![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a subacute onset of confusional state marked by fluctuating alterations of consciousness that progressively worsens if untreated? |
Metabolic encephalopathy |
|

What are these all signs and symptoms of? |
Metabolic encephalopthy |
|
|
How is pupil light reactivity, ocular motility, and motor activity affected? |

|
|

What are these all causes of? |
Chemical encephalopathy |
|

What are these all causes of? |
Non-chemical encephalopathy |
|
|
Which type of encephalopathy more commonly leads to permanent brain injury? Which are more likely to be completely reversible? |
Trauma Chemical |
|
|
What water soluble vitamin deficiencies may cause metabolic encephalopathy? |

|
|
|
What is the triad of Wernicke disease?
What is the component of Korsakoff syndrome?
What is the vitamin deficiency? Cause?
Treatment? What labs? |
Ophthalmoparesis, gait ataxia, and a confused state
Amnesia
B1 => alcoholism
Give thiamine BEFORE glucose for proper glucose metabolism
Labs = transketolase decrease |
|

|

|
|
|
What areas are damaged with Werkicke/Korsakoff encephalopathy? |
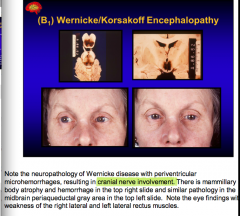
Mamillary body atrophy
|
|
|
What is the difference between wet and dry beriberi? What is the vitamin deficiency?
What are the components of niacin deficiency? (3Ds)
What does B6 deficiency cause in adults? In children? |

|
|
|
What are some causes of B12 deficiency? (think about what is required to absorb B12).
|

|
|

What are these all components of? |
B12 deficiency |
|
|
What will laboratory evaluation of blood smear reveal in patient with B12 deficiency? |
Macrocytic anemia Hypersegmentation of neutrophils B12 level low
If borderline low, check methylmalonic acid and homocysteine levels. |
|
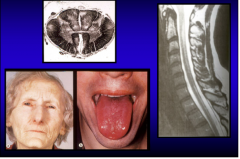
What are these all components of? |
B12 deficiency
Top = subacute degeneration of spinal cord (lateral and posterior spinal lesions) Right = demyelination from B12 deficiency Bottom = lemon yellow complexion with paleness from anemia, and atrophy of papillae of tongue |
|
|
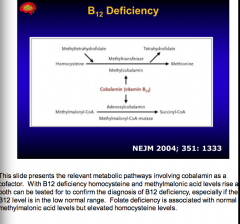
Draw the pathway of B12 metabolism.
What is folate deficiency associated with? |
|
|
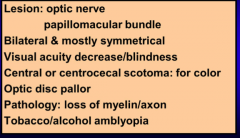
What are all of these?
These are more common when associated with what? |
Deficiency (toxic) ambylopia: B complex deficiencies
Alcohol and tobacco abuse |
|
|
Pupillary abnormalities with preserved accommodation reflex and absent light reflex is suggestive of what? |
Argyll Robertson pupil |
|
|
What are all of these associated with? |
Hypoglycemia => INCREASED sympathetic response |
|

What are all of these associated with? |
Hyperglycemia |
|
|
What are some symptoms of the nervous system associated with diabetes?
What do both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia cause? |
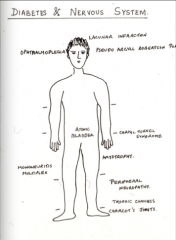
Encephalopathies |
|
|
Identify each: 1. Symmetric, painful, more often seen in lower than in upper limbs initially, disturbs night sleep. 2. Results in neurogenic atonic bladder 3. Infarction of the nerve with vascular insufficiency and causes diplopia, pain, ocular muscle weakness (6th or 3rd cranial nerve) 4. Caused from simultaneous infarction and ischemic of different peripheral nerves. 5. From involvement of nerve roots with proximal weakness seen in lower limbs. |
1. Diabetic (sensory) neuropathy 2. Autonomic neuropathy. 3. Diabetic ophthalmoplegia 4. Mononeuritis multiplex 5. Diabetic amyotrophy |
|

What are these all causes of? |
Hypoxia |
|
|
What are the three components of posthypoxic syndrome? |

|
|
|
What parts of the brain are most affected by hypoxic encephalopathy?
What are some of the clinical features? |
Hippocampus Watershed areas between vascular territories of major arteries Deep folia of cerebellum
Stupor or coma, seizures, myoclonus Amnesia if patient recovers due to hippocampal damage
|
|
|
What is cerebral hypoxia most commonly caused by? |
Cardiac arrest |
|
|
What does chronic bronchitis result in? |
Chronic hypoxia and hypercarbia |
|

What are these all causes of?
What are some resulting symptoms? |
Confusion, seizures, slow EEG with triphasic waves, peripheral asterixis, and myoclonus
|
|
|
Polyneuropathy seen in hepatic disease is often associated with what?
Are reflexes brisk with hepatic failure? Uremic encephalopathy? |
Alcoholic liver failure No Yes |
|
|
What are some complications of ureic encephalopathy? |
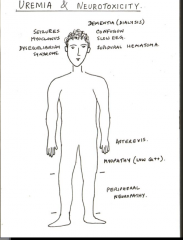
Proximal muscle weakness associated with low calcium levels seen with chronic renal disease |
|

These are all causes of what? |
Metabolic encephalopathy |
|

What can call of these disorders cause? |
Metabolic encephalopathy |
|

What can all of these cause?
Should you correct hyponatremia slowly or quickly? What could if cause if not corrected properly? |
Metabolic encephalopathy
SLOWLY (8mEq/day) Faster => central pontine myelinolysis => severe brainstem injury |
|

What can all of these cause? |
Metabolic encephalopathy |
|

|

|

