![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Capacity of STM |
Digit span is 9.3 items Letter span is 7.3 items Easier to recall digits as there are 10 while there are 26 letters. The magic number (Miller) is 7_+ 2 chunks. |
Digit span, letter span, magic number |
|
|
Evaluation of capacity |
May be more limited - only 4 chunks so lower end of magic number. Size if chunks matters - shorter memory span for larger chunks (a sentence) than smaller chunks (one syllable words.) Individual differences - Not same for everyone. Increases with age, eight yr olds have 6.6 digit span but 19 yr olds have 8.6. Increase could be due to learning to chunk. |
Limited, chunks, everyone |
|
|
Duration of STM |
Under 18 seconds. Study showed 90% correct in 3 seconds, 20% in 9 seconds and 2% after 18 seconds. Using a retention interval. (Peterson,1959) |
It's not long |
|
|
Evaluation of duration of STM |
Testing STM was artificial - memorising syllables doesn't reflect everyday memory. However we do memorise fairly meaningless things like phone numbers or postcodes so it has some relevance to everyday.
STM results may be due to displacement - criticism of peterson's study is the participants were counting the numbers in the STM so the forgetting was displacement, not decay. STM was longer is auditory tones were used instead. |
Artifical, displacement |
|
|
Coding in STM |
Difficulty remembering acoustically similar words in STM, semantic was fine. STM is encoded acoustically. |
Hear hear |
|
|
Evaluation for coding in STM |
STM may not be just acoustic - study found visual coding was used in STM with a visual task, if they were prevented from doing verbal rehearsal. Normally we translate visual images to verbal codes. |
Not entirely acoustic |
|
|
Capacity of LTM |
It is unlimited. |
|
|
|
Duration of LTM |
Could be infinite. Study - free recall test of people in their graduating class, vs photos. 15 years - 90% photos 15 years - 60% free recall 48 years - 70% photos 48 years - 30% free recall
|
Photos, free recall test |
|
|
Coding in the LTM |
LTM is largely encoded semantically. Not difficult to remember acoustically similar words in LTM, muddled LTMs if semantically similar words are used. |
Meaning. |
|
|
Evaluation of coding in LTM |
LTM may not be exclusively semantic - Study showed long term recall was related to visual and semantic and evidence of acoustic coding in the LTM. So it can vary. Baddeley may not have tested LTM - In the study, STM was tested by immediate recall, and LTM was tested by waiting 20 minutes. Is 20 minutes really the LTM? |
|
|
|
The Multistore model order |
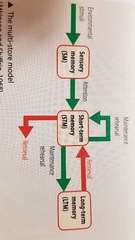
Sensory, short, long |
|
|
|
MSM - Sensory register |
Where infomation is held at the senses (eyes, ears, etc.). Capacity is very large. Constantly receiving infomation, but most is not paid attention to and remains in the sensory register for milliseconds. |
|
|
|
MSM - Attention |
If attention is paid to infomation in the sensory register, it is transferred to the short term memory. 1st step in remembering. |
|
|
|
MSM - Short term memory |
Infomation is held here for immediate tasks, e.g working on a maths problem. Has a limited duration, as it is fragile and will decay if not rehearsed. Infomation can be displaced if new infomation enters due to limited capacity. |
|
|
|
MSM - Maintenance Rehearsal |
Repetition keeps info in the STM, but eventually the repetition will create an LTM. The better the maintenance rehearsal, the better it is remembered. |
|
|
|
MSM - Long term memory |
LTM is potentially unlimited in capacity and duration. |
|
|
|
MSM - Retrieval |
The process of getting infomation from the LTM to the STM so it can be used. |
|
|
|
MSM - Evaluation - Brain scans |
Studies support capacity, duration and coding. Brain scans have shown a difference between STM and LTM. E.g Pre-frontal cortex is active in STM, but not in LTM tasks. Hippocampus is active when using LTM. |
|
|
|
MSM - Evaluation - Case Studies |
HM - brain damage to hippocampus from surgery to reduce epilepsy. Personality and intellect were fine, but he was unable to form new LTMs, but could remember things before the surgery. Supports seperate stores, as he couldn't transfer info from STM to LTM, but could retrieve infomation. |
|
|
|
MSM - Evaluation - MSM is too simple |
Research says that STM is divided into different stores for different kinds of memories. The same is true for the LTM. E.g maintenance can explain LTM storage in semantic memory (knowledge) but not for episodic memories (things you experienced.) |
|
|
|
MSM - Evaluation - more than maintenance rehearsal
|
Maintenance rehearsal does not explain the creating of all memories. It could be due to deep or shallow processing. Things that are processed deeply are more memorable. |
|
|
|
The Working Memory Model -
|
|
|

