![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Disorders of Fructose Metabolism |
|
|
|
Essential Fructosuria Defective Enzyme |
|
|
|
Essential Fructosuria Genetic Presentation |
|
|
|
Essential Fructosuria Severity |
|
|
|
Essential Fructosuria Pathology |
|
|
|
Essential Fructosuria Symptoms |
|
|
|
Fructose Intolerance Defective Enzyme |
|
|
|
Fructose Intolerance Genetic Presentation |
|
|
|
Fructose Intolerance Pathology |
|
|
|
Fructose Intolerance Presentation |
|
|
|
Fructose Intolerance Symptoms |
|
|
|
Fructose Intolerance Treatment |
|
|
|
Disorders of galactose metabolism |
|
|
|
Galactokinase Deficiency Pathology |
|
|
|
Galactokinase Deficiency Presentation |
|
|
|
Galactokinase Deficiency Symptoms |
|
|
|
Classic Galactosemia Defective Enzyme |
|
|
|
Classic Galactosemia Pathology |
|
|
|
Classic Galactosemia Presentation/Symptoms |
|
|
|
Classic Galactosemia Treatment |
|
|
|
Sorbitol pathway |

|
|
|
Sorbitol |
|
|
|
Sorbitol Dehydrogenase Deficiency |
|
|
|
Lactase Deficiency Primary |
|
|
|
Lactase Deficiency Secondary |
|
|
|
Glycogen regulation by Insuline and glucagon/epinephrine |
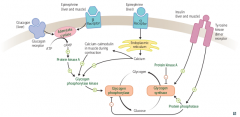
|
|
|
Glycogen Storage Disease Type I |
|
|
|
Glycogen Storage Disease Type II |
|
|
|
Glycogen Storage Disease Type III |
|
|
|
Glycogen Storage Disease Type IV |
|
|
|
Glycogen Storage Disease Type V |
|
|
|
Glycogen Storage Disease Type VI |
|
|
|
Glycogen Storage Disease Type 0 |
|
|
|
Von Gierke Disease Type I GSD Deficient Enzyme |
|
|
|
Von Gierke Disease Type I GSD Findings |
|
|
|
Von Gierke Disease Type I GSD Treatment |
|
|
|
Glycogen Synthase Deficiency Type 0 GSD Findings |
|
|
|
Pompe Disease Type II GSD Findings |
|
|
|
Pompe Disease Type II GSD Deficient Enzyme |
|
|
|
Cori Disease Type III GSD Deficient Enzyme |
|
|
|
Cori Disease Type III GSD Findings |
|
|
|
Andersen Disease Type IV GSD Defective Enzyme |
|
|
|
Andersen Disease Type IV GSD Findings |
|
|
|
McArdle Disease Type V GSD Deficient Enzyme |
|
|
|
McArdle Disease Type V GSD Findings |
|
|
|
Hers' Disease Type VI Deficient Enzyme |
|
|
|
Hers' Disease Type VI Findings |
|
|
|
Ketoacidosis Build up of what Ketone Bodies |
|
|
|
Ketoacidosis in starvation/diabetes |
|
|
|
Ketoacidosis in alcoholism |
|
|
|
Ketoacidosis Process |
|
|
|
Ketoacidosis Presentation |
|

