![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
298 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
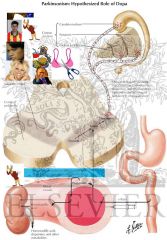
Parkinson's Disease -
What is it |
ACh and dopamine must be
in balance for normal, balanced movement dec. levels of dopamine in substantia nigra idiopathic hypokinetic |
|
|
When does it start
|
usu. starts ~50-60 y/o
|
|
|
Life expectancy
|
life expectancy ~ 9 yrs.
|
|
|
Parkinson's Disease -
|
Most cases are idiopathic
|
|

Insults that lead to
"parkinsonism" |

insults dec. dopamine -
postencephalitic |
|
|
toxic insults -
|
(carbon disulfide
manganese MPTP) |
|
|
others
|
bihemispheric ischemic
traumatic iatrogenic (neuroleptic meds) |
|
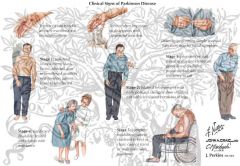
Parkinson's Disease -
History/PE |
Tremor at rest (pill rolling)
|
|
|
PD History/PE
|
cogwheel rigidity
|
|
|
PD History/PE
|
bradykinesia
|
|
|
PD History/PE gait
|
festinating(Sinirlilikten gelen hızlı yürüme eğilimi) gait
|
|
|
PD History/PE posture
|
stooped posture
|
|
|
PD History/PE posture
|
unstable posture
|
|
|
PD History/PE face
|
masked facies
|
|
|
PD History/PE memory ?
|
memory loss
|
|
|
PD History/PE writing
|
micrographia
|
|
|
PD History/PE
|
shy-dragger-
any autonomic dysfunction |
|
|
Parkinson's Disease -
Tx 1st - |
is it from a secondary cause
that can be reversed? |
|
|
Parkinson's Disease -
Tx then - 2nd question |
how does pt. function daily?
|
|

tremor but functioning -
> 60 y/o |
tremor but functioning -
> 60 y/o - amantidine |
|
|
tremor but functioning -
< 60 y/o - |

tremor but functioning -
< 60 y/o - anticholinergic |
|
|
PD tx if can't function -
|
l-dopa-carbidopa
most effective but most side effects |
|
|
l-dopa-carbidopa most side effects
|
"response fluctuations"
|
|
|
Tx fluctuations -
|
COMT or selegiline
|
|
|
list of meds -
|
L-dopa/carbidopa - mainstay
bromocriptine selegiline entacapone (COMT inhib) amantadine & anticholinerg - limited efficacy |
|
|
If meds fail & dis. advanced-
|
deep brain stimulation of
GPi and subthal nucleus, or pallidotomy - ablation of GPi (posteroventral GP) rarely done now |
|
|
Huntington's -
|

Hyperkinetic
|
|
|
Huntington's - genetics
|
AD
|
|
|
Huntington's - brain part
|
atrophy of caudate
|
|
|
Huntington's - biochemistry
|
lose GABA
|
|
|
Huntington's - genetics
|
CAG triple repeats on C4p
anticipation - prog. expansion > 39 repeats - mutant genes |
|
|
Huntington's -
History/PE |

Presents ~30-50 y/o
gradual onset of - chorea dementia altered behavior depression |
|
|
Huntington's -
Dx |
Clinical
CT MRI molecular genetic testing |
|
|
Huntington's -
Tx |
No cure
disease cannot be halted genetic counseling |
|
|
Huntington's -
Tx - psychosis |

haloperidol
|
|
|
Huntington's -
Tx minimize unwanted movements |

reserpine -
|
|
|
MCC of dementia in elderly
|

Alzheimer's -
|
|
|
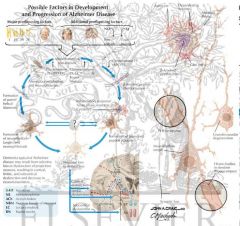
Alzheimer's -
What is it • senile plaques |
- B amyloid
|
|
|
Alzheimer's - • neurofibrillary tangles -
|
abnorm phosphorylated tau protein
|
|
|
Alzheimer's - • loss of ACh in cortex -
|
basal nucleus of Meynert
|
|
|
Alzheimer's - • amyloid angiopathy
|
=> lg lobar hemorrhage
|
|
|
Alzheimer's - brain localisation
|
• hippocampus affected early
|
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Risk factors - most important |
Age
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Risk factors syndrome |
family history
Down's (> 35 y/o) |
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Risk factors |
female gender
|
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Risk factors chromosomes |
21, 14
|
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Risk factors chromosome 1 - |
younger age
|
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Risk factors chromosome 19 |
- older
|
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Risk factors genetics of high rate of Alzheimer's |
homozygous for ApoE4 -
|
|
|
Alzheimer's -
????usually 1st sign then ?????deficits |
Amnesia usually 1st sign
then language deficits |
|
|
Alzheimer's -
History/PE |
Amnesia usually 1st sign
then language deficits acalculia depression agitation apraxia |
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Evaluation Dx |
Dx of exclusion
def. Dx only on autopsy |
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Evaluation MRI or CT - |
diffuse cortical
and subcortical atrophy |
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Evaluation Neuropsych testing - |
distinguish between
dementia and depression |
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Tx mentality |
Supportive therapy
|
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Tx first-line therapy |
Cholinesterase inhibitors -
|
|
|
Cholinesterase inhibitors -
|
donepezil
rivastigmine galantamine |
|
|
Alzheimer's - may slow cognitive decline
|
Vit E (a-tocopherol) -
|
|
|
Alzheimer's -
Complications |
death usually secondary to
aspiration pneumonia or other infections |
|
|
Alzheimer's - death
|
Survival is 5-10 yrs from
onset of sxs |
|
|
Delirium -
What is it |
impairment of consciousness -
dec. awareness of your envi can't maintain attention |
|
|
Delirium -
What is it caused by |
Caused by acute illness,
infection or drug toxicity |
|
|
Delirium -
Timing of onset |
Sudden onset
|
|
|
Delirium -
Course |
Reversible (usually)
|
|
|
Dementia -
What is it caused by Timing of onset Course |
Caused by anatomic changes
in the brain Slow, gradual onset Irreversible |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
What is it MCC |
Due to bleeding
from ruptured aneurysm MCC - head trauma (Circle of Willis) (considered separate d/o) spontan - ruptured aneurysm |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
spontan - |
(Circle of Willis)
(considered separate d/o) ruptured aneurysm usually congenital berry associated with APKD, coarctation of aorta |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
other cause |
- AV malformation
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
age of onset |
~50-60 y/o
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
mortality |
high mortality
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
History/PE onset |
Sudden-onset headache
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
History/PEjeneric sentences |
"worst headache of my life"
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
History/PE |
loss of consciousness
fever n/v neck stiffness seizure |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
History/PE CN3 palsy - |
if berry aneurysm
may be preceded by milder sentinel headaches weeks earlier |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Dx |
CT without contrast immed.
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Dx CT |
blood appears white
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Dx if CT neg - |
LP immediately
ck for xanthochromia |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Dx no LP if...... why |
inc. ICP -
sudden dec. in CSF pressure can cause further bleeding |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Dx to pinpoint location |
4-vessel angiography
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Tx to Prevent 2nd rupture - |
Prevent 2nd rupture -
most likely in 1st 48 hrs obliterate aneurysm |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Tx |
IV fluids
keep BP OK |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Tx to prevent vasospasm |
nimodipine
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Tx to prevent seizure |
phenytoin
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Tx to lower ICP - |
raise head of bed,
hyperventilation |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Tx surgery - |
clip aneurysm
IR (stent-assisted) coiling |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Tx pain meds - |
no NSAIDs
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Complications 2nd rupture - |
esp. with aneurysm
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Complications extend into brain parenchyma- |
esp. with AVM
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage -
Complications others |
arterial vasospasm
obstructive hydrocephalus |
|
|
Epidural Hematoma -
Often due to???? trauma usually ??????? fracture tear of ????????????Art. |
Often due to blunt trauma
usually lateral skull fracture tear of Middle Meningeal Art. |
|
|
Epidural Hematoma -
History/PE Lucid interval |
- min. to hrs.
then headache progressive obtundation hemiparesis "blown pupil" |
|
|
"blown pupil"
|
A mydriatic pupil will remain excessively large even in a bright environment and is sometimes colloquially referred to as a "blown pupil"
|
|
|
Epidural Hematoma -
Dx |
CT -
|
|
|
Epidural Hematoma - CT -
????shaped hyperdensity |
lens-shaped
convex hyperdensity close observation and serial neuro exams before surgery |
|
|
Epidural Hematoma -
Tx |
Neurosurgical evacuation
|
|
|
Subdural Hematoma -
What is it |
Usually after head trauma
rupture of bridging veins cortex to dural sinuses esp. elderly & alcoholics |
|
|
Subdural Hematoma -
History/PE |
Headache
change in mental status - |
|
|
Subdural Hematoma -
|
days to weeks
can present as dementia in elderly contralateral hemiparesis may have remote h/o fall |
|
|
Subdural Hematoma -
Dx |
CT -
|
|
|
CT -
|
crescent-shaped
concave hyperdensity |
|
|
Subdural Hematoma -
Tx |
Neurosurgical evacuation
blood may regress spontan- eously if chronic corticosteroids phenytoin |
|
|
Parenchymal Hemorrhage -
Causes |
HTN (usually in basal ganglia)
tumor |
|
|
Parenchymal Hemorrhage -
Causes - elderly |
amyloid angiopathy
|
|
|
Parenchymal Hemorrhage -
Causes vascular malformations - |
AVM
cavernous hemangiomas |
|
|
Parenchymal Hemorrhage -
History/PE |
lethargy
headache focal mtr & sensory deficits some obtundation |
|
|
Parenchymal Hemorrhage -
Dx |
CT without contrast
check for mass effect or edema |
|
|
Parenchymal Hemorrhage -
Tx |
Raise head of bed
antiseizure prophylaxis neurosurgical evacuation - if mass effect esp. in posterior fossa |
|
|
Coma -
What is Rule of 4 |
1. Thiamine, D50, naloxone
coma cocktail |
|
|
Coma -
What is Rule of 4 |
2. 2 mechanisms
bilateral hemisphere or RAS |
|
|
Coma -
What is Rule of 4 |
3. 3 general dis. processes
structural metabolism seizures |
|
|
Coma -
What is Rule of 4 |
4. 4 key aspects to exam
|
|
|
Coma -
General Processes: Structural |
Hematoma
Infarction Abscess Tumor Abnormal imaging lesion that occupies space |
|
|
Coma -
General Processes: Metabolism |
Electrolyte, endocrine or
metabolic functions substrate deprivation - O2, glucose vitamin deficiency organ failure - kidney toxins - meds etoh drugs infections inflammatory dis. Normal imaging |
|
|
Coma -
General Processes: Seizures |
Status epilepticus
postictal |
|
|
Coma -
4 aspects of exam |
Pupils
eye movement motor response ventilation pattern - acid-base status |
|
|
Coma - Stabilize the patient -
Tx |
Airway
Breathing Circulation |
|
|
Coma -
Tx Reverse the reversible - |
coma cocktail
O2 ID and tx underlying cause Prevent further damage |
|
|
Broca's Aphasia -
What is it What part of brain affected |
D/o of language production
motor broken speech comprehension is intact expressive or nonfluent aphasia post. inferior frontal gyrus |
|
|
Broca's Aphasia -
Features |
Repetition is impaired
|
|
|
Broca's Aphasia - why frustration -
|
cuz aware
|
|
|
Broca's Aphasia associated with -
|
arm and face hemiparesis
hemisensory loss apraxis of oral muscles |
|
|
Broca's Aphasia often secondary to
|
left superior MCA stroke
|
|
|
Broca's Aphasia -
Tx |
Speech therapy
tx underlying condition wide range of outcomes intermediate prognosis |
|
|
Wernicke's Aphasia -
What is it |
D/o of language comprehension
nonsensical production Wernicke's is wordy left post. superior temporal receptive or fluent aphasia |
|
|
Wernicke's Aphasia -
Features |
Neologisms
word substitutions unaware - no comprehension secondary to left inf./post MCA stroke |
|
|
Wernicke's Aphasia -
Tx |
Speech therapy
tx underlying condition poorer prognosis than Broca's |
|
|
Brain Neoplasms -
Mets vs. Primary |
Benign usually > 65 y/o
|
|
|
Brain Neoplasms -
Mets Metas - Lots of Bad Stuff Kills Glia |
Metas -
Lots of Bad Stuff Kills Glia Lung Breast Skin Kidney GI |
|
|
Brain Neoplasms -
Mets ?? Primary |
metas > primary
supratentorial at junction of gray and white matter |
|
|
Primary (1o) -MC primary in adults -
|
glioblastoma and meningioma
most 1o are supratentorial |
|
|
MC primary in kids -
|
medulloblastoma & astrocytoma
most 1o are infratentorial |
|
|
Brain Neoplas ms -
Dx CT with???? |
CT with contrast
|
|
|
Brain Neoplas ms -
Dx MRI with |
gadolinium
|
|
|
Brain Neoplas ms -
Dx CT-guided |
Bx
|
|
|
Brain Neoplas ms -
Dx |
Bx during surgical tumor
debulking |
|
|
Brain Neoplasms -
General Principles of Tx |
Resection (if possible)
radiation chemo palliative tx corticosteroids - reduce vasogenic edema type of therapy depends on - type of tumor histology progression site |
|
|
Brain Neoplasms:
Glioblastoma - Characteristics and Presentation |
Grade IV astrocytoma
MC primary brain tumor prognosis grave < 1 year to live can cross corpus callosum progresses fast headache ICP |
|
|
Brain Neoplasms:
Glioblastoma - Tx |
Surgical resection
radiation and chemo have variable results |
|
|
2nd MC primary
|
Meningioma -
|
|
|
Meningioma -Characteristics and
Presentation |
often incites osteoblastic
reaction in overlying cranial bones incidence inc. with age |
|
|
Meningioma - orig from
|
dura or arachnoid
|
|
|
Meningioma -prognosis
|
good prognosis
|
|
|
Brain Neoplasms:
Meningioma - Tx |
Surgical resection
radiation for unresectable |
|
|
Brain Neoplasms:
Acoustic Neuroma (Cihannoma) |
Derived from cihan cells
bilat cihannoma in NF2 |
|
|
Acoustic Neuroma (Cihannoma)Characteristics and
Presentation |
Ipsilateral hearing loss
tinnitus vertigo signs of cerebellar dysfunction facial weakness facial sensory loss |
|
|
Acoustic Neuroma (Cihannoma)
|
Surgical removal
|
|
|
Brain Neoplasms:
Astrocytoma -Sibelcanoma Characteristics and Presentation |
Grades 1 - pilocytic,
mainly kids grade 2 - diffuse grade 3 - anaplastic grade 4 - glioblastoma multif |
|
|
Sibelcanoma
Characteristics and Presentation |
headache
inc. ICP can cause unilat paralysis in CN 5-7 & CN10 |
|
|
Sibelcanoma Tx
|
Resection if possible
radiation |
|
|
Brain Neoplasms:
Medulloblastoma - sedanoma locations |
arises from cerebellum
and 4th ventricle can compress 4th ventricle may seed subarachnoid space inc. ICP |
|
|
sedanoma headache time
|
morning headaches
|
|
|
sedanoma malignancy
|
Highly malignant
|
|
|
sedanoma tx
|
Surgical resection
coupled with radiation and chemo |
|
|
Brain Neoplasms:
Ependymoma -zaranoma Characteristics and Presentation |
Common in kids
arises from ventricles and spinal cord commonly found in 4th ventricle can cause hydrocephalus |
|
|
-zaranoma
|
Surgical resection
radiation |
|
|
Neurofibromatoses -
What are they |
NF1 - HOUSE MD
von Recklinghausen AD chromosome 17 NF2 chromosome 22 |
|
|
HOUSE MD
|
2 or more of signs
|
|
|
HOUSE MD skin findingds
|
neurofibromas (2)
|
|
|
HOUSE MD skin findingds
|
cafe-au-lait spots (6)
|
|
|
HOUSE MD axillary or inguinal
|
freckling -
axillary or inguinal |
|
|
HOUSE MD eye findings
|
optic glioma
|
|
|
HOUSE MD eye findings
|
lisch nodules (2)
|
|
|
HOUSE MD eye findings
|
osseous abnorm
1st degree relative with NF1 |
|
|
NF2 - Dr Coddy
|
bilat acoustic neuromas
|
|
|
Dr Coddy or
|
1st deg. relative with NF2
and unilat acoustic neuroma |
|
|
Dr Coddy or
|
1st deg. relative with NF2
and neurofibroma, meningioma, glioma |
|
|
Dr Coddy or
|
schwannoma
|
|
|
HOuse md dx
|
MRI -
brain brain stem spine derm exam ophthal exam family Hx hearing test |
|
|
HOuse md
|
No cure
tx symptoms surgical removal for acoustic neuromas |
|
|
Tuberous Sclerosis - Kucuk zenci eleman neurologic
|
Seizures - start as infant
mental retardation |
|
|
Kucuk zenci eleman
|
skin and eye lesions
|
|
|
Kucuk zenci eleman
|
small benign tumors -
brain face eyes kidney other organs very variable clinical course |
|
|
Kucuk zenci eleman
|
AD
chromosome 9 |
|
|
Kucuk zenci velet as an infant
Hx/PE |
Infantile spasms
|
|
|
Kucuk zenci velet skin
|
ashleaf lesions -
hypopigmentation trunk and extremities |
|
|
Kucuk zenci velet saCRUM
|
shagreen patch - lumbosacral
|
|
|
Kucuk zenci velet - nose, cheeks
|
sebac. adenoma
|
|
|
Kucuk zenci velet tumors
|
mulberry tumors
|
|
|
Kucuk zenci velet tumors
|
phakomas
|
|
|
phakomas
|
benign growths seen as white patches on the retina
|
|
|
mulberry tumors
|
Nodular astrocytoma of the retina on or about the optic nerve head.
|
|
|
Kucuk zenci velet dX CT -
|
calcified tubers
periventricular areas can => astrocytomas (rare) |
|
|
Kucuk zenci velet Wood's UV lamp -
|
skin lesions
|
|
|
Kucuk zenci velet DX
|
EKG
renal US |
|
|
Kucuk zenci velet TX FOR SEIZURE
|
Levent kirca or Araklamaci gazeteci
|
|
|
Kucuk zenci velet TX
|
inc. ICP -
may indicate a tuber obstructing Foramen of Murro surgery |
|
|
Kucuk zenci velet TX
|
EKG
|
|
|
LEVENT KIRCA
|
Clonazepam
|
|
|
Araklamaci gazeteci
|
valproic acid
|
|
|
Von Hippel-Lindau -
genetics |
Dominant teyze
deletion of VHL gene on ch CIRA |
|
|
Von Hippel-Lindau - hemangioblastoma -
|
cerebellum
medulla |
|
|
Von Hippel-Lindau - Kidney
|
retinal angioma
RCC pheochromocytoma |
|
|
Von Hippel-Lindau -
Hx/PE |
Headache
N/V cerebellar Sxs |
|
|
Von Hippel-Lindau -
Hx/PE |
retinal angiomas -
|
|
|
retinal angiomas - place
complication |
usu. periphery
can => retinal detachment |
|
|
Von Hippel-Lindau -
Dx |
CT - head, abdo
MRI - post. fossa emphasis serpentine signal voids angiography - vascularity CBC - polycythemia VMA levels in urine ophthal US |
|
|
Von Hippel-Lindau -
Tx |
Surgical resection
or radiation |
|
|
Osler-Weber-Rendu BArbara-genetics
|
AD
|
|
|
BARBARA -also called -
|
Hereditary Hemorrhagic
Telangiectasia (HHT) |
|
|
BARBARA telangiectasia and AVM
in |
lungs, GI, brain
recurrent epistaxis |
|
|
BARBARA Hx/PE
|
Recurrent epistaxis
painless bleeding in bowel |
|
|
BARBARA hepatic AV fistula -
|
(hepatomegaly
RUQ pain pulsatile mass palpable thrill audible bruit high-output CHF liver failure) |
|
|
BARBARA hep. enceph -
|
portosys shunt
neuro complications |
|
|
BARBARA rt-to-left shunt -
|
(cyanosis
clubbing hypoxemia 2ndary polycythemia exertional dyspnea) |
|
|
BARBARA tx
|
Iron
folate symptomatic tx of epistaxis embolization, surgical excision or ligation of AV fistulas |
|
|
BARBARA???- contraindicated
|
ASA
|
|
|
Closed-Angle Glaucoma -
Hasan amca |
Med emergency
usu older pts. and Asians |
|
|
Hasan amca mechanism
|
iris root plugs opening of
trabecular meshwork acutely |
|
|
Hasan amca causes
|
pupillary dilation
anterior uveitis dislocation of lens |
|
|
Hasan amca Hx/PE
|
Intraocular pressure inc.
very fast extreme periocular pain acute red eye blurred vision |
|
|
Hasan amca Dx Best diagnostic test -
|
tonometry
|
|
|
Hasan amca Tx
|
acetazolamide
pilocarpine - when P drops |
|
|
Hasan amca - curative
|
laser iridotomy
|
|
|
Most common form
Glaucoma - |
Open-Angle Glaucoma mustesar kemal
|
|
|
Open-Angle Glaucoma bi unilateral??
|
almost always bilateral
|
|
|
mustesar kemal risk factors -
|
> 40 y/o
Black diabetic myopic family Hx diseased trabecular meshwork obstructs proper drainage |
|
|
mustesar kemal cause of vision lose
|
=> intraoc P inc. gradually
progressive vision loss |
|
|
mustesar kemal vision loss -
|
moves periph to central
|
|
|
mustesar kemal at end
|
=> blindness
|
|
|
mustesar kemal
Hx/PE |
Asymp initially
|
|
|
mustesar kemal suspect if pt. -
|
> 35 y/o
freq. lens changes mild headaches vision disturbances impaired adaptation to dark |
|
|
mustesar kemal earliest defect -
|
periph nasal fields
cupping of optic disk |
|
|
mustesar kemal dx
|
Tonometry
ophthalmic exam of optic n. central field testing eval on long-term basis can be hard to Dx until advanced stages |
|
|
Mustesar Kemal tx Prevention
|
> 40 y/o - exam every 3-5 yrs
inc. risk factor - annually |
|
|
Mustesar Kemal tx
|
timolol, betaxolol
pilocarpine acetazolamide |
|
|
Mustesar Kemal tx
|
laser trabeculoplasty -
if meds fail |
|
|
MCC of permanent bilat
vision loss in elderly |
Macular Degeneration -
What is it |
|
|
Macular Degeneration -
What is it vision loss - |
central do not lose periph
|
|
|
Macular Degeneration -
difference between atrophic and exudative form |
atrophic - gradual loss
exudative - faster damage more severe |
|
|
Macular Degeneration -
Hx/PE |
painless loss of
central vision |
|
|
Macular Degeneration -atrophic -
|
irreg pigmentation of
macular region |
|
|
Macular Degeneration -exudative -
|
hyperpigmentation
pimple-like elevation of macula - from hemorrhage |
|
|
Macular Degeneration -Laser photocoagulation -
|
may delay loss of central
vision in exudative |
|
|
Retinal Artery Occlusion -
What is it |
From emboli or thrombi
sudden painless unilat blindness |
|
|
Retinal Artery Occlusion -pupil
|
pupil accommodates but reacts
sluggishly to direct light |
|
|
Retinal Artery Occlusion - retina
|
cherry-red spot on fovea
artery may look bloodless retinal edema |
|
|
Retinal Artery Occlusion -?????within
8 hrs of onset of Sx |
Thrombolysis within
8 hrs of onset of Sx |
|
|
Retinal Artery Occlusion -dec. intraoc P -
|
drain ant. chamber
|
|
|
Retinal Artery Occlusion -
|
IV acetazolamide
|
|
|
Retinal Vein Occlusion - eye exam
|
Sudden
painless retinal hemorrhages cotton wool spots edema of fundus elderly |
|
|
Retinal Vein Occlusion -MCC
|
- HTN
can => macular dis., glaucoma |
|
|
Retinal Vein Occlusion -Tx
|
Laser photocoagulation
|
|
|
Inc. ICP -
Causes Blood - |
EDH, SDH, SAH, ICH
spontaneous or traumatic |
|
|
Inc. ICP -
Causes due to CSF - |
hydrocephalus
idiopathic intracranial HTN |
|
|
Inc. ICP -
Causes due to brain mass - |
tumor
|
|
|
Inc. ICP -
Causes due to trauma - |
cerebral contusions
|
|
|
Inc. ICP -
Causes due to edema - |
trauma
tumors |
|
|
Inc. ICP -Signs in approx. order
of appearance |
N/V and headache
altered mental status |
|
|
Inc. ICP -Signs in approx. order
of appearance than |
in kids - bulging fontanelles
|
|
|
Inc. ICP -Signs in approx. order
of appearance than |
papilledema
|
|
|
Inc. ICP -Signs in approx. order
of appearance than |
CN palsies - esp. CN6
|
|
|
Inc. ICP -Signs in approx. order
of appearance than |
Cushing's Triad -
(HTN brady irreg breathing) |
|
|
Inc. ICP -Signs in approx. order
of appearance than |
endstage -
cerebral herniation |
|
|
Inc. ICP -
Tx - in order |
Make sure BP and resp. good
|
|
|
Inc. ICP -
Tx - in order |
sedation
|
|
|
Inc. ICP -
Tx - in order |
elevate head of bed
|
|
|
Inc. ICP -
Tx - in order |
IV mannitol
|
|
|
Inc. ICP -
Tx - in order |
hyperventilate to CO2 30-35
|
|
|
Inc. ICP -
Tx - in order |
ventriculostomy
|
|
|
Inc. ICP -
Tx - in order |
surgery -
removal of hematoma decompressive craniectomy |
|
|
Herniation -
What is it Types Dx |
Endpoint of untreated masses
or inc. ICP specific signs and Sxs depends on type of hernia and mass lesion |
|
|
uncal herniation -
|
CN3 compression:
ipsilat dilated pupil midbrain compression: ipsilat hemiplegia |
|
|
tonsillar herniation -
|
resp. compromise
|
|
|
Dx -
|
CT without contrast -
r/o mass lesion or hemorrhage |
|
|
Guillain-Barre - La Ispanyol
What is it |
Acute
rapidly progressive acq. demyelinating autoimmune |
|
|
Ispanyol
|
d/o of periph nerves
|
|
|
Ispanyol
|
recent C. jejuni infection
viral infection recent vaccination |
|
|
Ispanyol process and involvement
|
Rapidly progressive
ascending paralysis involves trunk, diaph and CN autonomic Sxs areflexia |
|
|
Ispanyol dx Diffuse demyelination on -
|
EMG & nerve conduction studies
|
|
|
Ispanyol csf
|
albuminocytologic dissociation
CSF prot. > 55 mg/dL |
|
|
Ispanyol tx
|
ICU -
risk of respiratory failure plasmapheresis or IVIG aggressive rehab |
|
|
MS -
What is it |
Acq. demyelinating dis.
may have T cell-mediated autoimmune pathogenesis environmental and genetic |
|
|
MS female-to-male
|
2:1
|
|
|
MS age geography
|
20-40 y/o
inc. prev. with gtr distance from equator |
|
|
MS risk -
|
related to where lived
the 1st 15 yrs. of life |
|
|
MS subtypes -
|
benign
relapsing/remitting 2o progressive chronic progressive |
|
|
MS -
Hx/PE |
Mult. neuro complaints
|
|
|
MS -
Hx/PE |
sep. in time and space
can't be explained by a single lesion |
|
|
MS -
Hx/PE |
limb weakness
|
|
|
MS -
Hx/PE |
optic neuritis
paresthesias diplopia internuclear ophthalmoplegia |
|
|
MS -
Hx/PE |
urinary retention
|
|
|
MS -
Hx/PE |
vertigo
|
|
|
MS -
Hx/PE |
Sxs wax & wane or progress
|
|
|
MS -
Hx/PE exacerbations - |
stress
infections heat trauma vigorous activity |
|
|
MS -
Dx describe MRI finding |
Multiple, asymmetric periven-
tricular lesions in white mtr |
|
|
MS -
Dx corpus callosum lesions - |
pathognomonic
|
|
|
MS -
Dx active lesions enhance with |
Gado on MRI
|
|
|
MS -
Dx CSF |
inc. CSF IgG
oligoclonal bands |
|
|
MS -
Tx Acute - |
steroids
|
|
|
MS -
Tx treat Sxs - spasticity: |
baclofen or zanaflex
|
|
|
MS -
Tx treat Sxs - pain: |
phenytoin
|
|
|
MS -
Tx treat Sxs - fatigue: |
amantadine or provigil
|
|
|
MS -
Tx treat Sxs - |
depression
avoid hot climates |
|
|
MS -
Tx prophylaxis: |
immunomodulators
|
|
|
MS -immunomodulators
|
reduce no. of attacks, disability
|
|
|
MS Avonex -
|
once wkly IM
|
|
|
MS Betaseron
|
- every other day subq
|
|
|
MS Copaxone
|
- daily subq
|

