adapt to change; zero change over time
|
|
|
capacity flexibility - process
|
example: 1 black car, next white (no wait)
|
|
|
capacity flexibility - labor
|
encouraged so prepared when demand requires it
|
|
|
Considerations for changing capacity (4)
|
- monitoring system balance (find the 'sweet spot')
- frequency of capacity additions - external sources of capacity - decreasing capacity |
|
|
Determining capacity requirements (steps)
|
- forecast: use to predict sales for individual products
- calculate equipment and labor requirements - capacity utilization - machine requirement - labor requirement - project equipment and labor availability |
|
|
decision trees for capacity analysis
|
tool to determine a sequence of steps to solve a problem (see example ch 4 page 9)
|
|
|
project
|
unique 1 time activity or event (set of tasks completed only once)
- ex: writing a term paper, developing a supply chain IS, designing an iPod |
|
|
project management
|
planning, directing, and controlling resources to meet technical, cost, and time constraints
|
|
|
PMBOK
|
Project Manager Body of Knowledge
|
|
|
PMBOK - scope management
|
understand why you're taking project and expect results
|
|
|
PMBOK - quality management
|
what illustrates good or bad
|
|
|
PMBOK - cost management
|
project budget and controls
|
|
|
PMBOK - contracts/purchasing
|
establish and monitor the vendors
|
|
|
PMBOK - time management
|
schedules, resource planning
|
|
|
PMBOK - risk management
|
what risks should have a plan if it should occur
|
|
|
PMBOK - human resources
|
right people assigned at the right time
|
|
|
PMBOK - communication management
|
keep everyone on the same page
|
|
|
PMBOK - project integration
|
fitting project into the existing organization
|
|
|
Pure project
|
a team works full time on project
|
|
|
functional
|
one functional area of the firm
|
|
|
matrix
|
blend of pure and function projects
pure - a team works full time on project functional - one functional area of the firm |
|
|
project life cycle - concept study and organizational commitment
|
0 - establish need, consider/evaluate/select alternatives
|
|
|
project life cycle - development
|
1 - plans for scope, cost, quality, time, and resource utilization
|
|
|
project life cycle - implementation
|
2 - deploy and monitor resources, subcontractors, and materials to complete
|
|
|
project life cycle - project completion and operation
|
3 - deliver project to customer; complete payments and recieving
|
|
|
statement of work
|
written description of objectives to be achieved
|
|
|
task
|
further subdivision of a project (usually shorter than several months)
|
|
|
work package
|
group of activities combined to be assignable to a single organizational unit
|
|
|
project milestone
|
specific events in the life of the project
|
|
|
work breakdown structure (WBS)
|
top-down breakdown of all the tasks (schedule - make sure to capture all events needed to pull it off)
|
|
|
project control - Gantt charts
|
see at a glance behind, ahead, and on target (progress of project)
can show simultaneous events |
|
|
Earned value management (EVM)
|
technique for measuring project progress in an objective manner
|
|
|
Network Planning Models
|
a project is made up of a sequence of actities that form a network
|
|
|
Critical Path Method (CPM)
|
- identify each activity to be done and estimate how long it will take
- determine the require sequence and construct a network diagram - determine the critical path: the longest time it takes to get through the network |
|
|
project crashing
|
- prepare a CPM diagram
- determine the cost per unit of time to expedite each activity - compute the critical path and shorten the critical path at the point where costs are lowest |
|
|
production processes
|
used to make any manufactured item (customers need to be at center)
- source the parts needed - make the product - deliver the product |
|
|
lead time
|
the time needed to respond to a customer order (want low)
|
|
|
customers order decoupling point
|
inventory positioned to allow entities to operate independently (ex: Lowes colors)
|
|
|
lean manufacturing
|
high level of customer service with minimal inventory investment
|
|
|
make-to-stock
|
serve customers from finished goods inventory (balance inventory with customer service)
|
|
|
assemble-to-order
|
make the customer's product from raw materials, parts, and components
|
|
|
engineer-to-order
|
work with customer design and make the product
|
|
|
vertical integration (FWD & BKWD)
|
how to decide source, make, and deliver
- FWD: you do make - decide to start delivering - BKWD: you do make - buy suppliers to source or make something else |
|
|
product layout
|
value added resources travel in sequence
-: no flexibility, customer needs go down +: large quantity, low price |
|
|
process layout (functional)
|
value added resources arranged in groups
-: efficiency, complex +: flexibility |
|
|
fixed position layout
|
value added resources travel to site
-: lack efficiency +: selective, quality, experts |
|
|
Inventory turnover (formula)
|
cost of goods sold / avg aggragate value of the inv
|
|
|
total value (at cost) of inventory (formula)
|
SUM [(avg inventory for item i)*(unit value for item i)]
|
|
|
days of supply (formula)
|
average aggregate value of inventory / [cost of goods sold / 365]
|
|
|
Work Station Cycle Time
|
uniform time interval in which a conveyor passes a series of workstations
|
|
|
assembly line balancing
|
assigning tasks to a series of workstations (meet cycle time and minimize idle time) - see example ch 6 page 9
|
|
|
TAKT (customer polling)
|
trumps slowest work station - how often is customer pulling (usually slower than cycle time)
|
|
|
break even analysis (BEV) (formula)
|
(FCa - FCb) / (VCb - VCa)
FC - fixed cost VC - variable cost |
|
|
EVM - Planned value
|
PV, BCWS - what is planned when scheduling
|
|
|
EVM - Actual cost incured
|
AC - accounting records or what actually happens
|
|
|
EVM - Earned Value
|
EV, BCWP - actual cost of scheduled work
|
|
|
EVM - Cost performance index (CPI)
|
BCWP / AC
[EV / AC] |
|
|
EVM - spending performance index (SPI)
|
BCWP / BCWS
[EV / PV] |
|
|
EVM - schedule variance
|
BCWP - BCWS
[EV - PV] |
|
|
EVM - cost variance
|
BCWP - AC
[EV - AC] |
|
|
Operational classification services
|
classified according to customers they service and service they provide
|
|
|
customer contact
|
physical presence of customer in the process
- high customer contact more difficult to control |
|
|
creation of the service
|
work process involved in providing the service itself
|
|
|
design process (5 steps)
|
- service concept: what kind of experience do you want customers to have?
- service package: physical items? psychological benefits? - performance spec's: customers requirements and expectations - design: cost, skills, time, activities - delivery: schedule |
|
|
free flow service layout
|
+: encourage browsing, increase impulse purchases, flexible and visually appealing
-: loitering possible, wasted floor space, hard to clean EX: disney store |
|
|
grid service layout
|
+: customer familiarity, low cost, easy to clean, secure
-: plain, limited browsing EX: kroger |
|
|
loop and spline service layout
|
+: increase customer sight lines and exposure, circulate store
EX: Ikea |
|
|
pure virtual customer contact
|
companies enable cost to interact in an open environment
EX: Ebay |
|
|
mixed virtual and actual customer contact
|
customer interact in a server-moderated environment
EX: YouTube |
|
|
Service blueprinting
|
flowchart - optimize or eliminate customer interface options
|
|
|
Poka-Yokes
|
error proof (block inevitable mistakes from becoming a service defect)
EX: phone number format on a form |
|
|
psychology of waiting
|
- use of diversions
- preferential treatment |
|
|
waiting in line problems (queues)
|
- reducing wait time costs money but raises customer satisfaction and throughput
- balance time and cost |
|
|
queuing anaylsis
|
provides information not recommendation
|
|
|
managing queues
|
- segment customers
- train servers to be friendly - manage customer expectations - divert customer attention while waiting - encourage customers to come during slack periods |
|
|
Basic Single Server model - # customers in system queue and being served
|
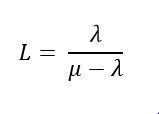
|
|
|
Basic Single Server model - average # of customers waiting in line
|

|
|
|
Basic Single Server model - average total time in system
|

|
|
|
Basic Single Server model - average time waiting in line
|

|
|
|
Basic Single Server model - probability of no system customers
|

|
|
|
Basic Single Server model - average service time
|

|
|
|
Basic Single Server model - average time between arrivals
|
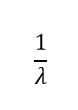
|

