![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
H.M. had what part of his brain resectioned to lessen his epilepsy? |
Medial temporal lobe |
|
|
Which of the types of memory did H.M. struggle with? Which did he not? What category do these both fall under? |
Episodic. Semantic. Explicit. |
|
|
What is autonoetic awareness? |
Place yourself in the past to help w/ current decision-making. |
|
|
How did K.C. and M.L. contribute to the body of amnesia knowledge? (Name 2 areas of damage) |
He had damage to the ventral PFC + the fibres connecting the ventral PFC to the temporal lobe. He had identical symptoms to K.C. who had widespread damage, so learned that explicit memory must be affected by 2 regions. |
|
|
What is semantic memory? Which areas does it involve? |
Facts and knowledge. NOT MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE. Areas adjacent to frontal + temporal lobe |
|
|
What are the 2 gyri in the hippocampus? Who receives input from where and projects to who? |
Ammon’s horn. Dentate gyrus. DG receives from neocortex, projects to AH. |
|
|
What are the 2 major pathways in the hippocampus. Where do they connect to? |
1) Perforant pathway: connects HC to temporal cortex 2) Fimbria fornix: connects HC to thalamus, hypothalamus, PFC, basal ganglia |
|
|
What are the 2 cortices in the temporal cortex? What are they responsible for? |
Perirhinal cortex and entorhinal cortex. Object recognition. |
|
|
What happens when the left temporal lobe is damaged? What happens with the right? |
Impaired verbal memory. Impaired non-verbal memory. |
|
|
What is the frontal cortex responsible for? Left and Right |
Left = encoding memories Right = retrieving memories |
|
|
Does implicit memory require higher cog processes to perform? |
No |
|
|
What is the order of transmission between regions in implicit memory? Use finger drawing |
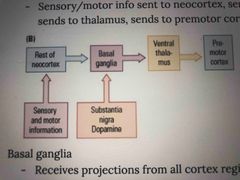
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the cerebellum involved w/ in implicit memory? |
Conditioning |
|
|
Emotional memory includes explicit and implicit memory (T or F) |
True |
|
|
What is fear conditioning? Which structure is necessary and why? |
Pair noxious stimulus w/ neutral stimulus to elicit response. Amygdala is connected to ANS-para(sympathetic) systems, cause fight or flight |
|
|
The amygdala has very close connections to which area? What type of memory does this create? |
The medial temporal structures. Emotional. |
|
|
In short-term memory, what are the 2 streams of sensory processing? |
Dorsal = motor + spatial Ventral = object recognition |
|
|
Damage to which area results in inability to recall short term memory and repeat it verbally? |
Posterior temporal regions |
|
|
What are the 3 NT systems involved w/ memory? |
Cholinergic, noradrenergic, serotonergic |
|
|
Profound amnesia cause by which NT cells being damaged? |
Serotonin and acetylcholine |
|
|
What is childhood amnesia? What are the 2 theories? |
Can’t remember events from childhood. 1) Brain structures related to episodic memory not mature yet. 2)Deleting memories to make room for new ones |
|
|
What is a fugue state? Which structure may be responsible and how? |
Sudden loss of episodic memory. Semantic + implicit remain intact Medial temporal lobe suppression |
|
|
What is anterograde amnesia? Retrograde? |
Can’t acquire new memories. Can’t require old ones up to a certain point (pre surgery) |
|
|
What are the 3 theories of amnesia? What are the main ideas? |
System consolidation - HC consolidates memory, stored elsewhere in brain - explains how old memories sometimes not damaged Multiple trace - memories encoded in many brain areas, explains why damage doesn’t affect all - every time we recall memories, they’re changed and restored Reconsolidation - every time you recall a memory, it becomes a new one, new phase of storage |
|
|
What is transient global amnesia? What causes it? |
Brief retrograde and anterograde amnesia. Some can be permanent Concussion, stroke, epilepsy |
|
|
What happens with herpes? What areas are affected (2) |
Some retrograde amnesia. Temporal lobe damage. Insula damage affects retrieval of old memories |
|
|
What is Korzakoff’s syndrome? What’s it caused by? Which 2 areas affected? |
Anterograde and retrograde amnesia, confabulation to make up for retro Caused by alcoholism and vitamin deficiency Mainly frontal lobe, probably medial temporal lobe and other adjacent areas |
|
|
What disorder associated w/ savant syndrome, and what is it? What is there a deficit it? |
Exceptional skills in an area, related to ASD. Often has problems understanding simple things like social communication |
|
|
What is superior autobiographical memory? What structures involved? |
Amazing memory after 10 y/o. Increased gray matter in temporal and parietal lobes. Increased fibre projections |

