![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Q - Describe Atkinson and shiffrin (1968) |
A - Atkinson and Shiffrin claimed that memory is made up of separate, distinct memory stores, and developed the Multi-store model of memory. |
MULTI |
|
|
Q - Name the 3 main elements included in the Multi-store model of memory. |
A - The Sensory register, the Short-term memory, and the Long-term memory.
|
|
|
|
Q - Briefly describe the process involved in storing a memory in the Long-term store (from the beginning) within the Multi-store model of memory. |
A - A stimulus from the environment will be stored in the Sensory register on one of the sensory stores.
- Some information will pass to the Short term memory through attention.
- The information can be passed into the Long-term memory through (Elaborate) rehearsal. |
Stimulus, attention, rehearsal |
|
|
Q- Briefly describe the 'Short-term memory' store, and give its Duration, Capacity and Coding. |
A - It is a limited capacity and duration store (meaning that it can only hold a certain number of 'things' before forgetting takes place.)
Duration - 18 - 30 seconds Capacity - Between 5 and 9 items (+/- 2) Coding - Acoustic |
LIMITED |
|
|
Q - Briefly describe the 'Long-term memory' store. Give its Duration, Capacity and Coding. |
A - It is a permanent memory store. When we want to recall information from the LTM it has to be transferred back to the STM by 'Retrieval'.
Duration - Potentially up to a lifetime Capacity - Potentially unlimited Coding - Semantically (in terms of meaning.) |
Permanent |
|
|
Q - Describe the 'Sensory register'. Give its Duration, Capacity and Coding. |
A - Stimuli from the environment pass into the sensory register. It is not only one store; but 5 (1 for each sense.)
Duration - Very brief (less than half a second) Capacity - Very high (Each cell in the eye stores data) Coding - Depends on the sense (e.g visual, auditory etc.) |
Environment |
|
|
Q - Briefly describe the transfer of information from the 'Sensory register' to the 'STM' |
A - Very little information will pass from the Sensory Register to the STM because it needs to be through attention. |
|
|
|
Q - Describe the Multi-Store model of memory, including the main components. |
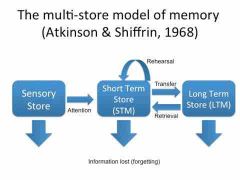
A - Stimulus -> Sensory register Sensory register -> STM (through attention) STM -> LTM (through rehearsal) |
|
|
|
Q - Describe the process of transferring information from the STM to the LTM. |
A - Information is transferred from the STM to the LTM by Maintenance rehearsal (repeating information to ourselves.) Information can be kept in the STM by rehearsing it, and if rehearsed long enough it can be transferred to the LTM. |
|
|
|
Q - What are the 3 types of Long-term memory? |
A - Episodic, Semantic, Procedural |
|
|
|
Tulving (1985) - suggestions about long-term memory. |
Tulving suggested that there are 3 different stores in the LTM; responsible for storing different types of information. (Episodic, Semantic , Procedural) |
|
|
|
Q - What is Episodic Memory? |
A - Episodic memory is a LTM store for personal events. It will include memories of when and where the event occurred, people involved, objects, and behaviours. Memories from this store have to be retrieved consciously and with effort. |
|
|
|
Q - What is Semantic Memory? |
A - This is a LTM store for our knowledge of the world, including facts and what concepts mean. These memories need to be recalled deliberately. |
|
|
|
Q - Define 'Interference' |
A - Forgetting because one memory blocks another, causing one or both memories to be distorted or forgotten. |
|
|
|
Q - Define 'Interference' |
A - Forgetting because one memory blocks another, causing one or both memories to be distorted or forgotten. |
|
|
|
Q - Define 'Proactive Interference' |
A - Forgetting occurs when Older memories interfere with Newer memories. |
|
|
|
Q - Define 'Retroactive Interference' |
A - Forgetting occurs when Newer memories interfere with Older memories. |
|
|
|
Q - Describe McDonald's study into the 'effects of similarity' on recall. |
A - Interference is worse when memories are similar
- Participants learned a list of 10 words - learned another list - Participants recall depended on the nature of the second list (more similar 2nd list = worse recall) |
|
|
|
Q - Describe Baddely (1977) as a support for interference . |
A - Asked rugby players to recall the names of teams they had played in that season week by week. - recall depended on the number of games played in the mean time rather than how long ago it took place |
Rugby players |
|
|
Q - What is meant by 'the use of artificial materials' as a negative evaluation of interference studies? |
A - The stimulus material being used is one different from the things we use in everyday life
- artificial materials makes interference more likely in a lab environment but not necessarily in real life |
|

