![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where do carbohydrates and proteins go to after they are absorbed from the GI tract?
|
Portal vein to liver for processing
|
|
|
Where do lipids go after they are absorbed from the GI tract?
|
Bloodstream
|
|
|
In the absorptive phase where is energy mainly obtained from?
|
Glucose
|
|
|
When does the liver synthesis TAGs?
|
When there is so much glucose after a meal that glycogen cannot account for all of it. Liver has to make TAG to compensate
|
|
|
Where do the TAGs go that the liver has synthesised?
|
Some stored in liver
Most released into bloodstream (very low density lipoproteins) |
|
|
What happens to the VLDL made by the liver when it is needed to be used by cells?
|
Broken down by lipoprotein lipase from very low density lipoproteins to fatty acids
|
|
|
What is lipoprotein lipase stimulated by?
In which type of cells does this occur |
Insulin
Adipocytes |
|
|
Which cells may use the fatty acids broken down by LPL?
|
Adipose - TAG synthesis and storage - insulin-dependent
Body tissue (muscle) - fatty acids used as fuel - insulin-independent |
|
|
What is glucose converted to in muscle cells?
|
Glycogen
|
|
|
What is glucose converted to in adipocytes?
|
Glycerol and fatty acids to make TAGs
|
|
|
What is important about the conversion of glucose to fatty acids in adipose tissue?
|
It is IRREVERSIBLE
Fatty acids cannot be converted to glucose |
|
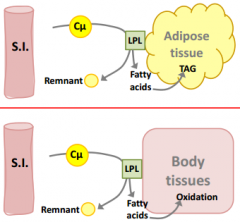
don't forget the remnant
|
remnant
|
|
|
Where are chylomicrons and VLDLs produced?
|
Chylomicrons - intestinal enterocytes
VLDLs - liver |
|
|
When are chylomicrons and VLDLs produced?
|
Chylomicrons - absorptive phase
VLDLs - continuous production |
|
|
What type of TG do chylomicrons and VLDLs carry?
|
Chylomicrons - dietary TG
VLDLs - endogenous TG (made from glucose when glycogen store is too high) |
|
|
What happens to chylomicron and VLDL remnants?
|
Chylomicron remnant - taken up by liver
VLDL remnant - taken up by liver or converted to LDL |
|
|
What happens to the chylomicron and VLDL remnants taken up by liver and what happens to VLDL remnants processed to LDLs?
|
Taken up by liver - broken down into constituent parts (may be used in bile)
LDLs - used to carry cholesterol to peripheral tissues |
|
|
What do LDL and HDL do?
|
LDL - carries cholesterol to peripheral tissues
HDL - carries cholesterol back to liver from peripheral tissues |
|
|
What might peripheral tissues use cholesterol for?
|
Plasma membranes
Steroid hormones Bile acids |
|
|
Is it good to have a high HDL:LDL ratio?
|
Yes
Less risk of atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease etc. |
|
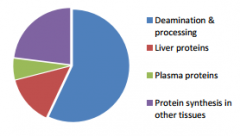
What does this diagram represent?
|
Processing of amino acids in liver
Liver proteins Plasma proteins Deamination and processing Protein synthesis in other tissues |
|
|
What happens if there is an excess of dietary protein?
|
Mammals do not store protein
Deaminated and carbon skeleton used as fuel, or converted to glucose/glycogen/fat |
|
|
How do carnivores obtain glucose?
|
Gluconeogenesis from amino acids
|
|
|
What are the products of deaminating an amino acid?
|
Ketoacid
NH4 - converted to urea in liver -> renal excretion |

