![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the three classifications of IBD
|
UC
Crohn's intermittent colitis - which just means we don't now if it's UC or Crohn's |
|
|
symptoms of IBD
|
Ab pain
diarrhea wt loss/ failure to grow (in kids) fever family Hx of IBD |
|
|
extraintestinal manifestations of IBD
6 sites name one from each or just get the common ones |

arthritis - periphral or central (axial)
Skin lesions - erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrenosum eye lesion - uvitis liver lesions - sclerosing cholangitis, cholangiocarcinoma |
|
|
common lab abnormalities in IBD
|
anemia - due to terminal ileum dysfunciton or occult blood loss
elevated CRP decreased albumin (negative acute phase reactant, or poor nutrition) fecal leukocytes |
|
|
definition of ulcerative colitis
|
mucosal ulceration (limited to mucosa)
rectum always involved inflammation extends in a continuous fashion (good indicator of prognosis) variable amount of colon involved |
|
|
complications of UC
|
bleeding
toxic megacolon (toxic refers to pt - fever, dehydration, hypotension) perforation strictures (either from UC or cancer |
|
|
the 2 patterns of Crohn's
|
inflammatory
stenotic fistulizing |
|
|
colonic characteristics of Crohn's
|
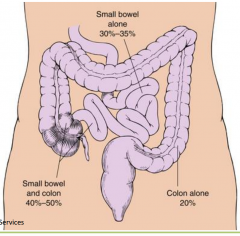
can effect anywhere in GI tract
ulcerations are linear effect all layers of the GI tract so can cause fistulas small bowel involvement and chronic presentation can cause malnutrition |
|
|
distinguishing features of Crohn's
|
small bowel involvement
rectal sparing perianal disease skip lesions fistulas granulomas |
|
|
treatment for IBD
|
5-ASA agents - Mesalazine (useful in UC)
steroids (useful in short term) immnosuppressives biologics (anti-TNF) surgery (can cure UC, used for complications of Crohn's) |

