![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Anabolism or catabolism?
|
Catabolism
|
|
|
Does oxidation of carbon compounds release or require energy?
|
Release
|
|
|
Oxidation is loss of an electron or a...
|
hydrogen atom
|
|
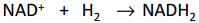
Oxidation or reduction?
|
Reduction
|
|
|
Give examples of 3 redox coenzymes
|
NAD, FAD, NADP
|
|
|
What is the ultimate electron acceptor?
|
Molecular oxygen
(hence why we need oxygen, ultimate stage of reactions) |
|
|
What is a redox pair?
|
While one thing is oxidised, another is reduced
|
|
|
In what way are coenzymes electron carriers?
|
They are reduced
|
|
|
What does glycolysis break glucose down into?
|
Pyruvate (3C)
|
|
|
How many molecules of ATP are formed from glycolysis?
|
2 ATP
|
|
|
How many NAD molecules are used in glycolysis?
|
2
|
|
|
In the aerobic and anaerobic parts of respiration what happens to NAD?
|
Regenerated in mitochondria or in anaerobic, regenerated by formation of lactate
|
|
|
How much ATP does anaerobic glycolysis produce?
|
2 ATP
|
|
|
What is the energy production like in anaerobic respiration?
|
Faster energy production
Short duration of energy e.g. white muscle fibres |
|
|
Which organ converts lactate back to pyruvate?
|
Liver
|
|
|
Where does the citric acid cycle occur?
|
Inner matrix of mitochondria
|
|
|
What is the carbon input to the citric acid cycle?
|
Acetic acid bound to coenzyme A = acetyl coA
|
|
|
What other inputs apart from pyruvate may be used for acetyl coA?
|
Acetate, butyrate - ruminants and hindgut fermenters
Acetoacetate - (ketones in starvation) Amino acids - carnivores |
|
|
What is the electron transport chain?
|
Electrons are transported from reduced coenzymes to oxygen -> water
Regenerates oxidised coenzymes |
|
|
What are the respiratory complexes found on the inner membrane of mitochondria?
|
I-IV + coenzyme Q and cytochrome C
Proton pumps which use energy from each redox reaction to pump hydrogen ions from the matrix to the intermembrane space |
|
|
What is the result of pumping hydrogen into the intermembrane space?
|
Proton gradient - Creates positive electrochemical potential
|
|
|
What is the proton gradient used for?
|
ATP synthase uses the gradient to produce ATP
|
|
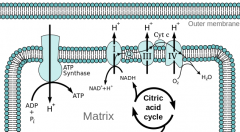
Oxidative phosphorylation
|
Regenerates oxidative coenzymes
Oxygen reduced to water ATP produced from proton gradient |
|
|
What is respiratory control?
|
When ADP is low and ATP is high, can turn off whether electrons are transported to oxygen
ADP low/ATP high ATP synthase stops Proton gradient builds up ETS stops NADH oxidation stops TCA cycle stops |
|
|
What is an uncoupling protein?
|
Can dissipate the proton gradient before it's used for oxidative phosphorylation (i.e. energy formation, energy lost as heat instead)
|
|
|
Give an example of a mitochondrial uncoupler
|
Cyanide, DNP slimming drug
|

